EQ Pharynx and Larynx Flashcards
Draw the normal anatomy of the larynx

What is the function of the pharynx
Transmits air to the larynx and food bolus to the oesophagus
What nerves supply the pharynx?
Pharyngeal vagus, mandibular trigeminal, hypoglossal
Taste from glossopharyngeal
Name in order from rostral to caudal the laryngeal cartilages.
Epiglottis
Thyroid
Cricoid
Arytenoid
Muscle which opens the larynx by abducting the arytenoids.
Cricoarytenoid dorsalis
Muscle which closes the larynx by adducting the arytenoid cartilage.
Cricoarytenoid lateralis muscle
Slap test
Thoraco-laryngeal reflex
Clinical signs associated with pharyngeal pathology
Noise
Dysphagia
Discharge
Cough
Dyspnoea
DDSP
Dorsal displacement of the soft palate - into the nasopharynx
May be intermittent or persistence
Intermittent - thyroid hormone problem, X, hyoid apparatus, inflammation
Persistent - secondary to congenital abnormality, neuromuscular
Tie forward surgery
Basihyoid to thyroid
DDSP
Staphylectomy
Soft palate resection
DDSP
Myectomy
Resection of the sternohyoid/ omohyoid to prevent caudal retraction of the larynx
DDSP
Palatal fibrosis
Cautery - increases stiffness of the soft palate
DDSP
Arytenoid chondritis
Ulceration, infection, progressive, obstructive - kiss lesions (due to compression of normal cartilage)
Caused by trauma or low grade infection

Sub-epiglottic cyst
May lead to DDSP?
ADAF
Axial displacement of the aryepiglotic folds - mucosal folds between the arytenoids and epiglottis
VCC
Vocal cord collapse
Describe the pathogenesis of RLN
Leads to atrophy of the cricoarytenoid dorsalis muscle and therefore failure to abduct the arytenoid cartilages. This causes the noise known as roaring.
Dx - noise, endoscopy, negative slap test, ultrasound
Tie back surgery
Dorsocaudal cricoid to muscular arytenoid cartilage process
Hobday surgery
Ventriculo-cordectomy
4BAD
Forth brachial arch defect - laryngeal cartilage defects - rostral displacement
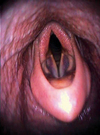
Epiglottic entrapment - under sub-epiglottic tissues


