Avian Questions Flashcards
What is the total time required from ovulation to oviposition?
24 hours
Which bone connects the mandible to the skull (temporal bone)
the quadrate bone
enables the upper and lower jaw to move simultaneously. While the quadrate bone turns, it increases the size of the gape
Which compartment of the cloaca do the vas deferens go to?
urodeum
The sebaceous gland responsible for waterproofing and insulating the feathers:
Uropygial gland
(“preen” gland)
Feathers in birds are concentrated in tracts called _________
Feathers in birds are concentrated in tracts called pterylae
These feathers are responsible for heating and insulating the body and helping maintain normal body temperature:
down feathers
What is the normal temperature for birds?
102-108oF
These feathers are specialized contour feathers responsible for flight:
**Wing feathers (remiges) **and tail feathers (retricles)
*These *feathers are new feathers in the growing stage:
blood feathers (pin feathers)
Which ovary is active in the chicken?
left
The fusion of the proximal row of the tarsus and the tibia is called the:
tibiotarsus
The fusion of the distal tarsal row with metatarsal 2, 3, and 4 form the:
Tarsometatarsus
Fusion along the dorsal spinous processes of most of the thoracic vertebrae:
notarium
Fusion of the last 2 or 3 thoracic vertebrae, all of the lumbar, all of the sacral, and the first few caudal vertebrae
synsacrum
Fusion of the most caudal 3-4 vertebrae that make up the bulk of the tail:
pygostyle
This bone allows for attachment of the large pectoral muscles and makes up the majority of the ventral body wall:
keel bone

The furcula is commonly known as the:
wish bone

What is significant about the radius and ulna in birds?
In birds, the ulna is larger than the radius
What is the name of the triangular fold of skin running from the shoulder to the carpus that provides an aerodynamic “lift”?
**propatagium **
What is pinioning?
This involves cutting the tendon of the extensor carpi radialis muscle at the level of its attachment on the carpus.
How many metatarsal bones are present on the avian pelvic limb?
4 (3 of which are fused)
Muscles take on different colors dependent on the relative amount of _____________ that is present.
Muscles take on different colors dependent on the relative amount of myoglobin that is present.
Which muscle will likely be darker in color: phasic muscles of endurance muscle?
endurance muscle
What is the most common site for collection of large volumes of blood in poultry and companion birds?
right jugular vein
Name three commonly used sites for blood collection in avians:
- right jugular vein (poultry & companion birds)
- cutaneous ulnar vein
- medial metatarsal vein (larger birds: ducks, raptors, large parrots)
Responsible for B-cell production in birds:
Bursa of Fabricius
The avian larynx lies on the floor of the oropharynx and opens on a small prominence called the _____________
laryngeal mound
Describe the unique positioning of the avian epiglottis.
They don’t have one. Get over it.
What is the landmark for endotracheal intubation in avians?
laryngeal mound
What is important to remember about the trachea in birds when placing an endotracheal tube?
The trachea in birds has complete cartilaginous rings
You should not use the cuffed endotracheal tubes, as over-inflation of the cuff can cause severe damage and necrosis of the trachea
How many air sacs are present in the chicken?
8
Birds do not have separate thoracic and abdominal cavities. Instead, they have a combined thoraco-abdominal cavity, also known as the ________________
coelomic cavity
In hatchlings, the sharp projection that is used to “pip” out of the shell is known as the:
egg tooth
The avian hard palate contains a longitudinal fissure that connects the oral and nasal cavities. What is this fissure called?
choana
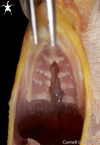
Out-pouching of the esophagus located just cranial to the thoracic inlet on the right side of the neck in chickens:
crop
Which portion of the avian stomach is the equivalent to the mammalian stomach?
the **proventriculus **(glandular portion)
In birds, the upper and lower ileum is divided by:
Meckel’s diverticulum
(a remnant of the fetal yolk sac)
Which compartment of the cloaca does the rectum lead to?
coprodeal compartment
What is the terminal region of the avian GI tract, urinary tract, and reproductive tract?
the cloaca
Which compartment of the cloaca serves as the termination for the GI tract?
the coprodeal compartment
Which compartment of the cloaca serves as the termination for the urinary and reproductive tracts?
the urodeal compartment

Which portion of the cloaca opens to the anus or vent?
the proctodeum
What is important to remember about the avian kidney with regard to prescribing drugs that act on the loop of Henle?
The avian kidney consists of “mammalian” and “reptilian” nephrons. The reptilian nephrons contain no loop of Henle.
What is the end product of the urinary tract in birds?
Uric acid
So, kidney function tests that we use in mammals (BUN & creatinine) are of very little use in birds
Blood supply to the ovary in birds is via the ________________
left ovarian artery
(a branch off the left cranial renal artery)
What is the site of calcification for the egg?
the uterus
Where are the testes located in birds?
The paired testes lie within the body cavity near the cranial pole of the kidney

How many accessory sex glands are found in male birds?
Zero.

areas of bare skin on a bird are called:
apteria

Which muscle is responsible for the downward motion of the wings (adduction of the wings)?
Superficial pectorals

Which muscle is responsible for the upward motion of the wings (abduction of the wings)?
deep pectorals

At which portion of the oviduct is albumin added to the egg?
the magnum

What is this ‘wing web’ referred to as?

propatagium


