Connective tissues Flashcards
19.08.01
classify the connective tissue

list and describe general cell types in connective tissue
- fibroblasts
- structure
- star shaped
- most numerous
- function
- prduce ECM
- proteoglycans
- glycoproteins
- procollagen
- elastin
- help in would repair
- prduce ECM
- structure
- macrophages
- structure
- location dependent
- kupffer cells in the liver
- osteoclasts in bone
- microglial cells in CNS
- very granular
- many lysosomes
- location dependent
- function
- dependent on location
- structure
- plasma cells
- structure
- from B lymphocytes
- cartwheel nucleus
- abundant ER and golgi
- mobile in matrix
- function
- synthesize and secrete Ig
- structure
- mast cells
- structure
- have same progenitor as bone marrow
- blood vessels
- CT
- function
- produce
- heparin -anticoagulant
- histamine-vasodilator
- produce
- structure
- adipocytes
list 3 fiber types and last property of CT
- fibers
- collagen
- most abundant
- parallel- strength
- soft and flexible- not elastic
- boiling turns in to gelatin
- elastin
- thin
- stretchy
- reticular fibers
- protein
- collagen
- glycoproteins
- similar to collagen, but thinner
- form reticular framework
- protein
- ground substance
- viscous material-gel like
- hyaluronic acid
- mucopolysacharide
- mucoproteins
- viscous material-gel like
- collagen
list tissue, types, location and function

- embryonic CT
- structure
- mesenchyme
- location
- found in embryo
- contents
- spindle shaped cells
- consist of reticular fibers with few collagen fibers
- location
- mucous connective ticcue
- location
- present in umbilical cord
- contents
-
whartons jelly
- homogenous ground substance
-
whartons jelly
- location
- mesenchyme
- structure
name tissue, structure, location, function
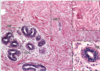
loose CT
- structure
- loosley arranges fibers and abundant cells
- location
- lies beneath epithelia and lines the internal surfaces of the body
- function
- the site of inflammatory and immune responses
DICT
- structure
- abundant fivers and few cells
- location
- respiratory tract, sub mucosa, deeper layer of dermis
- function
- with stand stresses on organs
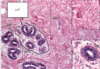
name tissue, structure, location, function

DRCT
- structure
- densely packes arrays of fibers and cells with very little ECM
- location
- tendons
- superior/inferior serratus
- ligaments
- aponeuroses
- tendons
- function
- provide strength in parallel stress
name tissue, structure, location, function

reticular connective tissue
- function
- provide a supporting framework for the cellular constiturents
- location
- lymph nodes
name tissue, structure, location, function

elastic tissue
- structure
- elastic fivers
- thinner than collagen
- arranged in branching pattern
- location
- dermis of skin
- aorta
- vertebral ligaments
- larynx
- function
- capable of stretch and distension
name tissue, structure, location, function

adipose tissue
- white
- predominantly in adults
- structure
- unilocular cells with single large fat inclusion, pushing the nucleus to the periphery
- function
- stor energy
- insulation
- cushioning of vital aorgans
- secretion of leptin and adipoleptin
- brown
- in newborn and reduced in adults
- structure
- 5 % of the body mass in newborn
- multilocular
- rich in mitochondria
- surrounded by blood vessels
- function
- generate heat
name tissue, structure, location, function

cartilage
- structure
- chondrocytes surrounded by collagen matrix
- surrounded by perichondrium
- location
- temporary skeleton of the embryo
- articular cartilage
- cartilage of nose
- larynx
- trachea
- bronchi
- costal cartilages
the black area, name tissue, structure, location, function

elastic cartilage
- structure
- chondrocytes surrounded by matric of elastic fibers
- location
- external ear
- epiglottis
- auditory tube
name tissue, structure, location, function

fibrocartilage
- structure
- avascular
- lacks perichondrium
- chondrocytes and fibroblasts surrounded by collagen fivers and less rigid ECM
- location
- IVD
- articular discs of knee
- sternoclavicular joints
- pubic symphisis
define the categories of bone. woven. types of lamellae vascular structures.
bone
- types
- structural
- compact/dense
- spongy/cancellous
- identified based on the organization of fibers
- lamellar bone
- woven bone
- structural
- lamelar bone
- lamellae
- composed of bone matrix and osteocytes
- lie in the lacuna, with radiating cnaliculi
- four types
- osteons/haversion canals
- concentric arranged lamallae around a longitucinal vascular channel
- interstitial lamallae
- between osteons
- outer circumferential lamallae
- just under the periosteum
- inner circumferential lamallae
- close to endosteum
- osteons/haversion canals
- composed of bone matrix and osteocytes
- lamellae
- structures
- vascular channels
- longitudinal capillaries
- run in the center of osteon with in haversian canal
- volkmanns cannal
- contain blood vessels from marrow and some periosteum which transverse/oblique canals conncting the haversion canals
- longitudinal capillaries
- bone matrix
- organic and inorganic components
- bone cells
- osteoblasts
- osteoclasts
- vascular channels
describe the processes in healing of a broken bone
bone repair after injury. 6-12 weeks
- neutrophils + macrophages begin to clear up site of injury
- fibroblasts and capillaries proliferate
- loose granulation tissue (scar) is formed
- as tissue becomes more dense, cartilage forms in parts of it.
- both fibroblasts and periosteal cells take part in this phase of healing
- the dense connective tissue and newly formed cartilage grow
- covering the bone at the fracture site
- generating a callus
- callus stabilizes and binds the fractured bone together
type of CT, what are the divisions of the tissue
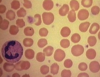
blood
- divisions
- granulocytes
- neutrophils
- eosinophils
- basophils
- agranulocytes
- lymphocytes
- monocytes
- thrombocytes
- granulocytes

