Electrochemistry Flashcards
What is the chemical process happening to Ag in this reaction?
Ag(s) ⇒ Ag+(aq) + e-
The Ag is undergoing oxidation.
The mnemonic to use in redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions is OIL RIG: Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons), Reduction Is Gain (of electrons).
In this case, the Ag is losing an electron, so it is being oxidized.
What is the chemical process happening to Fe in this reaction?
Fe3+(aq) + e- ⇒ Fe2+(aq)
The Fe3+ is undergoing reduction.
The mnemonic to use in redox (reduction-oxidation) reactions is OIL RIG: Oxidation Is Loss (of electrons), Reduction Is Gain (of electrons).
In this case, the Fe3+ is gaining an electron, so it is being reduced.
Define:
An electrochemical cell
An electrochemical cell is a set of chemical systems which either:
- undergo a reaction and generate electric current, or
- undergo a reaction when electric current is run through the system.
Identify the principle components of the electrochemical cell shown below.

An electrochemical cell has two half-cells, each of which has an electrolyte and an electrode. The electrodes are connected electrically.

The half-cells can be separate, as below, or share an electrolyte, but there will always be two separate electrodes.
What is the anode of an electrochemical cell?
The anode is the electrode of the half-cell in which oxidation is taking place.
What is the cathode of an electrochemical cell?
The cathode is the electrode of the half-cell in which reduction is taking place.
Define:
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is the act of using a voltage source to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction.
Electrochemical cells in which electrolysis is occuring are referred to as electrolytic cells.
In an electrochemical cell, at which electrode does oxidation occur? At which electrode does reduction occur?
In any electrochemical cell, oxidation occurs at the anode, while reduction occurs at the cathode.
A simple mnemonic to remember this by:
AN OX, RED CAT
OXidation = ANode, REDuction = CAThode.
In an electrochemical cell, what direction do electrons flow?
Electrons always flow from Anode to Cathode.
Remember: Reduction occurs at the Cathode (RED CAT), and Reduction Is Gain of electrons (OIL RIG), so electrons must be flowing to the cathode to facilitate reduction.
What type of electrochemical cell is being depicted below?

The cell is an electrolytic cell.
The two main types of electrochemical cells (electrolytic and galvanic) can be easily discerned by the presence or absence of a power source. In this case, the battery is the power source, indicating an electrolytic cell.

In the electrolytic cell depicted below, which electrode is the anode?

Electrode A is the anode.
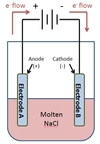
The positive end of the battery attracts electrons towards itself, and those electrons must be leaving Electrode A. Since electrons flow from anode to cathode, Electrode A must be the anode.
Note: Since the anode is attached to the positive end of the battery, in an electrolytic cell the anode is the positive (+) electrode.
In the electrolytic cell depicted below, which electrode is the cathode?

Electrode B is the cathode.

The negative end of the battery rejects electrons away from itself, and those electrons must reach Electrode B. Since electrons flow from anode to cathode, Electrode B must be the cathode.
Note: Since the cathode is attached to the negative end of the battery, in an electrolytic cell the cathode is the negative (-) electrode.
In the electrolysis of water shown below, which gaseous species will appear at the anode?

O2(g) will appear at the anode.

The anode is where oxidation occurs, so look for a species which can lose electrons.
Water can be thought of as consisting of O2- ions and H+ ions. The O2- ions can lose electrons to form molecular oxygen, O2, and this will occur at the anode.
In the electrolysis of NaCl shown below, which chemical species will appear at the anode?

Cl2(g) will appear at the anode.

NaCl is made up of Na+ and Cl- ions. Cl- ions will lose electrons at the anode to form molecular Chlorine, Cl2.
In the electrolysis of water shown below, which gaseous species will appear at the cathode?

H2(g) will appear at the cathode.

The cathode is where reduction occurs, so look for a species which can gain electrons.
Water can be thought of as consisting of O2- ions and H+ ions. The H+ ions can gain electrons to form molecular hydrogen, H2, and this will occur at the cathode.
In the electrolysis of NaCl shown below, which chemical species will appear at the cathode?

Na(s) will appear at the anode.

NaCl is made up of Na+ and Cl- ions. Na+ ions will gain electrons at the cathode to form Na metal.
What is an electrolyte, in the context of an electrochemical cell?
An electrolyte is any species added to the cell (in which an electrochemical reaction is occuring) which allows current to flow more easily.
Ex: in the electrolysis of water, either acid or salt must be added to the water to improve current flow, since pure water is not a good conductor of electricity.
What are the units of current, I?
The units of current are amperes, A.
Current is defined as charge over time Q/t, so 1 A = 1 C/s.
If 2.0 A of current flows for three minutes, how many C of charge flow in this time?
360 C
I = 2.0 A = 2.0 C/s
Q = I x t = 2.0 * 3 min * 60s/min
= 360 C
What is the equation relating current to number of moles of electrons?
Faraday’s Equation,
I x t = n x F
where:
- I = current in A
- t = seconds the current flows
- n = # of moles of electrons
- F = Faraday’s constant, 96,485 C/mol e-
Note: for the MCAT, approximate F = 105 C/mol e-
In the electrolytic cell shown below, if a current of 1.0 A flows for 10 seconds, how many grams of Na(s) are plated onto the cathode?

2.3x10-3 g of Na will be deposited.
Use Faraday’s equation to calculate the number of moles of electrons which flow through the circuit:
n = I x T / F
= (1)10/105 = 1x10-4 mol e-
Each mole of electrons reduces one mole of Na+. Calculate the mass of 10-4 mol of Na(s)
m = 1x10-4 * 23g/mol
= 2.3x10-3 g Na
What type of electrochemical cell is being depicted below?

The cell is an galvanic cell.

The two main types of electrochemical cells (electrolytic and galvanic) can be easily discerned by the presence or absence of a power source. In this case, the lack of a battery indicates that this is a galvanic cell.
In the galvanic cell depicted below, which electrode is the anode?

The Zn electrode is the anode.

In any electrochemical cell, electrons flow from anode to cathode. Electrons are leaving the Zn electrode, so it must be the anode.
In the galvanic cell depicted below, which electrode is the cathode?

The Cu electrode is the anode.

In any electrochemical cell, electrons flow from anode to cathode. Electrons are arriving at the Cu electrode, so it must be the cathode.












