Exam 3 (Chs. 20, 21, 23-26) Flashcards
Each of the following statements regarding film mounting is correct EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Mounted films are easy to store.
b. Mounting decreases the chance of error caused by confusing the patient’s right and left sides.
c. Lingually mounted radiographs allow for easy transfer of findings to the patient’s record.
d. Patient communication is enhanced when films are mounted.
c. Lingually mounted radiographs allow for easy transfer of findings to the patient’s record.

When films are mounted _labially,_ radiographic findings can be easily transferred to the patient’s dental chart. This orientation corresponds to the order in which teeth and anatomic structures are drawn on most dental and periodontal charts.
Which of these statements is FALSE?
a. The lingual method of film mounting is recommended by the American Dental Association and the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
b. With the labial method of film mounting, the radiographs are mounted so that the embossed dot is convex.
c. With the lingual method of film mounting, the radiographs are mounted so that the embossed dot is concave (dimple).
d. With the labial method of film mounting, the viewer’s right is the patient’s left.
a. The lingual method of film mounting is recommended by the American Dental Association and the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.
* The labial method of film mounting is the method recommended by the American Dental Association and the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology.*

Which of the following statements regarding film mounting methods is correct?
a. With the labial method, the embossed dot is concave.
b. With the lingual method, the embossed dot is convex.
c. With the lingual method, the viewer is reading the radiographs as if facing the patient.
d. With the labial method, the viewer is reading the radiographs as if facing the patient.
d. With the labial method, the viewer is reading the radiographs
as if facing the patient.
With the labial method, what the viewer observes on the right side of the radiograph corresponds to the patient’s left side. The viewer’s right is the patient’s left.

Which of the following statements regarding film mounting is correct?
a. Anterior periapical radiographs are placed in the oral cavity with the long dimension of the film packet positioned horizontally.
b. Size #1 film is usually used to radiograph the anterior regions.
c. Size #4 film is usually used to radiograph the posterior regions.
d. Posterior periapical radiographs are placed in the oral cavity with the long dimension of the film packet positioned vertically.
b. Size #1 film is usually used to radiograph the anterior regions.
* When mounting a full mouth series of radiographs, it is helpful to use film sizes and orientation in the oral cavity to help with the mounting process.*
From the following, select the correct generalization
that aids in mounting radiographs.
a. Most roots curve toward the mesial.
b. Premolars have the longest roots when compared to adjacent teeth.
c. Maxillary anterior teeth are larger than mandibular anterior teeth.
d. Maxillary molars have two roots.
c. Maxillary anterior teeth are larger than mandibular anterior teeth.
* Most roots curve toward the distal. Canines generally have the longest roots. Maxillary molars generally have three roots. Base knowledge of radiographic anatomy helps the operator mount radiographs correctly.*
From the following, select the correct generalization that
aids in mounting radiographs.
a. Posterior films are oriented to give a slight “smile” appearance.
b. The presence of a third root on mandibular molars makes it difficult to view bone in the furcation area.
c. Roots and crowns of mandibular anterior teeth are larger and longer than those of the maxilla.
d. Large, radiolucent areas denoting the nasal fossa or sinus indicate that the image is of the mandibular arch.
a. Posterior films are oriented to give a slight “smile” appearance.
The body of the mandible has a distinct upward curve toward the ramus in the molar area.
Which of the following would indicate that a film was mounted incorrectly?
a. The radiographs appear in anatomical order.
b. The identification dots are not all oriented in the same way.
c. The roots are pointing up for the maxilla and down for the mandible.
d. The radiographs are firmly secured in the mount.
b. The identification dots are not all oriented in the same way.
Identification dots must all be either convex or concave and not some one way and some another way,
to distinguish the patient’s right and left sides.
Which of these statements is FALSE?
a. Dental radiographs may be viewed by the dentist, dental hygienist, or dental assistant.
b. Diagnosis is defined as identification and determination of the nature of an abnormal condition or disease.
c. Dental radiographs may be interpreted by all members of the oral health care team.
d. Diagnosis is the responsibility of the dental assistant and dental hygienist.
d. Diagnosis is the responsibility of the dental assistant and dental hygienist.
Diagnosis** is the responsibility of the **dentist.
Which of these statements regarding viewing equipment is FALSE?
a. A magnifying glass may be used to aid the viewer.
b. Clear plastic film mounts help reduce glare and enhance the detail of the images.
c. Subdued room lighting is best for viewing radiographs.
d. Viewbox lighting must be of uniform intensity and evenly diffused.
b. Clear plastic film mounts help reduce glare and
enhance the detail of the images.
- The use of black plastic or gray cardboard mounts helps to reduce glare*
- and enhance the detail of the images.*
Which of these statements is FALSE?
a. Once exposed and processed, heat can no longer affect dental film.
b. Misplaced radiographs can result in risk-management problems.
c. Radiographs should be retained indefinitely.
d. Radiographs should be handled with care to avoid smudging or scratching.
a. Once exposed and processed,
heat can no longer affect the dental film.
Radiographs should be protected from heat damage by storage in a cool, well-ventilated area.
To mount radiographs, the radiographer must possess knowledge of:
a. film brands and sizes.
b. pathology and diagnosis.
c. normal anatomy.
d. All of the above.
c. normal anatomy.
* Thorough knowledge of the normal anatomy of the teeth and jaws*
* is needed* to mount radiographs correctly.
Each of the following is an advantage of film mounting EXCEPT one.
Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Aids viewing and interpretion
b. Prevents unnecessary retakes
c. Facilitates storage of radiographs
d. Provides meaningful patient education
b. Prevents unnecessary retakes
Advantages of film mounting include: easier viewing and interpretation; decreased chance of error caused by confusing the patient’s right and left sides; viewing films side by side allows for easy comparison between different views; less handling of individual radiographs results in fewer scratches and fingerprint marks; film mounts can mask out distracting side light, making radiographs easier to view and interpret; film mounts provide a means for labeling the radiographs with the patient’s name, date of exposure, name of the practice, and so on; they are easy to store; patient education and consultations are enhanced when films are mounted; when mounted labially, radiographic findings can be easily transferred to the patient’s dental chart.
If a film packet is placed in the patient’s mouth correctly,
which side will face the source of radiation?
a. The white, unprinted side with the embossed dot concave
b. The white, unprinted side with the embossed dot convex
c. The colored, printed side with the embossed dot concave
d. The colored, printed side with the embossed dot convex
b. The white, unprinted side with the embossed dot convex (pimple)
* Placing the white, unprinted side of the film packet toward the lingual surface of the teeth positions the tube side of the film facing the radiation source. In this position, the embossed dot will be correctly positioned convex.*
With the lingual method of film mounting, the embossed dot will be ____________, and the viewer will interpret the radiographs as if ___________________________.
a. convex, facing the patient
b. concave, facing the patient
c. convex, standing behind the patient
d. concave, standing behind the patient
d. concave (dimple)
standing behind the patient
With the lingual mounting method, the radiographs are mounted so that the embossed dot is concave. In this position, the viewer is reading the radiograph as if standing behind the patient. Therefore, what the viewer observes on the right side of the radiograph would correspond to the patient’s right as well. Essentially, the viewer’s right is the patient’s right.
With the labial method of film mounting, the embossed dot will be ____________, and the viewer will interpret the radiographs as if ___________________________.
a. convex, facing the patient
b. concave, facing the patient
c. convex, standing behind the patient
d. concave, standing behind the patient
a. convex (pimple)
facing the patient
With the labial method of film mounting, the radiographs are mounted so that the embossed dot is convex. In this position, the viewer is reading the radiograph as if standing in front of, and facing, the patient. Therefore, what the viewer observes on the
right side of the radiograph would correspond to the patient’s left side.
Which of these mandibular teeth generally have the longest roots?
a. Central incisors
b. Lateral incisors
c. Canines
d. Premolars
c. Canines
Canine teeth generally have the longest roots when compared to adjacent teeth.
Dental assistants and hygienists may:
a. make a final diagnosis from dental radiographs alone.
b. make a final diagnosis from dental radiographs and the clinical examination.
c. interpret dental radiographs and use them to help educate the patient regarding oral conditions.
d. place and expose dental radiographs but not read them.
c. interpret dental radiographs and use them to help educate the
patient regarding oral conditions.
Interpretation is explanatory and may be defined as reading the radiograph and explaining what is observed in terms the patient understands. The dentist, dental assistant, and dental hygienist may interpret radiographs and use them in patient education.
Black opaque or cardboard film mounts are preferred because they:
a. are less expensive and more readily available from the manufacturer.
b. are more common and therefore easily shared with other practices.
c. make placing films in the windows easier.
d. block extraneous light to aid in interpretion.
d. block extraneous light to aid in interpretation.
Black plastic or gray** cardboard mounts are often **preferred over clear plastic mounts** because they can **block out** extraneous **light** from the **view box,** enhancing **viewing and interpretation.
Which statement(s) regarding film mounting is (are) true?
a. It allows the radiographs to be viewed in a systematic order.
b. It helps to prevent lost films.
c. It provides a means for labeling the films with pertinent data.
d. All of the above.
d. All of the above.
Advantages of film mounting include: easier viewing and interpretation; decreased chance of error error caused by confusing the patient’s right and left sides; viewing films side by side allows for easy comparison between different views; less handling of individual radiographs results in fewer scratches and fingerprint marks; film mounts can mask out distracting side light, making radiographs easier to view and interpret; film mounts provide a means for labeling the radiographs with the patient’s name, date of exposure, name of the practice, and so on; they are easy to store; patient education and consultations are enhanced when films are mounted; when mounted labially, radiographic findings can be easily transferred to the patient’s dental chart.
After orienting the embossed dots all the same way, the next suggested step when systematically mounting dental radiographs is to:
a. separate anterior periapical radiographs from posterior periapical radiographs.
b. separate maxillary periapical radiographs from mandibular periapical radiographs.
c. separate bitewing radiographs from periapical radiographs.
d. label the film mount with the patient’s name and date.
c. separate bitewing radiographs from periapical radiographs.
* After orienting the embossed dots all the same way, the next suggested step when systematically mounting dental radiographs is to separate the bitewing from the periapical radiographs.*
All radiographs, whether intraoral or extraoral, should be mounted.
True
False
False.
Film mounting** refers **only to intraoral films.
Extraoral radiographs must be labeled to identify the right and left sides of the patient and placed in an envelope labeled with the patient’s name and date of exposure.
A single intraoral radiograph should be placed in a coin envelope and
attached to the patient’s chart.
True
False
False.
It is better to mount even a single radiograph or small group of radiographs. The film mount provides a place to record the patient’s name, date of exposure, and other pertinent information and helps to prevent damage from handling.
Clear plastic mounts are preferred over black plastic or gray cardboard mounts.
True
False
False.
Black plastic or gray cardboard mounts are preferred over clear plastic mounts because they block out extraneous light from the viewbox.
Mandibular premolar and molar radiographs should be oriented
so that a slight “smile” appearance is viewed.
True
False
True.
The body of the mandible has a distinct upward curve toward the ramus in the molar area.
Radiographs may be best interpreted by holding the film up
to the overhead room light.
True
False
False.
Holding a radiograph up to the overhead room light will not provide adequate conditions in which to observe detailed, subtle images on the radiograph.
Some view boxes are equipped with a magnifying glass.
True
False
True.
A viewbox and magnifying glass are required for optimum film viewing. Some viewboxes are equipped with a magnifying glass. Otherwise, a handheld magnifying glass should be used to aid the viewer.
Patient radiographs should be retained indefinitely.
True
False
True.
Radiographs should be preserved until the statute of limitations has expired. However, laws vary from state to state and may not always apply under certain conditions.
Therefore, radiographs should be retained indefinitely.
The identification dot on intraoral radiographs is used to distinguish the patient’s left and right sides.
True
False
True.
Since the radiograph may be viewed from either side, it is important that the radiographer understand the role the identification dot plays in film orientation.
The lingual method of film mounting is the preferred method.
True
False
False.
The labial method of film mounting is the preferred method.
Mandibular molars generally have two divergent roots that are distinctly observed radiographically.
True
False
True.
Because of the divergence of the two roots of mandibular molars, bone can be seen between them on the radiograph. Maxillary molars have three roots. The presence of a palatal root on maxillary molars makes it difficult to visualize three distinct roots.
A practice may contact a manufacturer of film mounts to order a custom-designed mount for that practice.
True
False
True.
Film mounts are available in many sizes and with numerous combinations of windows or frames to fit films of different sizes. Standard commercially made mounts are available, or companies will make custom mounts to suit special needs.
When a film packet is positioned correctly in the oral cavity, the embossed identification dot will automatically be oriented so that the convexity or concavity may be used to identify the patient’s left and right sides.
True
False
True.
If the film packet was placed in the patient’s oral cavity correctly, the raised portion of the identification dot (the convexity) automatically faces the x-ray tube and the source of radiation.
Therefore, when the radiograph is viewed later, the identification dot may be relied on to determine which are the patient’s left and right sides.
A radiograph may only be viewed correctly from the side with the embossed dot convex.
True
False
False.
A radiograph may be viewed from either side, so it is important that the radiographer understand the role the identification dot plays in film orientation.
Clues that assist the radiographer in the mounting process include using the
size and orientation of the film packet.
True
False
True.
Size #1 film is often used to radiograph the anterior region. Additionally, anterior periapical radiographs are placed in the oral cavity with the long dimension of the film packet positioned vertically, whereas posterior periapical radiographs are placed in the oral cavity with the long dimension of the film packet positioned horizontally. These clues may be used to help the radiographer determine where to position the films in the mount.
Roots and crowns of the mandibular anterior teeth are larger and longer than those of the maxillary teeth.
True
False
False.
Roots** and **crowns** of the **maxillary anterior teeth** are l**arger and longer** than those of the **mandibular teeth.
The incisive foramen, the median palatine suture, and the genial tubercles are all anatomical landmarks that can be found on radiographs of the maxillary anterior region.
True
False
False.
The genial tubercles are anatomical landmarks that can usually be recorded on anterior radiographs of the mandible.
The oblique ridge, mylohyoid ridge, and submandibular fossa are all anatomical landmarks that can be found on radiographs of the mandibular posterior region.
True
False
True.
The oblique ridge, mylohyoid ridge, and submandibular fossa are all anatomical landmarks that can be found on radiographs of the mandibular posterior region.

To optimize viewing of digital radiographs, the computer monitor should be located in an area of bright light.
True
False
False.
Coping with overhead room lighting reflecting off the monitor screen is a consideration the radiographer will have to manage. Setting up the monitor in a position to minimize reflections from overhead room lighting or ambient lighting entering the room through windows will assist with reducing glare that can interfere with interpretation.
The interpretation of radiographs is improved if the radiographer develops a systematic method for reading the images.
True
False
True.
The mounted radiographs must be viewed in a systematic order to prevent errors in interpretation.
All available radiographs should be examined for a specific condition, and then the examination process should be repeated for the next condition.
The lingual method of mounting radiographs positions the embossed dot
convex (pimple).
True
False
False.
The lingual method of mounting radiographs positions the
embossed dot concave (dimple).
The labial method of mounting radiographs positions the
embossed dot convex (pimple).
Each of the following must be added to radiographic findings for accurate diagnosis EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Medical and dental history
b. Clinical observations
c. Signs and symptoms
d. Past radiation exposure
d. Past radiation exposure
Radiation exposure history does not contribute any information that would assist in diagnosis.
Which of the following restorative materials appears the most radiolucent (dark)?
a. Silicate
b. Gutta-percha
c. Stainless steel crown
d. Implant
a. Silicate
Older composite restorative material such as silicate often appears radiolucent or about the same density (darkness) as dentin.
Which of the following restorative materials
may appear radiopaque (light) or radiolucent (dark)?
a. Amalgam
b. Sealants
c. Composite
d. Gold
c. Composite
In the past, older composite restorative materials appeared radiolucent.
Manufacturers of composite materials now put radiopaque fillers into the material. Radiographs may reveal the presence of both radiolucent and radiopaque composite restoratives.
Base material (calcium hydroxide pastes) and cement exhibit approximately the same degree of radiopacity as:
a. enamel.
b. dentin.
c. bone.
d. amalgam.
b. dentin.
Enamel, bone, and amalgam would all appear more radiopaque (light).
Radiographs are helpful in revealing each of the following EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Amalgam particles in soft tissue
b. Bluish-colored gingiva
c. Base material
d. Overhanging restorations
b. Bluish-colored gingiva
Bluish-colored gingiva may indicate the presence of amalgam particles in the soft tissue. However, soft tissue does not image on a radiograph.
Which of these statements regarding the radiographic appearance of dental materials is FALSE?
a. A full metal crown may be distinguished from amalgam by its smooth margins.
b. A stainless steel crown has a see-through appearance.
c. A porcelain jacket appears more radiopaque than a full metal crown.
d. Porcelain appears about the same density as dentin.
c. A porcelain jacket appears more radiopaque (light) than a full metal crown.
Porcelain appears about the same density as dentin (dark). Therefore, a porcelain jacket would appear less radiopaque (light) than a full metal crown.
Which of these statements is FALSE?
a. Post and core restorations resemble implants radiographically.
b. Retention pins have a shape that is easy to identify on the radiograph.
c. Retention pins are located in the dentin only.
d. Post and core restorations are always observed in conjunction with endodontic filling material.
a. Post and core restorations resemble implants radiographically.
Post and core restorations build up a tooth so that it can support a crown.
A post and core would appear within a pulp chamber of a tooth that has been treated endodontically. An implant takes the place of a missing tooth.
Which of the following restorative crown types
appears the least radiopaque (light)?
a. Porcelain fused to metal
b. Full metal
c. Stainless steel
d. Porcelain
d. Porcelain
The lack of metal in a porcelain crown would make this
restoration appears less radiopaque (light).
Which of these dental anomalies will NOT be recorded on a dental radiograph?
a. Dilaceration
b. Mesiodens
c. Gingival recession
d. Dens in dente
c. Gingival recession
Radiographs do not image the soft tissue of the gingiva accurately enough to observe gingival recession.
Which of these will appear radiopaque (light)?
a. An abscess
b. A cyst
c. A granuloma
d. Osteosclerosis
d. Osteosclerosis
Osteosclerosis occurs in regions of abnormally dense bone, making this condition appear radiopaque.
An abscess, cyst, and granuloma will appear radiolucent (dark).

On a radiograph, an amalgam tattoo may appear as a(n):
a. radiolucency.
b. radiopacity.
c. bluish-colored irregularity.
d. overhang.
b. radiopacity.
Amalgam that fractures during an extraction and falls into the root socket or under the gingival tissue may impart a bluish-purple color to the tissue, called an “amalgam tattoo.” Because the amalgam is dense, it will
appear radiopaque (light) on the radiograph.
Which of these sequences of interpreting radiographic images is recommended?
a. Examine the teeth, determine the location of the suspected caries and periodontal disease, check the condition of restorations, and identify landmarks.
b. Identify landmarks, examine the teeth, check the condition of restorations, and determine the location of the suspected caries and periodontal disease.
c. Determine the location of the suspected caries and periodontal disease, examine the teeth, identify landmarks, and check the condition of restorations.
d. Check the condition of restorations, determine the location of the suspected caries and periodontal disease, identify landmarks, and examine the teeth.
b. Identify landmarks, examine the teeth, check the condition of restorations, and determine the location of the suspected caries and periodontal disease.
* The radiographer should first identify normal radiographic anatomy, then systematically progress through a sequence of evaluation, naming each radiopaque and radiolucent structure observed. This sequence is suggested to assist the beginning radiographer with developing a comprehensive approach to this process.*
Each of the following should be determined from the radiographic image EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. The identity of the anatomical landmark
b. The normal size and shape of the anatomical landmark
c. Whether the anatomical landmark is in the appropriate region
d. Whether pathosis if the anatomical landmark is absent
d. Whether pathosis if the anatomical landmark is absent
* Depending on the position of the image receptor and the angle of the x-ray beam, not all anatomical landmarks will be recorded on the image receptor. Not recording a structure on the radiographic is not indicative of pathosis.*
Which of these restorative materials will appear the most radiopaque (light)
on a dental radiograph?
a. Post and core
b. Composite
c. Porcelain
d. Gutta-percha
a. Post and core
A post and core restoration is metal and therefore will attenuate more of the
x-ray beam, resulting in a more radiopaque appearance.
Which of these restorative materials will appear the most radiopaque on a dental radiograph?
a. Cement
b. A temporary filling
c. Gold
d. Base material
c. Gold
The metal gold will attenuate (weaken) more of the x-ray beam, resulting in a more radiopaque (light) appearance.
Each of the following dental materials might not be imaged on a dental radiograph or may be only slightly visible EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Acrylic resins
b. Sealants
c. Silver points
d. Base materials
c. Silver points
The endodontic restorative material silver points are metal and therefore will attenuate (weaken) more of the x-ray beam, resulting in a
more radiopaque (light) appearance.
Each of the following is true regarding the radiographic appearance of composite restorations EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. They may appear either radiopaque or radiolucent.
b. They may appear with irregular or diffuse margins.
c. They may mimic caries.
d. They may appear about the same density as cementum.
b. They may appear with irregular or diffuse margins.
Restorations appear** to have **straight margins** and a **prepared look**, whereas **caries appears more diffuse.
Which of the following dental materials will most likely have a see-through appearance radiographically?
a. A stainless steel crown
b. Gutta-purcha
c. A temporary filling
d. Acrylic resin
a. A stainless steel crown
* As a temporary restoration, this metal is less dense and will allow the passage of more x-rays, giving the material a “see-through” appearance.*
Each of the following dental materials may be observed within the pulp chamber and/or root canals of the tooth EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. Post and core
b. A silver point
c. Gutta-percha
d. An implant
d. An implant
An implant is located in the area of a missing tooth.
Which of the following terms means “the absence of teeth”?
a. Supernumerary
b. Anodontia
c. Anomaly
d. Mesiodens
b. Anodontia
Anodontia refers to a congenital absence of teeth. Any tooth in the dental arch may fail to develop.
Hypercementosis appears radiopaque (light) and is caused by excessive cementum formation.
True
False
True.
The excessive cementum on the root often causes a bulbous enlargement, with the area near the apex being the most bulbous. The excessive cementum will appear radiopaque.
Hypercementosis is distinguished from other radiopacities in bone by the absence of the periodontal ligament space (PDL).
True
False
False.
When observing hypercementosis, the periodontal ligament contains the radiopacity (light) and separates it from the bone.
A taurodont tooth is a single tooth bud that divides and forms two teeth.
True
False
False.
A taurodont tooth is characterized by very large pulp chambers
and very short roots.
Germination = a single tooth bud that divides and forms two teeth.

A condition where the cementum of adjacent teeth is joined together is called “condensing osteitis.”
True
False
False.
Condensing osteitis refers to the formation of compact sclerotic bone.
Fusion is a condition where the cementum of adjacent teeth is joined together

A cyst is an epithelium-lined sac containing fluid or other fibrous or solid material that appears radiolucent.
True
False
True.
A cyst is an epithelium-lined sac containing fluid or other fibrous or solid material that appears radiolucent.
An acute abscess may be barely discernable radiographically.
True
False
True.
In the very early acute stages, there may be no radiographic evidence at all. The earliest radiographic sign is a break in the lamina dura.
A granuloma is a mass of granulation tissue.
True
False
True.
Granulomas**, masses of **granulation tissue**, are **continuous** with the **periodontal ligament space** and **appear attached to the root apices.** Under certain conditions, **epithelial elements** within the granuloma **proliferate** to **form a cyst.
Unless a cyst is completely removed at the time of tooth extraction, it will remain and is then called a “radicular cyst.”
True
Fasle
False.
Cystic material remaining after an extraction is called a “residual cyst.”
The dentigerous cyst is an odontogenic cyst that develops at the apex of a nonvital tooth.
True
False
False.
The dentigerous cyst is an odontogenic cyst that develops around the
crown** of an **impacted tooth.

Internal root resorption is most often characterized by root-end resorption where the roots of the teeth appear shorter than normal.
True
False
False.
External resorption is most often characterized by root-end resorption, where teeth roots appear shorter than normal as the resorption progresses
Internal root resorption appears as a radiolucent (dark) widening of the root canal, representing the resorption process taking place from the inside out.
When a developmental anomaly occurs in which the enamel invaginates within the body of the tooth, it is called “mesiodens.”
True
False
False.
A developmental anomaly in which the enamel invaginates within the body of the tooth is called _“dens in dente.”_
*tooth within a tooth

Dilaceration occurs as an unnatural or sharp bend in the tooth root.
True
False
True.

An unnatural or sharp bend in the tooth root is called “dilaceration.”
A torus is a bony growth projecting outward from the surface of a bone.
True
False
True.
A bony growth projecting outward from the surface of a bone, occasionally encountered on the palate or the lingual surface of the mandible, are tori (plural of torus).
Fusion occurs when a single tooth bud divides and forms two teeth.
True
False
False.
When a single tooth bud divides and forms two teeth, it is called _“germination.”_

The term “idiopathic resorption” can apply to either external or internal resorption.
True
False
True.
Idiopathic resorption** refers to a **loss of bone** or **tooth structure** as the **result of unknown causes.

Resorption that follows a path from inside out, or a widening of the root canal of the tooth, is external resorption.
True
False
False.
Tooth structure lost evidenced by a radiolucent (dark) widening of the root canal is indicative of internal resorption.

A _nonodontogenic cys_t arises from epithelial cells associated with the development of a tooth.
True
False
False.
Nonodontogenic cysts arise from epithelium other than that
associated with tooth formation.
An odontoma often appears as a mixed radiopaque and radiolucent mass of enamel and dentin
True
False
True.
An odontoma forms when enamel, dentin, and cementum form irregular shapes resembling small misshaped teeth whose number varies widely. These toothlike structures appear radiopaque and are located within a radiolucent fibrous capsule that can resemble a cyst

Radiographs can be used to determine an overhang.
True
False
True
#2
An overhang is a restoration that is not contoured to the tooth properly. Radiographs may be used to detect this imperfection on the proximal surfaces of the teeth.

The endodontic filling materials gutta-percha and silver points cannot be distinguished radiographically.
True
False
False.
Radiopacities observed within the pulp chamber may be either silver points**, a **very radiopaque (dark) metal root canal filling;
or gutta-percha (non-metallic), a less radiopaque filling.

Which of the following statements is FALSE?
a. The detection of caries is one of the most common reasons for exposing dental radiographs.
b. The carious process is one of remineralizationof tooth structure
c. Caries appears radiolucent (dark) on the radiograph.
d. The presence of caries allows more x-rays to pass through the tooth and darken the image receptor.
b. The carious process is one of remineralization of tooth structure
* The carious process is one of demineralization*
* of tooth structure (enamel, dentin, and cementum).*
An optical illusion caused by the overlapping of teeth that mimics decay is called the “Mach band effect.”
True
False
2
True.
The increased radiopacity produced by the overlapped teeth is often outlined by a radiolucent halo called the “Mach band effect.”

Nonmetallic radiolucent restorations may mimic decay radiographically.
True
False
1
True.
To aid in distinguishing a restoration from caries, look for the restoration to have straight borders, or a prepared look, with an overall even radiolucency.

The high contrast between normal enamel and overlapped enamel can produce an optical illusion called “cervical burnout.”
True
False
False.
#2
The high contrast between normal enamel and overlapped enamel can produce an optical illusion called “Mach banding.”

List four advantages of mounting film-based radiographs?
- ease of viewing when radiographs are in the correct anatomical position
- facilitation of comparison between radiographs in side-by-side position
- masking out of distracting side light, enhancing viewing and interpretation
- decreased chance of confusing right and left sides
- Provides a means for labeling (patients name, date of exposure, name of the practice)
- provision a means of filing and storage
- Facilitates enhancement of patient education and consultations
- when mounted labially, that radiographic findings can be easily transferred to a dental chair
Which of these landmarks would be likely to appear on a maxillary radiograph?
a. genial tubercles
b. mental fossa
c. oblique ridge
d. zygoma
d. zygoma
Which of these is NOT a characteristic of a quality film mount?
a. provides space to document patient name and date of exposure
b. constructed of clear plastic that does not mask light around radiograph edges
c. supports and protects radiographs from scratches that may occur during handling
d. contains enough windows to secure the number of radiographs exposed
b. constructed of clear plastic that does not
mask light around radiograph edges
Which of these helps to determine whether a radiograph was exposed on a patient’s left or right side?
a. slight “smile” appearance
b. distally curved roots
c. large crowns
d. embossed film dots
d. embossed film dots
- *Labial method** film mounting positions the identification dot concave
- *Labial method** is the recommended film mounting method.
a. the first statement is true. the second statement is false
b. the first statement is false. the second statement is true
c. both statements are true
d. both statements are false
b. the first statement is false.
the second statement is true
Lingual method film mounting positions the identification dot convex.
When utilizing the lingual method, the viewer’s right is the patient’s left.
a. the first statement is true. the second statement is false.
b. the first statement is false. the second statement is true
c. both statements are true
d. both statements are false
d. both statements are false
Which of the following should be done first when mounting film-based radiographs?
a. orient all identification dots the same way
b. separate bitewing from periapical films
c. separate anterior from posterior films
d. orient the teeth roots to point in the correct direction
a. orient all identification dots the same way
Each of the following will aid in correctly orienting radiographic images EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. anterior image receptors are positioned with the long dimension vertically
b. canine teeth generally have the longest roots
c. maxillary molars usually have three roots
d. roots and crowns of mandibular teeth are usually larger than maxillary teeth
d. roots and crowns of mandibular teeth are usually larger than maxillary teeth
Which of these is NOT a consideration when viewing digital radiographic images?
a. glare off a computer monitor must be managed to enhance interpretation
b. image must be checked to ensure exposure was placed into correct template window
c. a magnifying glass is required for optimal viewing and interpretation
d. multiple mouse clicks may be required to view a full mouth series of radiographs
c. a magnifying glass is required for optimal viewing and interpretation
Reading and explaining what is observed on a radiographic image is…
a. diagnosing
b. interpreting
c. viewing
d. mounting
b. interpreting
Viewing correctly oriented radiographic images in a systematic sequence can help prevent errors in interpretation
Digital imaging software provides special features such as magnification enhancement that aid in interpretation?
a. the first statement is true. the second statement is false
b. the first statement is false. the second statement is true.
c. both statements are true
d. both statements are false
c. both statements are true
In which region is it best to begin the interpretation process when
viewing a full mouth series of radiographs?
a. maxillary right posterior
b. maxillary left posterior
c. mandibular right posterior
d. mandibular left posterior
a. maxillary right posterior
Following a dentist’s diagnosis, radiographic findings must be recorded in the patient’s record by
a. a dental assistant
b. a dental hygienist
c. a dentist
d. any of the above
d. any of the above
the angle of the x-ray beam may distort the appearance of an anatomical structure because some landmarks may take on a different appearance on the right and on the left sides?
a. both the statement and reason are correct and related
b. both the statement and reason are correct but NOT related
c. the statement is correct, but the reason is NOT
d. the statement is NOT correct, but the reason is correct
e. NEITHER the statement NOR the reason is correct
b. both the statement and reason are correct but NOT related
Which of the following facial bones could appear on a periapical radiograph?
a. occipital
b. parietal
c. frontal
d. zygoma
d. zygoma #4

Bone sometimes has a mixed radiopaque-radiolucent appearance due to the nature of the
a. cortical plates
b. trabeculae patterns
c. alveolar process
d. lamina dura
b. trabeculae patterns
Which of the following will most likely appear as a radiopacity outlining the tooth root?
a. PDL space
b. lamina dura
c. nutrient canal
d. cementum
b. lamina dura

When nutrient canals open at the surface of the bone, they often appear radiographically as…?
a. small radiolucent dots
b. large radiopaque lines
c. small radiolucent lines
d. small radiopaque dots
a. small radiolucent dots

#1
Which of these structures appears radiolucent (dark)?
a. enamel
b. cementum
c. dentin
d. pulp
d. pulp #3

Which of the following is the best recommended sequence for identifying a normal radiographic anatomical landmark?
a. 1. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible views
2. determine if radiograph is anterior or posterior view
3. determine if structure is radiopaque/radiolucent
b. 1. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible view
2. determine if structure is radiopaque or radiolucent
3. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible view
c. determine if structure is radiopaque or radiolucent
2. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible view
3. determine if radiograph is anterior or posterior view
d. 1. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible view
2. determine if structure is radiopaque or radiolucent
3. determine if radiograph is anterior or posterior view
a. 1. determine if radiograph is maxilla or mandible views
2. determine if radiograph is anterior or posterior view
3. determine if structure is radiopaque/radiolucent
Which of the following structures may be recorded radiographically
superimposed over the roots of the maxillary molars?
a. mastoid process
b. maxillary tuberosity
c. zygomatic process
d. mylohyoid ridge
c. zygomatic process #3

Each of these features will appear radiolucent (dark) EXCEPT one.
Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. foramen
b. suture
c. canal
d. spine
d. spine #7

Each of these features will appear radiopaque EXCEPT one.
Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. ridge
b. sinus
c. tubercles
d. process
b. sinus #4

Each of the following may appear on a periapical radiograph of the
maxillary anterior region EXCEPT one. Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. nasal septum
b. median palatine suture
c. maxillary tuberosity
d. inverted Y
c. maxillary tuberosity

Each of the following may appear on a periapical radiograph of the
maxillary posterior region EXCEPT one? Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. maxillary sinus
b. incisive foramen
c. zygomatic arch
d. hamaulus
b. incisive foramen

Which of these mandibular anatomical features may be recorded on a periapical radiograph of the maxillary posterior region?
a. mandibular cnanal
b. submandibular fossa
c. inferior border of the mandible
d. coronoid process
d. coronoid process

Each of the following may appear on a periapical radiograph of the
mandibular anterior region EXCEPT one? Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. genial tubercles
b. mental ridge
c. coronoid process
d. mylohyoid foramen
c. coronoid process #8
Each of the following may appear on a periapical radiograph of the
mandibular posterior region EXCEPT? Which one is the EXCEPTION?
a. mental foramen
b. pterygoid plate
c. mandibular canal
d. mylohyoid ridge
b. pterygoid plate #4
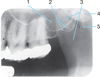
The inverted Y landmark is composed of the intersection of what two structures?
a. lateral wall of the nasal cavity and anterior border of the maxillary sinus
b. anterior border of the maxillary sinus and inferior border of the mandible
c. lateral wall of the nasal cavity and soft tissue shadow of the nose
d. inferior border of the zygomatic process and the anterior nasal spine
a. lateral wall of the nasal cavity
and
anterior border of the maxillary sinus

Describing the density of an object is relative because density depends on the appearance of adjacent tissues.
a. The statement is correct but the reason not related.
b. Both the statement and the reason are correct and related.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
b. Both the statement and the reason are correct and related.
Which of the following does NOT describe object density?
a. lucent-opaque
b. radicular
c. radiolucent
d. radiopaque
b. radicular (radiating)
Lesions detected by radiographs may appear round, oval, scalloped, or linear. Lesions with these shapes are expanding in different directions at differing rates.
a. The first statement is true. The second statement is false.
b. The first statement is false. The second statement is true
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
a. The first statement is true.
The second statement is false.
what term describes a radiopaque border that outlines and encapsulates a lesion detected on a radiograph?
a. lucent-opaque
b. focal
c. corticated
d. idiopathic
c. corticated
* Refers to a thin or thick border that appears as a radiopaque outline*
encapsulating a lesion.

what term describes the architecture of a lesion with radiolucent compartments?
a. focal opacity
b. multilocular
c. target lesion
d. unilocular
b. multilocular
Descriptive radiographic term for a radiolucent lesion with more than one compartment that appears to be separated by radiopaque walls or septa.
what term describes a lesion located around an unerupted tooth crown?’
a. interproximal
b. periapical
c. pericoronal
d. interradicular
c. pericoronal
refers to a location around a tooth crown.
the failure of a tooth or multiple teeth to develop is call
a. hyperdontia
b. hypodontia
c. supernumerary
d. dens in dente
b. hypodontia

which of the following is the best preliminary documentation for a
radiolucency surrounding the root tips of a tooth?
a. periapical abscess
b. granuloma
c. cyst
d. periapical radiolucency
d. periapical radiolucency
which of the following radiographic finding is associated with a nonvital tooth?
a. condensing osteitis
b. pulp stones
c. osteosclerosis
d. hypercementosis
a. condensing osteitis

raidographic evidence of resorption that appears to shorten a tooth root is call
a. internal
b. primary
c. external
d. secondary
c. external resorption

what is the most likely interpretation of a radiographic lesion that resembles misshaped teeth?
a. dens in dente
b. odontoma
c. mesidens
d. germination
b. odontoma

which of the following appears radiolucent in its early stages and as a
radiopaque mass in later stages?
a. globylomaxillary cyst
b. carotid stenosis
c. osteoporosis
d. periapical cemental dysplasia
d. periapical cemental dysplasia

Dental radiographs should be prescribed as an opportunistic screening tool for carotid stenosis because a radiographic examination can be used to predict a vascular event.
a. Neither the statement nor the reason is correct.
b. Both the statement and the reason are correct and related.
c. Both statements are true.
d. Both statements are false.
a. Neither the statement
nor the reason is correct.
1
Identify the following:

Dentin

2
Identify the following:

Enamel
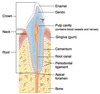
3
Identify the following:

Pulp Chamber

4
Identify the following:

PDL Space
5
Identify the following:

Lamina Dura

6
Identify the following:

Root Canal

7.
Identify the following:

Cancellous bone

Identify the following:
(tube-like passageways through bone supplying blood vessels and nerves to maxillary teeth and bone, appear as narrow bands)

Nutrient Canals in Max Sinus
1
Identify the following:

Primary Canine
2.
Identify the following:

Primary first molar with partially resorbed roots.
3.
Identify the following:

Permanent Canine
4.
Identify the following:

Permanent first premolar
1.
Identify the following:

Outline of nose
2
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmarks

Incisive Foramen
(exit of nasopalatine nerve, appears ovoid between
roots of maxillary central incisors in radiographs)
3
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmarks
(smooth depression located between lateral and canine, appearance varies in area between maxillary canines and lateral incisors)

Lateral fossa
4
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmarks
(pear shaped compartment of bone located superior to maxilla and divided by nasal septum, appears as a large area above maxillary incisors in radiographs)

Nasal fossa
5
Identify the following Radiopaque Anatomical Landmarks
(vertical bony wall dividing nasal cavity, appears as a vertical partition, and may be superimposed over median palatine suture)

Nasal Septum
6.
Identify the following:

Border of nasal fossa
7
Identify the following Radiopaque Anatomical Landmarks
(sharp projection located at the anterior and inferior portion of nasal cavity, appears v-shaped, intersection of floor of nasal cavity and septum)

Anterior nasal spine
8
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmarks
(immovable joint between two palatine processes of maxilla, appears as a
thin line between maxillary central incisors in radiographs)

Median palatine suture
1
Identify the following
(exit of nasopalatine nerve, appears ovoid
between roots of maxillary central incisors in radiographs)

Incisive foramen
2.
Identify the following:

Outline of the nose
3
Identify the following
(smooth depression located between lateral and canine, appearance varies in area between maxillary canines and lateral incisors)

Lateral fossa
4
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmark
(pear-shaped compartment of bone located superior to maxilla and
divided by nasal septum, appears as a large area above maxillary incisors in radiographs)

Nasal fossa
5
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmark
(vertical bony wall dividing nasal cavity, appears as a vertical partition, and may be superimposed over median palatine suture)

Nasal Septum
6.
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmark

Border of nasal fossa
7.
Identify the following Radiopaque Anatomical Landmark
(sharp projection located at anterior and inferior portion of nasal cavity, appears
v-shaped, intersection of floor of nasal cavity and septum)

Anterior nasal spine
8
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmark
(immovable joint between two palatine processes of maxilla, appears as a thin line between maxillary central incisors in radiographs)

Median palatine suture

1.
Identify the following Radiolucent Anatomical Landmark
(smooth depression located between lateral and canine, appearance varies in area between maxillary canines and lateral incisors)

Lateral fossa
Identify # 2.
(pear-shaped compartment of bone located superior to maxilla and divided by nasal septum, appears as a large area above maxillary incisors in radiographs)

Nasal fossa
3.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(intersection of anterior border of maxillary sinus and lateral wall of nasal fossa, appears as an upside-down Y, located above maxillary canine)

Inverted Y landmark
4.
Identify the following radiolucent anatomical landmark
(paired cavities located above maxillary molars and premolars and extend into furcations, interdental bone, and tuberosity region, appear over apices
of maxillary posteriors)

Maxillary sinus
5.
Identify the following:

Superimposition of first premolar over canine
Identify #1.

Lateral fossa
Identify #2.

Nasal fossa
Identify #3.

Inverted Y landmark
Identify #4.

Maxillary sinus
Identify 5.

superimposition of premolar over canine
Identify #1.

Border of maxillary sinus
Identify #2.
(paired cavities located above maxillary molars and premolars and extend into furcations, interdental bone, and tuberosity region, appear over apices of maxillary posteriors)

Maxillary sinus
3.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(bony projection appears J or U shaped
superior to maxillary 1st molar region)

Zygomatic process of maxilla
4.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(bony walls dividing maxillary sinus into compartments, appears as
lines within maxillary sinus, presence varies with anatomy)

Septum in maxillary sinus
5.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(formed by zygomatic process of maxilla and temporal bone, appears as diffused band extending posterior from zygomatic process of maxilla)

Zygoma
Identify #6.

Border of zygomatic arch
Identify #1.

Border of maxillary sinus
Identify #2.
(paired cavities located above maxillary molars and premolars and extend into furcations, interdental bone, and tuberosity region, appear over apices of maxillary posteriors)

Maxillary sinus
Identify 3.
(bony projection appears J or U shaped superior to maxillary 1 st molar region)

Zygomatic process of maxilla
Identify #4.
(formed by zygomatic process of maxilla and temporal bone, appears as diffused band extending posterior from zygomatic process of maxilla)

Zygoma
Identify #5.

Lateral pterygoid
Identify #6.

Border of zygomatic arch
7
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(rounded prominence posterior to 3rd molar region
blood vessels and nerves enter maxilla to supply posterior teeth)

Maxillary tuberosity
8
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(prominence of bone on anterior ramus, attachment site for muscles of mastication, triangular in appearance, appears superimposed over maxillary tuberosity region in radiographs)

Coronoid process of mandible
1.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(linear prominence extending from premolar to premolar, appears as a thick band superimposed over anterior teeth)

Mental ridge
Lingual view

2.
Identify the following radiolucent anatomical landmark
(tubelike passageways through bone containing nerves and blood vessels to teeth, appear as vertical lines in thin bone)

Nutrient canal
lingual view

Identify #3.

Nutrient foramen

4.
Identify the following radiopaque anatomical landmark
(tiny bumps of bone on lingual aspect of mandible, appears as
ring shape opacity apical to incisor)

Genial tubercles
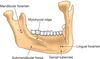
5.
Identify the following radiolucent anatomical landmarks
(tiny opening in bone on internal surface of mandible, surrounded by genial tubercles appears apical to mandibular incisors)

lingual foramen

Identify # 6.

Inferior border of mandible

1.
Identify the following radiolucent anatomical landmarks
(tubelike passageways through bone containing nerves and blood vessels to teeth, appear as vertical lines in thin bone)

Nutrient canal
2.

Torus mandibularis
1.

PDL space
2.

Lamina dura
3.

Mental foramen
4.

Submandibular fossa

Turus mandibularis
1.

Oblique Ridge
2.

Mylohyoid ridge
3.

Mandibular canal
4.

Submandibular fossa
1.

Radioluscent composite resin
2.

Radioluscent dental base
3.

Radioluscent glass ionomer
4.

Radiopaque cement under crown
5.

Porcelain crown
6.

PFM crown
7.

Silver point endodontic filler
1.

Dental base
2.

Amalgam
3.

Retention pin
1.

Irregular margins of amalgam
2.

Smooth edges of full metal crown
3.

Broken dental bur
1.

Amalgam
2.

Overhang
1.

Composite resin
(Appears slightly more radiopaque than dentin)

2.

Amalgam

1.

Glass ionomer bonding
2.

Orthodontic wire
1.

Full metal crown
2.

PFM
(Porceline Full Metal Crown)
1.

Radiopaque metal shell
PFM metal part
2.

Less radiopaque ceramic porcelain crown
PFM porcelain part
1.

Stainless steel crown
(Notice the see through appearance)
1.

Full metal crowns form bridge abutments
2.

Metal pontic
3.

amalgam
4.

Composite resin
5.

Gutta-percha
6.

Post and core
7.

PFM crown
8.

Base material
9.

Retention pin
1.

Radiopaque pins
2.

Radiopaque amalgam restorations

PFM
(Implant replaced tooth)

External Resorbtion


Surgical wire

Amalgam tattoo

Odontoma
An odontoma forms when enamel, dentin, and cementum form irregular shapes resembling small misshaped teeth whose number varies widely. These toothlike structures appear radiopaque and are located within a radiolucent fibrous capsule that can resemble a cyst
1.

Second premolar did not develop under primary tooth
2.

Severe caries

Supernumerary tooth

Distomolar
1.

Supernumeray tooth with dilacerated root
2.

Periapical radiolucency

Dens in dente

Dilaceration

Fusion of mandibular lateral and central incisors
1.

Caries
2.

Radioluscent lesion
(Abscess, granuloma, or cyst)
1.

Dentigerous cyst involving
2.

Impacted third molar

Follicular cyst

Incisive canal cyst

Globulomaxillary cyst

Radiopaque lesion

Radiopaque lesion

Hypercementosis
excessive formation** of **cementum** along a **tooth root**, this enlargement will usually take on a **bulbous appearance** toward the **root apex

Retained root fragment

External resorption

Internal resorption
(Widening of the pulp chamber)

Periapical cemental dysplasio (PCD)
Dense outer layer of bone.
Cortical bone

Soft spongy bone that is located
between two layers of dense cortical bone.
Cancellous bone

Outer most layer of the crown of a tooth.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Enamel

Radiopaque
Contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic on x-ray.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Pulp
Radiolucent

Found beneath the enamel and surrounds the pulp cavity.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Dentin
Radiolucent

Thin line around the root of a tooth.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Periodontal Ligament
Radiolucent
5
Wall of the tooth socket that surrounds the root of a tooth.
Dense cortical bone surrounds the root of the tooth.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?

Lamina Dura
Radiopaque

Located between the roots of the teeth.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Alveolar bone
Radiopaque

Very radiopaque outer layer of bone?
Cortical Plate of the Mandible

Linear prominence of cortical bone located on the external surface of the anterior portion of the mandible (premolar/incisor region).
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Mental ridges
Radiopaque

Opening or hole in bone located on the external surface of the mandible in the region of the mandibular premolars.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Mental foramen
Radiolucent

Tiny tube-like passageways through bone that house blood vessels and nerves supplying the maxillary teeth and the interdental areas.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Nutrient canals
Radiolucent
Pear-shaped compartment of bone located superior to the maxilla.
Large area above maxillary incisors.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Nasal fossa (cavity) #4
Radiolucent

Vertical bony wall or partition that divides the nasal cavity
into the right or left nasal fossa.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Nasal Septum #5
Radiopaque
Sharp projection of the maxilla located at the
anterior and inferior portion of the nasal cavity.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Nasal Spine
Radiopaque
Bony walls that appear to divide the maxillary sinus into compartments.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Wall in Maxillary Sinus #1
Radiopaque

Bony wall formed by the palatal processes of the maxillae
& the horizontal portions of the palatine bones.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Floor of Nasal Fossa
Radiopaque
Intersection of the maxillary sinus & the nasal cavity
as viewed on a dental radiograph.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Inverted Y
Radiopaque

Tiny bumps of bone that serve as attachment sites for the muscle.
Appear as ring shape around the lingual foramen.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Genial tubercles
Radiopaque

Tiny opening or hole located on the internal surface of the mandible,
below the mandibular incisors.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Lingual Foramen
Radiolucent

Round or ovoid hole in bone on the lingual
aspect of the ramus of the mandible.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Mandibular Foramen
Radiolucent

Scooped out depressed area of bone located on the internal surface of the mandible inferior to the mylohyoid ridge, molar region.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Submandibular fossa
Radiolucent

Linear prominence of bone located on the internal surface of the mandible that extends downward & forward from the ramus?
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Internal oblique ridge

Radiopaque
Linear prominence of bone located on the
external surface of the body of the mandible.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
External oblique ridge
Radiopaque

Marked prominence of bone found on the anterior ramus of the mandible,
triangle shape in maxillary tuberosity region.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Coronoid process
Radiopaque

Opening or hole in bone located at the midline of the anterior portion of the
hard palate directly posterior to the maxillary central incisors.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?

Incisive foramen #1
Radiolucent

Immovable joint between the two palatine processes of the maxilla.
Extends from the alveolar bone between the
maxillary central incisors to the posterior hard palate.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Median palatine suture
Radiolucent

Cheekbone that articulates with the
zygomatic process of the maxilla.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Zygomatic arch or Zygoma

Radiopaque
J or U shape located above the maxillary first molars.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?

zygomatic process of maxilla #4

Radiopaque
Rounded prominence of bone that extends
posterior to the third molar region.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Maxillary Tuberosity #2
Radiopaque

Bony projection of the sphenoid bone located distal to the maxillary tuberosity region
(**not seen on PA radiographs)
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Lateral pterygoid plate #5
Radiopaque

Small hook-like projection of bone that extends from the
medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid bone.
Radiolucent/Radiopaque?
Hamulus #5
Radiopaque



