Exam 1 Flashcards
What type of tissue is depicted?

Elastic CT
What articulates with the trochlea of humerus?
The trochlear notch of the ulna

What are the direct branch(es) of the roots of the brachial plexus?
Dorsal scapular nerve and long thoracic nerve

Which of terminal nerve(s) carries fibers from spinal cord levels C8-T1?
Ulnar nerve

What are the direct branch(es) of the medial cord of the brachial plexus?
Medial pectoral nerve, medial cutaneous nerve to arm, and medial cutaneous nerve to the forearm

Which terminal nerve of the brachial plexus innervates the glenohumeral joint; teres minor and deltoid muscles?
Axillary nerve

Which landmark of the scapula serves as an origin for teres major?
The inferior angle, specifically the dorsal surface (2)

Which of terminal nerve(s) carries fibers from spinal cord levels C5-C7?
Muscolcutaneous nerve

What tissue is depicted?

Adipose tissue (white fat)
What type of secretion is thin and watery and cell is not damaged during secretion?
Merocrine
What are the direct branch(es) of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus?
Upper subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve, and the lower subscapular nerve
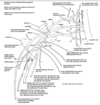
Which terminal nerve of the brachial plexus innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm?
Musculocutaneous nerve

What does the glenoid process articulate with?
The head of the humerus

Which landmark of the scapula serves as an origin for the deltoid?
Scapular spine (23)

What type of bone is depicted?
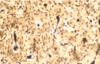
Compact bone
What cartilage is depicted?

Fibrocartilage
Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the clavicular head of the pectoralis major?
Lateral pectoral nerve

The posterior cord is formed by the union of the posterior divisions of which of the following trunk(s)?
Upper, middle, and lower (i.e. all of them)

Which landmark of the scapula serves as an origin for the subscapularis?
The subscapular fossa (4)

In the brachial plexus C5 and C6 unite and form the:
Upper trunk

Which of terminal nerve(s) carries fibers from spinal cord levels C5-C6?
Axillary nerve

Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the latissimus dorsi muscle?
Thoracodorsal nerve

Which terminal nerve of the brachial plexus innervates all muscles of the posterior compartments of the arm and forearm?
Radial nerve

Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the rhomboid muscle?
Dorsal scapular nerve

Which landmark of the scapula serves as an origin for the triceps-long head?
The infraglenoid tubercle (10)

Which of terminal nerve(s) carries fibers from spinal cord levels C5-T1?
Median nerve and radial nerve

Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the subscapularis muscle?
Upper subscapular nerve

Which landmark of the scapula serves as an origin for the infraspinatus?
Infraspinous fossa (1)

What secretion is think and the whole cell is destryed during secretion?
Holocrine
What tissue is depicted?

White fibrous/Dense regular
What are the terminal nerves of the brachial plexus?
Musculocutaeous nerve, axillary, radial, median, ulnar

Which terminal nerve of the brachial plexus innervates the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Median nerve

Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the serratus anterior muscle?
The long thoracic nerve

What cartilage is depicted?

Elastic
In the brachial plexus C7 forms the:
Middle trunk

What tissue is depicted?

Reticular CT
The medial cord is formed by the union of the anterior divisions of which trunk(s)?
Lower trunk

What tissue is depicted?

Adipose tissue (brown fat)
Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the subscapularis and the teres major muscles?
Lower subscapular nerve

What are the direct branch(es) of the superior trunk of the brachial plexus?
Suprascapular nerve and nerve to subclavius
Which branch of the brachial plexus supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus?
Suprascapular nerve

What tissue is depicted?

Areolar CT
What type of bone is depicted?

Developing membrane bone
What are the direct branch(es) of the lateral cord of the brachial plexus?
Lateral pectoral nerve

In the brachial plexus C8 and T1 unite to form the:
Lower trunk

What cartilage is depicted?

Hyaline
The lateral cord of the brachial plexus is formed by the division of the anterior divisions of which trunk(s)?
Upper and middle

What secretion is thick and cell is partially lost during secretion?
Apocrine
What type of bone is depicted?

Spongy or Cancellous
What does the head of the radius articulate with?
The capitulum of the humerus (6 and 10)

Which terminal nerve of the brachial plexus innervates the flexori carpi ulnaris and ulnar half of flexor digitorum profundus?
Ulnar nerve
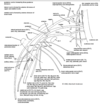
What type of tissue is depicted?

Loose aerolar tissue
Loose areolar tissue has a high ratio of fibroblsats to fibrous components and consists of type I collagen fibers and elastic fibers. This type would be most characteristic of what anatomical structure(s)?
Beneath epithelial tissues of most organs and tunica adeventitia of blood vessels
White fibrous/dense regular connective tissue consists of thick bundles of collagen which are seperated by single rows of fibroblasts. This type would be most characteristic of what anatomical structure(s)?
Tendons and ligaments
What are large, negatively charged linear polymers consisting of repeated disaccharide units that make up most of the amorphous substances of connective tissue?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
What anatomical structure(s) is hyaline cartilage associated with?
Ears, nose, movable joint surfaces
What anatomical structure(s) is elastic cartilage associated with?
Parts of larynx
What anatomical structure(s) is fibrocartilage associated with?
Less movable joints and intervertebral discs
What is the best way to describe the joints of the pubic symphysis and intervertebral discs?
Cartilaginous - Symphysis
What is the best was to describe the joint of the epiphyseal plate and first sternocostal joint?
Cartilaginous - Synchondrosis
What is the best way to describe the joint between the bones of calvaria?
Fibrous - Suture
What is the best was to describe the joint of teeth in alveoli?
Fibrous - Gomphosis
What is the best way to describe the joint of the interosseous membrane?
Fibrous - Syndesmosis
What is the best way to describe the joint of the elbow or knee?
Synovial - Hinge
What is the best way to describe the joint of the atlantoaxial o the radioulnar?
Synovial - Pivot
What is the best way to describe the joint of the metacarpophlangel or atlantooccipital?
Synovial - Condyloid
What is the best way to describe the joint of the first carpometacarpal?
Synovial - Saddle
What is the best way to describe the joint of the glenohumeral or femoroacetabular?
Ball-and-socket
What is the best way to describe the joint of the sternoclavicular or scapuloclavicular or zygapophyses?
Synovial - Plane


