Exam II - Canine Head Flashcards
What are the muscles of mastication?
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Digastricus
- Pterygoid
Which muscle acts to open the mouth?
Which cranial nerve(s) provide innervation to this muscle?
Digastricus m.
Mandibular branch of Trigeminal n (CN V) and Facial n (CN VII)

List the lingual muscles. These muscles are all innervated by which cranial nerve(s)?
- Styloglossus m.
- Hyoglossus m.
- Genioglossus m.
All innervated by CN XII: Hypoglossal n.
Genio- is a prefix meaning _______
*Genio- *is a prefix meaning chin
Example: Geniohyoideus m.
Mylo- is a prefix meaning _______
*Mylo- *is a prefix meaning molar
Example: Mylohyoideus m.
Which thin, flat muscle is the most superficial facial muscle?
Platysma m.

The molar salivary gland is only found in which species?
feline.
The molar salivary gland is on the lingual side of the last lower premolars.

Which lymphatic structure is found rostral to the parotid sliavary gland?
parotid lymph node
Which lymphatic structure straddles the linguofacial vein?
mandibular lymph node
Which lymphatic structure is found between the wing of the atlas and the larynx?
**retropharyngeal lymph node **(medial and lateral)
Name the gland that may be removed unintentionally if you are surgically extracting the thyroid gland
parathyroid gland
_________ laterally connects soft palate to nasopharynx
palatopharyngeal arches laterally connect soft palate to nasopharynx
_________ laterally connects tongue to soft palate
palatoglossal arches: laterally connects tongue to soft palate
What is the purpose of the larynx?
Protects trachea against food aspiration, and aids in breathing and phonation
A rapid narrowing and widening of the glottis by fast twitch muscles in the feline is also known as _________
purring

List the 4 cartilaginous structures of the Larynx
- Epiglottic cartilage
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Thyroid cartilage
- Cricoid cartilage
Which muscle(s) of the larynx tense(s) the vocal fold (phonation)?
cricothyroideus
Which muscle(s) of the larynx open(s) the glottis?
**cricoarytenoideus dorsalis **
Which muscle(s) of the larynx close(s) the glottis?
cricoarytenoideus lateralis
Which muscle(s) of the larynx relax(s) the vocal fold & contrict the glottis?
thyroarytenoideus
The __________ supports the tongue and acts as attachments for lingual mm.; supports the larynx
hyoid apparatus
The opening to the _________ duct is at the 4th premolar
The opening to the parotid duct is at the 4th premolar
The circular opening at the front of the skull where the nose would be is the ___________
nasal aperture
The rostral alar foramen is connected to the caudal alar foramen by a tube called the _________
Alar canal
The location where the nasal cavities open into the nasopharynx is referred to as the _________.
Choanae
Which tooth is also called the Superior shearing tooth?
4th premolar
The _____________ pierces cheek mucosa to drain serous fluid into buccal vestibule
parotid salivary gland
This is the largest lymph node of the head and neck. When inflamed, ability to swallow is affected
medial retropharyngeal lymph node
This laryngeal cartilage forms a complete ring that lies partially within the trough of the thyroid cartilage
cricoid cartilage
The cuneiform process is found on which laryngeal cartilage?
Arytenoid cartilage

The _______ consists of the vocal folds, the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages, and the rima glottidis
The glottis consists of the vocal folds, the vocal processes of the arytenoid cartilages, and the rima glottidis
The __________ is the narrow passageway through the glottis.
rima glottidis
If an animal is unable to close its eye when the veterinarian is touching its cornea, it probably has an injury to which nerve?
facial nerve
The _______ nerve crosses the pterygoid muscles and enters the cheek lateral to the zygomatic salivary gland
The buccal nerve crosses the pterygoid muscles and enters the cheek lateral to the zygomatic salivary gland
The mandibular and sublingual glands open in the oral cavity at the ____________
sublingual caruncle
The geniohyoideus m. is innervated solely by which nerve?
hypoglossal n.
The ________ muscle is responsible for retraction of the upper lip
caninus m.
Identify the nerve indicated by the red arrow.

auriculopalpebral n.
Identify the nerve indicated by the red arrow.
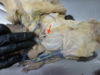
auriculotemporal n.
Identify the nerve indicated by the red arrow.

dorsal buccal n.
Identify the structure indicated by the red arrow.

parotid duct
Identify the nerve indicated by the red arrow.

ventral buccal n.
Identify the muscle indicated by the red arrow.

digastricus m.
Identify the nerve indicated by the red arrow.

hypoglossal n.
Identify the maxillary vein

There it is

Identify the external jugular vein


Locate the masseter muscle

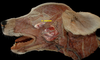
Locate the digastricus m.

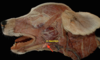
Locate the facial v.


Locate the lingual vein


Locate the linguofacial v.

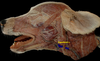
Locate the zygomatic arch
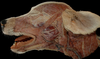

Locate the palpebral n.


Locate the ventral buccal n.

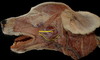
Locate the parotid duct


Locate the mandibular lymph node


Locate the mandibular salivary gland


Locate the parotid salivary gland

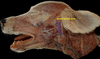
Locate the buccinator m.
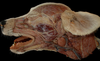

Locate the temporalis m.


Identify the infraorbital n.

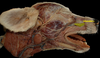
Identify the monostomatic sublingual salivary gland


Locate the orbital ligament

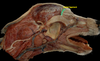
Locate the facial nerve


Locate the accessory nerve


Locate the facial vein
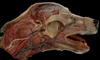
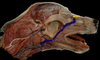
Identify the external sagittal crest


Identify the temporal fossa


Identify the zygomatic bone

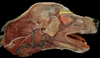
Identify the coronoid process


Locate the condylar process
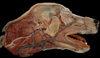

Locate the zygomatic salivary gland
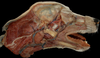
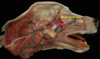
Locate the pterygoid muscle
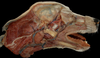

Locate the caudal auricular a.
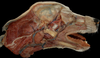
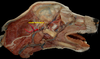
Locate the facial vein
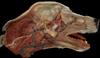
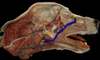
Locate the maxillary artery

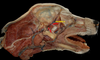
Locate the medial retropharyngeal lymph node

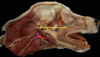
Locate the palatoglossal fold


Locate the thyrohyoideus


Locate the zygomatic muscle

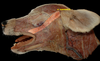
Whther it is large animal or small animal, the opening of the parotid duct is always at the level of ______________
4th premolar
In dogs with chronic dental disease, which lymph node would you normally see enlarged?
mandibular lymph node
The **pharynx **is divided into three parts. Name them:
- Oropharynx
- Nasopharynx
- Laryngopharynx
The ________ is a protective mechanism that closes off the opening of the trachea so that when we are eating, food does not get into the trachea
larynx
What do we notice in the feline larynx that is different than the canine?
Felines do not have cuneiform or corniculate proccesses of the arytenoid cartilage
When passing an endotracheal tube, you pass it through the __________.
The __________ forms the seal around the endotracheal tube.
When passing an endotracheal tube, you pass it through the rima glottidis.
The glottis forms the seal around the endotracheal tube.

List the 4 cartilaginous structures of the larynx
- Epiglottic cartilage
- Arytenoid cartilage
- Thyroid cartilage
- Cricoid cartilage
In laryngeal hemiplagia, we may have opening of the glottis on one side but not the other. Clinically, on which side do we tend to see this more often? Why?
We tend to see this more often on the left side.
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is wrapping around the aortic arch, has more pressure associated with it, and has a longer distance to travel, making it more prone to damage.
What is the main job of the hyoid apparatus?
to support the tongue and act as an attachment for lingual muscles


