Exam 2 Path II Flashcards
(275 cards)
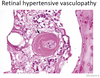
What can occur to the aorta during excitement, physical activity (racing horses), and stallion breeding?
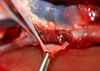
Aortic rupture
Which tickborne disease enters the brain via a “trojan horse” and results in Acute polioencephalomyelitis, Neuronal degeneration, neuronophagia, Lymphocyte cuffing, gliosis & meningitis?

Louping-ill (Flavivirus) - common in sheep
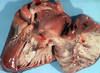
Dilated cardiomyopathy is seen in _______. Which breed are most susceptible?
Dogs, especially males
Larger dog breeds like:
- Doberman pinschers
- Portuguese water dogs
- Dalmatians
- Saint Bernards etc.,
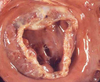
What parasite is highly zoonotic in people that ingest undercooked meat due to the formation of cycts in the muscles and heart (parasitic myositis)?
Trichonella spiralis
In cattle, myocardial lymphosarcomas are associated with what?

enzootic leukosis
Lamb. Mdx? Etiology?
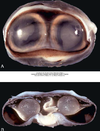
Cyclopia/Synophthalmos
Incomplete seperation of the orbits during embyrogenesis
Etiology: Veratrum Californicum ingestion on day 14
Determine cause via thourough history
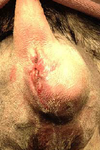
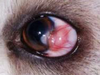
Mdx?
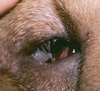
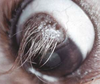
Entropion and secondary trichiasis
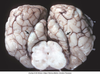
Which of the following components of the CNS are least sensitive to hypoxia:
- Neurons
- Astrocytes
- Oligodendrocytes
- Microglia & Vascular endothelium
Microglia & Vascular endothelium= Mesoderm origin
All others are ectoderm origin and sensitive to hypoxia
What are 3 ways that viruses enter the brain?
- Haematogenous via BBB or choroid plexus- usually via trojan horse
- Replication in vascular endothelium (CAV, BMCF, EHV-1, FIP) –> vasculitis
- Neural Routes (Rabies, Borna, ADV)
What kind of brain lesions due parasites usually create?
inflammatory and space occupying
T/F: Hyperemia alone does not necessarily indicate conjunctivitis?
True
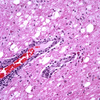
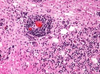
What are common organism in septic emboli in the CNS?
- Cattle – Actinomyces/Trueperella pyogenes, Haemophilus somni, Staph aureus
- Lambs – staph aureus (tick pyemia)
- Horse- strep equi
- Dog- staph aureus
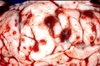
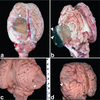
MDx?
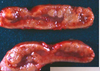
Nodular adrenocortical hyperplasia
senile change
Thyroid hyperplasia (goiter) will result in….
a. hyperthyroid
b. Euthyroid
c. Hypothyroid
b. Euthyroid & c. Hypothyroid
What plants/products contain thiaminases and cause CCN?
- Braken fern (Pteridium) intoxication in horses
- Male fern (Felix mas) and Molasses/Urea toxicity in cattle
- Cooked meat (thiamine is heat labile) in dogs/cats
- Fish diets in foxes/mink/cats - Chastek paralysis with polioencephalomalacia (below)

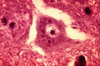
What is the term for phagocytosis of neurons by microglia/monocytes?

Neurophagia
What three circulatory bypasses/shunts are present during fetal development?
Ductus venosus - bypasses the liver
Foramen ovale- bypasses lungs (R atrium to L atrium)
Ductus arteriosus- bypasses lungs (Pulmonary a. to Aorta)
What is it called when acute cardiac dysfunction causes collapse and unconsciousness (due to abnormal heart rhythm, defective heart valves, etc) ?
Cardiac syncope
What lesions might you find as a result of renal secondary hyperparathyroidism?
Metastatic calcification,
fibrous osteodystrophy
hypercalcemia
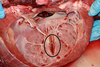
Mdx? Sequela?

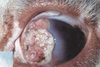
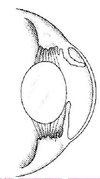
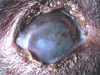
Ciliary (Iridociliary) adenoma/carcinoma
Sequela = Glaucoma, hyphema, retinal detachment
DOGS >>>>>> cats
Most benign
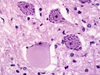
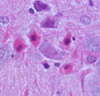
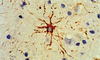
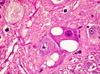
What is a gemistocyte?
***KNOW THIS***
Swollen astrocytes- cytoplasm contains pink “glassy” material

What is a Dysautonomia? and what disease causes it in horses? dogs/cats?
Dysautonomia- degeneration of neurons in a ganglion= see chromatolysis
Horses= Grass Sickness
Cats/Dogs= Heriditary Key Gaskell Syndrome

In dogs, the majority of pituitary adenomas are active and from what part of the gland?
pars distalis or pars intermedia
pars distalis
What cells consist of the neuroglia (supporting cells within the brain)?
–Astrocytes
–Oligodendrocytes
–Ependymal cells
–Microglia