Exam 4 - Reproductive Flashcards
(57 cards)
What are the current recommendations regarding self-breast exams?
- USPSTF* recommends against teaching BSE d/t evidence that it doesn’t reduce mortality and may lead to higher rates of benign breast biopsies
- American Cancer Society* recommends against BSE, but states all women should be familiar with how their breasts normally look and feel
What are the current recommendations regarding breast cancer screening - USPSFT?
Mammography
- 50-74 years - biennially
- <50 years - individualize screening based on patient specific factors
- >75 years - insufficient evidence to recommend
Clinical breast exam
- >40 years - insufficient evidence to assess additional benefits and harms of CBE beyond screening mammography
What are the current recommendations regarding breast cancer screening - American Cancer Society?
Mammography
- 40-45 years - optional annual screening
- 45-54 years - annual screening
- >55 years - biennial screening w/ option to continue annual screens
- Continue screening if good health and life expectancy >10 years
Clinical breast examination
- Not recommended d/t lack of evidence showing clear benefit
What are the current recommendations regarding breast cancer screening - American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists?
Mammography
- >40 years - annually
Clinical Breast Examination
- 20-39 years - every 1-3 years
- >40 years - annually
What are the seven characteristics of a breast nodule that should be described?
- Location - by quadrant or clock, w/ cm from nipple
- Size - in cm
- Shape - round or cystic, disclike, or irregular in contour
- Consistency - soft, firm, or hard
- Delimination - well circumscribed or not
- Tenderness
- Mobility - in relation to skin, pectoral fascia, chest wall
What history, exam findings, and risk factors are consistent with a fibroadenoma?
Usual age: 15-25 years, usually puberty and young adulthood
Shape: round, disclike, or lobular; typically small (1-2 cm)
Consistency: soft
Delimination: well delineated
Mobility: very mobile
Tenderness: nontender
Retraction signs: absent
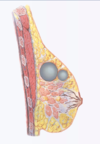
What history, exam findings and risk factors are consistent with a cyst?
Usual age: 30-50 years, regress after menopause except w/ estrogen therapy
Shape: round
Consistency: soft to firm, usually elastic
Delimination: well delineated
Mobility: mobile
Tenderness: often tender
Retraction signs: absent

What history, exam findings and risk factors are consistent with cancer?
Usual age: 30-90 years, most common >50 years
Shape: irregular or stellate
Consistency: firm or hard
Delimination: not clearly delineated from surrounding tissues
Mobility: may be fixed to skin or underlying tissues
Tenderness: usually nontender
Retraction signs: may be present

What are some visible signs of breast cancer?
Retraction, dimpling, edema, abnormal contours, nipple retraction and deviation, Paget diease of nipple

What could milky nipple discharge indicate?
Milky discharge unrelated to prior pregnancy and lactation is nonpuerperal galactorrhea
Causes: hyperthyroidism, pituitary prolactinoma, dopamine antagonists (psychotropics and phenothiazines)
What could bloody nipple discharge indicate?
Spontaneous unilateral bloody discharge from one or two ducts indicates:
- Intraductal papilloma
- Ductal papilloma in situ
- Paget disease of the breast

What could clear, serous, green or black nipple discharge indicate?
Usually benign
What are considered normal findings of the breasts of newborns?
Breasts of the newborn in both males and females are often enlarged from maternal estrogen effect (may last several months)
May be engorged w/ white liquid (“witch’s milk”) which lasts 1-2 weeks
What is premature thelarche?
Breast development occurs, most often between 6 months and 2 years
Other signs of puberty or hormonal abnormalities not present
What are the current recommendations regarding testicular self-exams?
USPSTF - inadequate evidence for the benefit of screening, either by clinician or self-examination
- Advised against screening for testicular cancer in asymptomatic adolescent or adult males
American Cancer Society - recommends that testicular examination should be part of general physical exam, but no recommendation for self-examinations
- Advises males to seek medical attention for any of the following: painless lump, swelling, enlargement in either testicle, pain or discomfort, feeling of heaviness or sudden fluid collection in scrotum, dull ache in lower abdomen or groin
What symptoms and exam findings are consistent with a testicular torsion?
- Tender painful scrotal swelling
- Retracted upward in scrotum
- Absent cremasteric reflex on affected side
- No associated urinary infection
Most common in neonates and adolescents; surgical emergency

What is the cremasteric reflex and how is it performed?
Examine the child when he is relaxed b/c anxiety stimulates the cremasteric reflex
Have patient sit cross-legged, give him a balloon to inflate, or an object to lift to increase intra-abdominal pressure
Option 1: Warm hands, palpate lower abdomen, work way down towards scrotum along inguinal canal (minimizes retraction of testes into the canal)
Option 2: Scratch medial aspect of thigh (testes on side being scratched will move up)

What is the difference between a direct and indirect inguinal hernia?
Indirect inguinal hernias develop at the internal inguinal ring, where the spermatic cord exits the abdomen
Direct inguinal hernias arise more medially d/t weakness in the floor of the inguinal canal and are associated w/ straining and heavy lifting
What exam findings are consistent with gonococcal urethritis vs. nongonococcal urethritis?
Gonococcal urethritis
- Profuse yellow penile discharge
Nongonococcal urethritis
- Scanty white or clear penile discharge
What are some benefits of circumcision?
AAP and experts recommend circumcision d/t reduced rates of HIV and other infections among circumcises males
What type of anticipatory guidance would the FNP provide to the child of the uncircumcised male?
- When bathing your child, wash the penis. Then dry it thoroughly.
- Never forcibly pull back (retract) the foreskin when washing your infant or young child
- When the foreskin is able to retract, gently pull it back and bathe the area. Dry the penis thoroughly.
- Return the foreskin to its natural position by pulling it back over the penis. This is important because if the foreskin is left retracted, it could put pressure on the penis. This can cause pain and swelling and may require medical attention.
What are hypospadias?
Congenital ventral displacement of urethral meatus to the inferior surface of penis
Meatus may be subcoronal, midshaft, or at junction of the penis and scrotum (penoscrotal)

What is chordee?
Fixed, downward bowing of the penis (may accompany a hypospadias)
What are considered to be normal scrotal findings of the newborn? The premature newborn?
- Nonretractable at birth, but may retract enough to visualize external urethral meatus
- Foreskin completely covers glans penis; gradually loosens over months to years
- Testes should be 10mm in width and 15mm in length
- Scrotal edema may be present for several days following birth b/c of maternal estrogen