Femal reproductive system and breast Flashcards
What parts of the female reproductive tract are in the pelvic cavity?
Ovaries
Uterine tubes
Uterus
Superior vagina
What parts of the female reproductive tract are in the perineum?
inferior vagina
Perineal muscles
Bartholin’s glands
Clitrois
Labia
What is the pouch between the utereus and and the bladder
uterus and rectum
Vesico uterine pouch
recto-uterine pouch
What do you put a needle through to drain the pouch of douglas?
posterior fornix of the vagnia
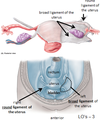
Where is the broad ligament

What is the broad ligament made up of?
Double layer of peritoneum
What is the function of the broad ligament?
Maintains uterus in the midline
What is contained within the broad ligament?
Uterine tubes
Proximal round ligament
What does the round ligament attatch to?
Lateral aspect of uterus
through deep inguinal ring
superficial tissue of the female perineum
Where is the round ligament?
What supports the utereus in place?
Uterosacral ligaemnts
Endopelvic fascia
Levator ani
What are the 3 layers of the uterus body?
Perimetrium
Mymometrium
Endometrium
What are the two ways the utereus can sit?
What does this mean?
what is more common?
Anteverted anteflexed (flopped over bladder)
Retroverted retroflexed ( flopped over colon)
vertered means cervix and flexed means utereus
anteverted anteflexed is most common
Where does fetilisation usually occour?
Ampulla
What are the parts of the fallopian tube

What do you call the space in the vagina around the cervix?
Fornix
What forms the majority of the pelvic diaphram?
Levator Ani
What nerve supplies the levator ani and where does it come from?
nerve to the levator ani
S3,S4,S5 sacral plexus
what nerve supplies the perineal muscles?
Pudendeal nerve
What is the perineal body?
bundle of collangenous elastic tissue which the perineal muscles attatch too
What do you call the little anchor point the perineal muscles attatch too?
The perineal body
Where are the bartholins glands?
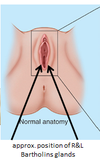
what is the area anterior to the pubic bone?
mons pubis
Label dans la vaginous

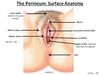
What are the borders for the bed of the breast?
Ribs 2-6
Lateral border of sternum
mid axillary line
Label the breast


How would you describe where a breast lump was?

How does limph drain in the breast




What are the layers of the adomen from the side and from the top ?

What way do the fibres run in external obliques?
Hands in pockets
What way do the internal obliques run?
Towards your bum
What is important to remember about the rectus sheath?
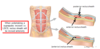
Whats the line down the middle of your abs called?
Linea Alba
What supplies blood to the anterior abdominal wall?
Superior epigastric arteries
Inferior epigastric arteries
What artery can get fucked up in a lateral port insertion?
Inferior epigastric artery
Where does the inferior epigastric artery come from?
External iliac artery
Where does the inferior epigastric artery emerge from?
Medial to the deep inginal ring
(mid way betweem ASIS and pubic tubrecle)
What transmits pain for the pelvic organs and what transmits pain from the perineum?
visceral affertens from the pelvic organs
pudendal nerve from the pernieum
Where does the viseral afferent nerve supply come from for the suprior aspect of the pelvic organs?
T11-L2
Where does the visceral afferent supply for the inferior aspect of the pelvic organs come from?
S2,3,4
what nerve roots supply the pudendal nerve?
S2,3,4
How does the pain travel at the (a) superior aspect of a pelvic organ and (b) the inferior aspect?
Superior aspect
visceral afferent follows sympathetics to T11 - L2
Inferior aspect
visceral afferent follows parasymapthic to S2,S3,S4
what are the 3 types of injectible asathesia in pregancny?
Spinal anaesthetic
Epidural anaesthetic
Pudendal nerve block

What does the spinal cord become the cauda equina?
2 people can fit on a horse
L2
Where does the subarchnoid space end?
Two people can ride a spider
L2
What layers does a spinal anaesthetic pass through?
Supraspinous ligament
Interspinous ligament
Ligamentum flavum
Epidural space
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
CSF

Where do you put in an epidural anaesthetic?
L3-L4
What will happen to the legs after a spinal anaesthetic?
loss of symapthic vessle tone = vasodilation
Reduced sweating
Hypotension risk
What does the pudendal nerve come from?
Branch of the sacral plexus
s2,s3,s4
Where does the pudendal nerve travel?
greater sciatic foramen
posterior to sacrospinous ligament
pudendal canal (obturator fascia)
What way do you do an episiotomy?

Where does the pudendal nerve pass in relation to the sacrospinous ligament?
nerve crosses the lateral aspect of the sacrospinous ligament
What nerve dmg can happen during a prolonged difficult vaginal labour?
pudendal nerve can be stretched
week pelvic floor and inconinece
What are the three layers of the pelvic floor?
Pelvic diaphragm
Muscles of the perineal pouches
Perineal membrane
What are the two muscles in the pelvic Diaphram
Levator Ani
Coccygeus


Is the levator Ani usually contracted or relaxed?
Normally contracted
Relaxes to poo and pee


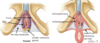
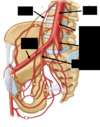

What does the gonadal artery come from?
L2 Abdominal Aorta
Where does the sperior rectal artery come from?
Continuation of inferior mescenteric artery