Exam 2 - Spring Flashcards
spine is ___ shaped in utero and then what?
c-shared… then C and L become lordosis

TP of C1 is located…
behind the mastoid process of the skull
what has the largest cervical SP
C7 and then C2
fx of c-spine (3)
- protection
- exit for spin-N from cerv and brachial plexus
- mobility and support of head in environ
what is the keystone of the body
neck
what is major conduit of body?
c-spine b/w head and rest of body
superficial cervical fascia
b/w dermis and deep layer
N, bv, lymph
deep cerv fascia
3 layers: investing, pretracheal, prevert
supports viscera

posterior cerv M
nuchal line –> sacrum
- LBP can cause motion restriction to upper cervical region
sig mod of M at c2
- lots of oblique M txverse atlas and axis to occiput
cerv M act as…
“auto balancing system”
- keep head lvl during mvmt
- high concentration of proprio
- N reflexes to suboccitpal M
anterior cerv M
T3 –> occiput: mandible to hyoid, sternum, clavicle
- “strap M”
SCM
sup anterior M
imp for BALANCE
- high concentration of proprioceptors
fx:
- SB and R head in opposite direction
- bilateral flexor of c-spine
congenital torticollis
trapezius
superficial posterior M
- primary connection b/w head, neck, UE
nuchal line –> distal 1/3 of clavical and scapula
- elevates and retracts scapula
- extend, laterally flex, contralateral rotate head
levator scapulae
upper 4 c-vert –> medial border of scapula
fx: elev scapula
* lifting arm distributes forces to head
referred pain from acute herniated disc at mid c-spine lvl
scalene M
lateral stabilizers
- anterior and middle attached to rib 1
- posterior attaches to rib 2
- origin @ tubercles on C-TP
fx:
- flex c-spine
- breathing assist
restriction of OA or AA can cause restriction in what N?
vagus

cerv vasc
SC
- can be impinged by hypertonic scalene muscles or elevated 1st rib
carotid (anterior to c-vert)
- can listen for bruits
vert
- comes off SC
Vertebral Artery parth
C6 to TP of atlas –> Turns 90 degrees posteriorly –> Turns 90 degrees medially around the posterior edge atlas –> Turns to pass anteriorly and superiorly into the cranium where right and left vertebral a. form the basilar artery of the brain
what combo of mvmts on the c-spine causes the MOST structural challenge on vasc flow to brain?
extension, SB, rotation on SAME SIDE
- dixxiness
VERY impt to not put head into _____ during HVLA
extension
bony structure of c-vert
7 vert
vert foramina LARGEST at C1 and tapers down to C7 BUT vert become progressively LARGER
allow for sig mobility w/o restricting cord
Orientation of
Zygopophyseal (Facet) Joints
45 deg horizonal, face superior and posterior
b/w hori and coronal plane
STEEPER caudally (towards tail)
limits flex and extension

zygophyseal joints get more ________ more inferiorly
angle becomes flatter, more horizontal
Articular Pillars
lateral masses that lie b/w superior and inferior facets
- posterior to c TPs
cerv TP characteristics
short and stubby
have txvrse foramen for vert A
each TP cradles a c-N which passes POSTEIROR to position of vert A
Joints of Lushka
C3-C7: synovial
- formed by uncinate process and superior adj vert
- create stab of heavy head and smaller neck
- babies do not have b/c they do not need to support head wt @ birth
fx:
- main stab upright position of head
- guides flex/ext
- LIMIT LATERAL FLEXION
- support disc

Degeneration of joints of Lushka can cause
“side slip” –> cerv N root stenoisis and impingement
The relative disc thickness is greatest in the
c-spine: 2/5! disk height: c-vert height
More flexion and extension is possible when the disc is thick and the AP diameter is relatively small.

c motion
- Flexion: 80°-90°
- Extension: 70°
- Sidebending: 20-45°
Rotation: 70-90
Disc Motion in Flexion and Extension
On flexion, disc shifts more posteriorly
On extension, disc shifts more anteriorly

CERVICAL DIVISIONS
Upper Cervical Division
- Occiput, Atlas, Axis
- As a unit provide >50% of rotation, flexion/extension
Lower Cervical Division
- C3-C7 vertebral segments
- SB and rotates in SAME direction
flex/ext mostly controlled by
OA
rotation mostly controlled by
AA
SB controlled mostly by
C3-C7
gross cerv motion is guided by…
facet joint orientation
M
ligaments
coupled motions of c-spine
OA: SB and R in opp directions
AA: only R
C3-C7: SB and R in same direction
- due to facet joints
Extension places facets more ____ therefore _____ is easier
vert
SB
Flexion moves the facet plane _____ facilitating ______
horizontal
rotation
typical c vert:
atypical c vert:
c3-c6
c1 (no body), c2, c7
Typical Cervical Vertebrae (6)
v-formaen is large and triangular
TP has foramina for vert A and V
BIFID SP
superior facets face superior/posterior
inferior facets face inferior/posterior
rectangular body

C1 (5)
no body –> RING-LIKE
no TRUE SP
articulation for dens
NO IV DISC
very palpable TPs

c2 (4)
dens (odontoid process) = superior axis of rotation
NO disc above
SP palpable
superior facets are CONVEX

c7
prominent SP, SELDOM BIFID!
- appears like thor vert
NO vert-A
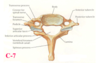
AA jt motion
ONLY R via odontoid process
- txverse ligament allows SLIGHT flex
NO SB (lateral flex)
OA joint
“single” joint that is actually 2 sep joints
- anterior: b/w dens and anterior arch: synovial
- posterior: b/w dens and strong txverse lig of atlas
- pivot about which AA joint rotates
convex condyles of occiput –> concase superior facets of atlas
LIMITED motion due to lig attachements
forms R and L “ellipsoid”, congruent synovial joints
superior facets of atla face: BUM - back, up, medial
OA ligaments
ALL, PLL
anterior and posterior OA membrance
tectorial membrane:
- base of skull –> PLL in c-area
OA motion…
what is it limited by?
“makes smallest yes motion with head”
flex: lim by skull contact with dens
ext: lim by tectorial membrane
what can destab cerv lig?
RA
steriods
down syndrome
OA motiong
limited by M and lig
primary = flex/ext
- flex –> posterior slide of occiput
- ext –> anterior slide of occiput
SB and R are opposite!
- due to lateral OA lig
- rotation is linked to translatory SLIDE
Biomechanically, Occiput acts like
sphere
- major motion = flex/ext
- minor motion = SB, R
in motion testing (SB test) of C3-C7, translation to the R produces SB to the…
L
do fryettes principles apply to c-spine?
NO! - No group curves or neutral mechanics!
epidemiology of neck pain
9-102
peaks b/w 20-40 y/o due to MVA
peaks b/w 30-49 in gen pop
neck pain high in females than males
what is the most common complain of pts seen by pcp?
neck pain
what is the most common cause of neck pain
mech neck disorder
neck pain is the ____ most common reason that pts seen manual med tx
neck pain
LBP is first
Most neck pain as a result
cervical paraspinal spasm or other musculoskeletal factors
- decr ROM
- pain WORSE with mvmt, BETTER with rest
- lack of organic/systemic pathos
non-trauma neck pain can be caused by…
soft tissue disorders:
- poor posture
- repetitive activity @ work
- sports
emotion/mental state
what is a stronger association? neck pain due to mental stress or due to repetitive occupational activities?
mental stress
when pain stricks, focusing on _____ is key
emotion
Risk Factors For Neck Pain
- depression
- incr age
- hx LBP, headache
- physical work, job demans
- lack of control over work (low job statisfaction), social support
- obesity
- smoking
- unusual postures
osteoarth usually appears…
after 60
edema where can cause difficulty swallowing and thus neck pain
overstretched ALL and retroesophageal tissues
spurlings manuver
neck compression with SB
tests for cerv radiculitis:
- stenosis
- cer spondylosis
- osteophytes
- trophic facet joints
- herniated disc
distraction test
“lifts head up” to decrease/releieve pain of nerve root compression
wallenburg’s test
test vert A insufficiency:
supine –> SB (both sides) –> rotate –> wait 30 sec
postive = dizzy, nausea, lighthead

with erect posture, wt of head is….
in forward head position, head is approx ___ with which wt of head is…
10 lbs
3in in front of COG = 30 lbs