Exam 1 Flashcards
What 6 questions about parasites are Veterinarians asked by their clients?
- What is it?
- How can you tell my animal has it?
- Where did it come from? How did my animal become infected/infested?
- What harm does it cause?
- How can it be gotten rid of? How can it be prevented? Controlled?
- Will it infect people?
type of host that a parasite is (in/on) in which the parasite can develop
host spectrum
its called _____ when a host can develop completely in one host
host specific
its called ___ when a parasite can develop in several different hosts
broad host spectrum
True or false?
A parasite may require 1 or more hosts for development or may utilise a host (ex. insect) simply for transmission between hosts.
True
_______ is the term used when endoparasites, such as helminths and protozoa, infect the host internally
Infection
_______ is the term used when ectoparasites, such as acari and insects, attach to or occupy the host
Infestation
______ is the preferred site in or on the host, which is characteristic for a parasite species
Predilection site
______ is the site in or on a host which is not a normal location for a parasite.
Aberrant site
______ is is the mechanism of how a disease develops
Pathogenisis
Pathogenisis includes chronological changes that give rise to gross changes and clinical signs in which (3) host structures?
- cells
- organs
- tissues
________ are the differences found in tissues of an animal from what is normal, and are observed by eye or microscopically.
Lesions
Lesions seen with your eyes
gross lesions
Lesions seen with microsopy
microscopic lesions
these are somewhat similar to bacterial or viral infections; the host is infected, and in most cases, species, or strain-specific, immunity develops, the parasite is eliminated, and the host is protected against a subsequent infection,
self limiting infections
the infection may be long standing, sometimes for years
chronic infection
True or false?
The pathogenesis of a parasite does not directly relate to the importance of a parasite and the need (or not) to treat for the parasite
false
(does directly relate)
True or false?
The clinical signs associated with disease may be a result of both the parasite and the host response to it
True
Describe helminth diagnosis techniques
- presence of adults, developing stages, eggs, or larvae in feces, blood, or urine remains the most common
- Serology (ELISA)
Describe protozoa diagnostic techniques
examination of
- fecal samples
- blood
- skin
- muscle
- other tissues
Ectoparasite diagnostic techniques dependent on?
- the collection and identification of the parasite(s)
- stages concerned
PPP
Prepatent period
time from infection to when eggs, cysts, or larvae appear in body fluids of, or excretions from, the difinitive host
What type of parasite does this “spaghetti” remind you of?

Nematodes
What type of parasite is this?

Nematode
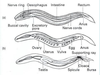
What are the major parts of the nematode?
Classify the parasite name?

Ancylostoma caninum
Classify the type of nematode?
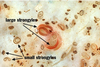
Large Strongyles
What type of nematode is this and what is the arrow pointing to?

Strongyloides papillosus
arrow pointing to the esophogus (1/3 of parasite body length)
This “y” representation is common with _____ nematodes?

Mammomonogamus spp
What is this type of nematode and what is this structure?

Haemonchus contortus: bursa of male
What is the common name of the nematode in this picture?
Hookworm
What type of nematode is this?
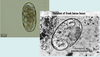
Name the structures in this cross section

Cross-section through Ascaris
d. n. Dorsal nerve
n. c. non-contractile portion of muscle cells
c. Cuticle
e. Epidermis
l. l. lateral line
e. v. excretory vessel
m. contractile portion of muscle cells
v. n. ventral nerve
ov. Ovary ut. Uterus g. gut
What is this?

Heartworm adults
What is this?

Heartworm in blood slide
Hwat type of nematode is this?

Toxocara cati: “arrow” head
What type of nematode is this?

Large strongyle
Name the type of nematode and the important structure to notice

Haemonchus contortus: female vulva
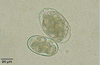
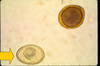
What type of nematode egg is A?

Nematodirus
What type of nematode egg is B?
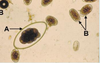
Trichostrongyloid
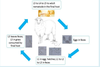
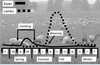
What stages are found in animal/environment/feces?

Animal: L3, L4, L5, adult, egg
Feces: egg
Environment: L1, L2, L3
What type of life cycle is this and what stage is infective?

Direct: Infective third-stage larva (L3)
What stages of this parasite are found in the final host/mosquito?

Animal: L3, L4, L5, adult, L1 (mff)
Mosquito: L1, L2, L3
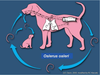
What type of life cycle is this and what is the infective stage?
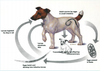
Direct: Infective third-stage larva (L3)
What type of lifecycle is this and what is the infective stage(s)?

Direct: Infective egg with a larva (L1 or L2 or L3; depending on the species)
What type of life cycle is this and what is the infective stage?
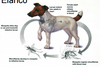
Indirect: Infective third-stage larva (L3)
Indirect: Adult-egg-L1-L2-L3-L4-L5
-iasis = parasite is_____
present
-osis = _____ is caused by parasite
disease
What category of parasite is this representing?

Nematode
What type of life cycle is this representing?

direct
What is the common name of these?

hookworm
What is the superfamily of the egg labeled A?

Ancylostomatoidea
Which is a more accurate sample to be used for diagnostics?

fresh sample
What type of nematodes are these examples of?
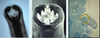
Ancylostomatoidea
Which one is the male and which is the female?

male left and female right
What is the name of this parasite and its gender?

Ancylostoma caninum (male)
What type of egg is this?

Ancylostoma caninum
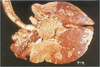
What is this parasite?

Ancylostoma caninum
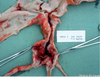
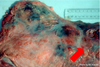
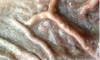
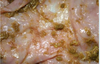
What nematode made this damage to small intestine?

Ancylostoma caninum
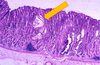
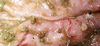
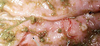
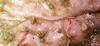
What types of little wormies are these pointing to?

Ancylostoma caninum
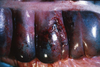
What are pale mucus membranes a clinical sign of?

Ancylostoma caninum