epithelium Flashcards
19.0725 (23 cards)
what are the four tissue type?
- epithelium-lines and covers surfaces
- connecive tissue- protect, support and bind together
- muscle tissue - produces movement
seven general functions of epithelial layer
- skin
- small and large intestines
- cilia
- glands
- tubules of kidneys
- lung alveolus
- mesothelium
- functions
- protection-skin
- absorption-small and large intestines
- transport of material at the surface- cilia
- secretion-glands
- excretion-tubules of the kidneys
- gas exchange-lung alveolus
- gliding-mesothelium
characteristics ofepithelium
- derivations from which layers of development
- what does the epithelium cover? except
- vasularity?
- cell density?
- attachment/renewal
- how is it replenished?
- derive from
- ectoderm
- mesoderm
- endoderm
- line and cover all of body surface, aside from
- cartilage
- teeth enamel
- anterior surface of iris
- avascular
- mostly cellular
- basal membrane
- continuously renewed
What does it mean for cells to structural and functional polarity?
describe these areas and structures of importance
- epithelia have structural and function polarity
- apical domain
- structures important for
- protection
- absorption,
- microvillicilia
- stero cilia
- structures important for
- lateral domain
- have structures needed to anchor epithelial cells to each other
- occuluding junctions
- desmosomes
- cell-cell attachment
- have structures needed to anchor epithelial cells to each other
- basal domain
- have structures needed to anchor cells to basement membrane
- cell to extracellularmatrix junctions
- basal cell membrane infoldings
- have structures needed to anchor cells to basement membrane
- apical domain

Describe two apical structural modifications. five a location and function.
- microvilli
- location
-
brush border of the small intestine
- highly packed and have a uniform height
- stomach lining
-
brush border of the small intestine
- function
- increase the suface area for absorption/secretion
- location
- cilia
- location- columnar cell surface of
- oviduct
- bronchi
- function
- transport matter along the cell surface and highly motile
- location- columnar cell surface of
Jerry has celiac disease and must avoid? What happens to the apical side of some cells?
celiac disease or gluten sensitivit enteropathy, is a disorder of the small intestines
- first pathological changes is loss of microvilli brush border of absorptive cells
removing gluten from the diet will allow the brush border(microvilli) to grow back over several years
Jim has been diagnosed with infertility and is subject to frequent lung infections. His disease is associated with a mutation in an apical specilaztion. what is his disease? explain
Kartagener’s syndrom
- type of immotile cilia syndrome
- manifests as
- lack of cleansing action of cilia
- chronic respiratory infection
- infertility
- immotile spermatozoa
- lack of cleansing action of cilia
ciliary dysfunction is involved in many hereditary disorders grouped under primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD)
autosomal recessive, 1/20000 live births
list the three cell-cell attachments, stucture, location and function

- tight junction
- location
- apical/lateral domain
- structure
- specialized proteins in the plasma membranes of adjacent cells
- function
- “stitch together” adjacent cells to form a tight cellular junction
- limit movement of items between cells
- location
- desmosome
- location
- lateral
- structure
- protein complexes that link to adjacent cell desmosome and intermediate filaments cytosolically
- funciton
- communication
- rivet cells
- allow mechanical stress to translate communcation to adjacent cells
- location
- gap junctions
- location
- lateral
- structure
- proteins that generate a channel(pore) between adjacent cell membranes
- function
- create cytoplasmic communication bridges between cells allowing for chemical and electrical signals to be passed rapidly
- location
Jim has H. Pylori in his stomach. if these bacteria loosen the cells what are they effecting?
H. Pylori targets the occludens, tight junctions. this will lossen the cell
cytomegalovirus, cholera and H. Pyloris target which cellular protein for entry into the tissue?
junctional complexes
- tight junction
- desmosome
- gap junctions
Describe the cell in the photo, give name and
- location
- structure
- function
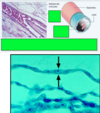
simple squamous epithelium
- location
- blood vesselsd- endothelium
- body cavities- mesothelium
- bowman’s capsule
- alveoli
- structure
- sinble layer, flat, sheet of cells, held together by tight junction
- nucleaus is also flat and oval and lies in the center of the cell
- function
- fluid transport
- gas exchange
- lubrication
what are the three locations where the surface does not have epithelium covering it?
- articular cartilage
- enamel of teeth
- anterior surface of the iris
describe the photo list the following about this cell types
- location
- structure
- function

simple columnar epithelium
- location
- lining the stomach
- intestines
- gall bladder
- uterus
- oviduct
- structure
- long rectangular cells
- rests on the basement membrane
- has ovoid nucleus
- projections
- microvilli
- cilia
- function
- protection
- secretion
- absorption
- projections
- microvilli
- increase the surface area for absorption/secretion and are found in cells lining stomach and intestines
- cilia
- transport matter alond the cell surface and are found on columnar cells lining the oviduct, bronchi
- microvilli
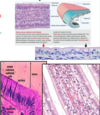
Describe the cell in the photo, give name and
- location
- structure
- function

simple cuboidal epithelium
- location
- small ducts of exocrine glands
- kidney tubules
- theyroid follicles
- structure
- single layer of cube shaped cells having a central roung nucleus
- function
- protection
- absorptin
- secretion
- conduit

Describe the cell in the photo, give name and
- location
- structure
- function

stratified squamous epithelium
- location
- oral cavity
- esophagus
- vagina
- structure
- 2 + layers of SSE cells
- two categories
- nonkeratinized
- keratinized
- function
- protection

give location of stratified epithelium
- cuboidal
- columnar
- stratified cuboidal epithelium
- location
- sweat glands
- location
- stratified columnar epithlium
- location
- conjuctiva of the eye
- ducts of some glands
- location
Describe the cell in the photo, give name and
- location
- structure
- function

pseudo stratified epithelium
- location
- cilliated
- respiratory tract
- trachea
- primary bronchi
- nasal cavity
- respiratory tract
- non cilliated
- male
- urethra
- epididymis
- male
- cilliated
- structure
- appear stratified but is actually a single layer with all cells attached to the basal lamina. the location of nuclei at different heights give it a stratified appearance.
- types
- cilliated
- non cilliated
- function
- protection
- motility
- sensory perception
- types
- pseudostartified columnar ciliated epithilium
- pseudostartified columnar nonciliated epithilium

Lucy has been smoking for 5 years and decided to stop. what has happened to her bronchial epithelium? will it revert? what is this called?
epithelial metaplasia
- adaptive response to stress, chronic inflammation leading to one type of epithlial cell into another
- most common is columnar to squamous
- the tissue may revert back
another example is barretts esophagus, from reflux of the acidic content of stomach
describe the cell in the photo give the location, structure and function

transitional epithelium
- location
- urinary system
- lines the bladder
- ureter
- parts of urethera
- urinary system
- structure
- lower cell layers are cuboidal, but apical layers can vary in shape.
- when bladder is distended
- the apical cells look flattened
- when bladder is empty
- the apical cells look rounded
- function
- protective
- form barrier between urine and tissue
-
plaques
- form a physical shield
- distentible property
- protective

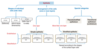
list the gland types:
- placement
- function
- types
- exocrine
- placment
- remain connected to the surface by excretory duct
- function
- secrete products outside
- placment
- endocrine
- placement
- with in tissues- lack excretory ducts
- function
- secrete product into blood circulation
- placement
- exocrine

classify the glands nd secretion types
- glands
- duct
- simple
- compound
- secretory
- tubulur
- alveolor
- exmaples-see photo
- duct
- types of secretions
- serous
- pancreas
- parotid
- mucus
- sublingual gland
- mixed
- submandibular gland
- serous

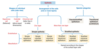
list the types of secretions and mechanism
- types
- serous
- pancrease, parotid
- mucus
- sublingual
- mixed
- submandibular
- serous
- mechanism
- merocrine
- exocytosis
- example
- pancreatic acinar cells
- holocrine
- cell ruptures
- example
- sebaceous gland
- apocrine
- one end of cell pinched off
- lactating mammary gland
- one end of cell pinched off
- merocrine



