Environmental Diseases Flashcards
Emphysema
Permanent enlargement of airspaces due to destruction of alveolar walls

How does smoking cause thrombosis?
- Toxins injury enothelial cells –> increased permeability of lipids into arteries
- Induce procoagulant state
- Increase HR, BP, and contractility
- Decrease blood oxygen-carrying capacity
Smokers macrophages
Macrophages in air spaces with brown pgiment inside –> look similair to hemophages with hemosiderin
Carbon monoxide signs
“cherry red” discoloration of skin and mucous membranes
Symptoms of CO poisoning
Headache and exertional dyspnea –> eventually coma and death
Microscopic finding of lead poisoning
Basophilic stippling of red blood cells due to ribosomal clumping
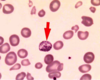
Manifestations of lead poisoning in children at low concentrations
- Cognitive impairment
- Hyperactivity
- Hearing loss
Manifestations of lead poisoning in children at high concentrations
- Colicky abdominal pain
- arthralgia
- Renal insufficiency
- Constipation
Manifestations of lead poisoning in adults at low concentration
- Short-term memory loss
- Difficulty concentrating
- Anxiety
- Phobias
Manifestations of lead poisoning in adults at high concentration
- Peripheral demyelinating neuropathy
- Myalgia
- Arthralgia
- Constipation
How does lead cause stippling?
Inhibition of pyrimidine 5’ nucleotidase causing degradation of rRNA
How does lead cause neurological problems?
Competes with Ca2+ in neurons
Urothelial carcinoma from smoking
Carcinogens are excreted in urine and rest in the bladder
How does smoking cause pneumonia
Loss of mucociliary elevator prevents removal of bacteria
Signs and symptoms of arsenic exposure
Garlicy breath
Scaly (pigment changes) papular rash
WTF is cotinine?
Cotinine is a breakdown product of nicotine detectable in the blood up to 7 days after smoking
Main effects fo chronic alcoholism
- Fatty liver
- alcoholic hepatitis
- cirrhosis
What is steatosis?
Fatty liver deposits that give it a yellow-tan color instead of red-brown –> caused by alcohol, obesity, and diabetes
Pathological mechanism of steatosis
- Excess NADH produced in alcohol metabolism shunts toward lipid biosynthesis
- Impaired assembly and secretion of lipoproteins
- Increased peripheral catabolsim of fat
What is steatohepatitis?
Steatosis with neutrophil inflammation and dying hepatocytes
What causes steatophepatitis?
Acetaldehyde and alcohol affect cytoskeleton, ROS generated during EtOH breakdown, and cytokines/TNF
What are Mallory-Denk bodies?
Broken down cytoskeleton filaments seen in cirrhosis and other conditions eliciting hepatic damage; hypereosinophilic braided rope appearance on H&E
Microscopic pathology of liver cirrhosis
Round nodules of regenrating hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous tissue
Fetal alcohol syndrome characteristics
- Dysmorphic facial features
- Growth retardation
- CNS abnormalities
Acetaminophen metabolite
NAPQI –> accumulation leads to centrilobular hepatic necrosis
Cocaine
Cardiovascular effects mediated by norepi and CNS effects mediated by dopamine
Alcohol consumption and pancreatitis
Causes acute pancreatitis with coagulative necrosis, hemorrhage, degenerating polys, and fat necrosis
First sign of radiation injury
Nausea
First blood sign of radiation injury
Lymphopenia –> within hours
Neutropenia within several days
Thrombocytopenia within a week
Anemia 2 to 3 weeks


