Embryology - Face, Palate, Nasal - ACht Flashcards
The oropharyngeal membrane marks the division between what two types of surface covering?
What will be the the difference on either side of this dicision for the human adult?
The source of endothelium lining of the oral cavity changes from surface ectoderm to primitive gut
In the adult this marks the transition betwen keratinized and non-keratinized mucosa

Very general location of nasal, otic, and lens placodes in development?
The nasal placodes are on the very front of the head.
The otic places are very lateral on the sides of the head.
The lens placodes are lateral on the head
Failure of the oronasal membrane to rupture will produce what abnormality?
choanal atresia
THe intermaxillary segment will form:
The primary palate
What forms from the palatine shelves of the maxillary prominences
the secondary palate

The posterior secondary palate forms?
The soft palate and uvula
Ossification of the primary palate and anterior secondary palate forms the?
Hard palate
When talking about congential defects of the lip and palate, what is affected in anterior vs posterior defects?
Anterior (fail to fuse maxillary prominences with medial nasal)
**Involve upper lip, maxilla, primary palate
Posterior (fail to fuse palatine shelves, nasal septum to primary palate)
**Involve hard and soft palate
Identify defect:

Incomplete unilateral cleft lip
(anterior defect)
Identify defect:

Unilateral cleft lip, involving, lip, jaw, and primary palate
Identify defect:
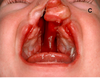
Bilateral Cleft lip, cleft jaw, primary palate plus cleft secondary palate
combined anterior + posterior defect
Identify the defect:

Cleft secondary palate
posterior defect
Theory for why FASD has facial feature abnormalities?
Alcohol may interfere with migration of cells in the CNS and neural crest cells in the head


