EENT Flashcards
1
Q

A
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Staph aureus (adults)
- Strep pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis (children)
- S/s: rapid onset, drainage causing sticky/matting of eyes
- Tx
- Azithromycin (1gt bid 2d, then 1gt daily 5d)
- Bacitracin (1-2gtt q3-4h 7-10d)
- Trimethoprim (1-2gtt q3-4h 7-10d)
2
Q

A
Hyperacute Bacterial Conjunctivitis
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- S/s: severe discharge, lid swelling, chomosis (swelling of conjunctiva), VISION LOSS
- Tx: hospitalization
- Trimethoprim (1-2gtt q3-4h 7-10d)
- Bacitracin (1-2gtt q3-4h 7-10d)
- Azithromycin (1gt bid 2d, then 1gt daily 5d)
3
Q

A
Viral Conjuntivitis
- adenoviruses (common cold virus)
- S/s: “scratchy/gritty” eye, may have hx upper respiratory prior, drainage thicker in morning/clearer as day progresses
- Tx:
- allow 2-3 weeks to resolve on its own
4
Q

A
Allergic Conjunctivis
- IgE mediated mast cell degranulation with release of histamine & others
- S/s: itching, no significant discharge
- Tx:
- Olopatadine hydrochloride 0.1%/0.2% (Patanol)
- Azelastine hydrochloride 0.05% (Optivar)
5
Q
Nonallergic Conjuntivis
A
- irritant or chemical exposure
- Tx:
- removal of foreign body
- irrigation after chemical splash
- removal of irritant and time
6
Q
Dx of Conjunctivitis
A
- no dx testing unless:
- The presence of ocular pain, headache, foreign body sensation, fixed pupil and/or vision changes requires further investigation
- always ask about contact lens wear
7
Q

A
Uveitis (irititis)
- inflammation of uvea structures: iris, ciliary body (anterior), choroid (posterior)
- causes: infections, SID, drug rx, ocular disease
- S/s:
- anterior: PAIN, redness at limbus, photophobia
- posterior: less pain, vision change/floaters
- Tx:
- refer to opthalmologist - slit lamp exam reveals leukocytes
- ocular steroids (MD Rx only)
8
Q

A
Bacterial Keratitis
Infection of the cornea: anterior surface of eye
- Staph aureus, Pseudomonas, Strep pneumoniae, Klebsiella pneumoniae
- contact lens wear, corticosteroid eye drops
- Dx:
- corneal round, white opactity visible w/ penlight
- also acute red eye, discharge, foreign body sensation, photophobia
- Tx:
- emergency requiring same-day referal to opthalmology
9
Q

A
Viral Keratitis
Infection of the cornea: anterior surface of eye
- Herpes simplex 1 & 2 (latent HSV1 recurrence primarily)
- laser UV tx; eye rx: corticosteroids, epiniphrine, b-blockers, prostaglandins; immunosuppressed
- Dx:
- dendritic lesions seen w/ fluorescein stain
- blurred vision, injection near limbus, decr. corneal sensation, variable pain, watery drainage, photophobia
- Tx:
- refer to opthalmologist- will Rx topical antivirals NO topical steroids
- Trifluorothymidine drops, ganciclovir gel, oral acyclovir
10
Q

A
Episclaritis
inflammation of fine vascular tissue covering anterior sclera
- idiopathic (rarely systemic: dry eye, TB/syphilis, immune-mediated rxn)
- Dx:
- very vascular: bright red, NO PAIN, no vision change
- if recurring: CBC, CMP, UA, ESR, CRP for underlying disease
- Tx:
- referral to optholmologist
- self-limited, resolves in ~3wks, artificial tears & NSAIDs for pain
11
Q

A
Scleritis
white avascular, fibrous outer coating of eye
- associated with systemic disease 50% of time - inflammation/infection
- Dx:
- deep red/purplish color to sclera
- pain w/ palpation, severe, constant “boring” pain, radiating to periorbital region, worse with eye movement, can impair sleep
- Tx:
- URGENT refer to opthalmology - NSAIDs and immunosuppressants
12
Q

A
Blepharitis
inflammation of both eyelids
- thought to be staph colonization
- Dx:
- crusty/flaking skin on lashes, red/itchy eyes, gritty/burning, incr. tear, eyelid swelling/erythema, blurred vision
- Tx:
- lid hygiene: warm compress, massage, q-tip wash
- topical Azithromycin (erythromycin topical, bacitracin oinment also)
- oral abx: azithromycin, doxycycline, tetracycline
13
Q

A
Corneal Abrasion
- foreign body impacting the eye - history important
- Dx:
- fluorscein stain uptake
- Tx (all topical):
- rythromycin ointment -or- sulfacetamide
- contanct lens abrasion:
- ofloxacin
- ciprofloxacin
- tobramycin drops
- REFER IF:
- corneal infiltrate, white spot, ulceration (top & middle pic)
- hypopyon: pus in anterior chamber (bottom pic)
- increasing pain
- significant vision change (2 lines on Snellan chart)

14
Q

A
Hordoleum (“stye”)
- Staph aureus (most commonly) but can be sterile
- Dx:
- acute/rapid onset w/ erythema
- arises from eyelash follicle
- Tx:
- warm compresses qid
- Abx not helpful unless cellulitis present
- usually resolves on its own in 7-10 days
15
Q

A
Chalazion “lazy one”
- may begin as hordoleum and result with Zeis or Meibomian gland obstruction
- Dx:
- rubbery and painless, lacks erythema
- Tx:
- hot compresses - but can take weeks
- refer to opthalmololgist for I&D or glucocorticoid injection if no resolution
16
Q

A
Dacryoadenitis (Dacryo = tears)
- S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, Pseudomonas, N. gonnorhoeae, measles, mumps, flu infection of lacrimal gland
- Dx:
- S-shaped eyelid
- fever, fatigue, red/swollen eyelid, erythema of bulbar conjunctiva, tender to palpation
- Tx:
- CT of orbits and sinuses to rule out involvement
- Abx:
- Cephalexin (beware MRSA)
- Clindamycin 150-300mg q6h
- IV vancomycin followed by TMP-SMX PO
17
Q

A
Daryocystitis (daryo = tears)
- S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, H. influenza infection of lacrimal duct
- Dx:
- rapid onset of erythema/swelling of lacrimal gland
- infection can spread to orbital cellulitis, abscess, or enter conjunctiva
- infants & old w/ obstruction or narrowing of duct
- Tx:
- refer to opthalmologist
- Abx:
- cephalexin (beware MRSA)
- clindamycin 150-300mg qid
18
Q

A
Orbital Cellulitis
- mcc: S. aureus, streptococci in ethmoid sinuses then extends
- orbital (inflammation of extraocular mm. and fatty tissue):
- ocular pain/swelling, fever, PAIN w/ EYE MOVEMENT, ophthalmoplegia/diplopia
- can lead to abscesses, vision loss, cavernous sinus thrombosis, death
- Tx:
- CT to distinguish from preseptal
- opthalmology consult w/ hospitalization
- vancomycin+ceptriaxone/ampicillin-sulbactam/pipercillin-tazobactam
- preseptal cellulitis (outside orbit):
- ocular pain and swelling (milder)
- clindamycin or TMP-SMX
- orbital (inflammation of extraocular mm. and fatty tissue):
19
Q

A
Pterygium (the triangle)
- triangular wedge of fibrous conjuntival tissue forming medially and extending laterally, due to UV exposure causing RNA/DNA change
- mainly cosmetic but can involve cornea, impair vision, restrict movement
- Tx:
- supportive: artificial tears
- surgery (but frequently recur)
20
Q

A
Pinguecula
- white to yellow thickened area of limbus, looks “fatty” and adjoins the limbus
- often bilateral and more common with age
- Tx:
- topica corticosteroids and opthalmic NSAIDs (both carry long-term risks)
21
Q
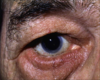
A
Entropion
- INWARD rotation of eyelids
- can cause corneal abrasions and scarring, sensation of foreign body, tearing and irritation worsens with time
- Tx:
- referral to opthalmologist for surgery
22
Q

A
Ectropion
- OUTWARD turning eyelid
- acquired and congenital causes
- exposes conjuntival surface causing keratinization of epithelium, foreign body sensation, dryness, photophobia, tearing, conjunctivitis, vision can be affected
- Tx:
- referral to opthalmology
23
Q

A
Hyphema
- blood in anterior chamber most commonly from trauma or spontaneous: tumors/melanoma, neovascularization disease (ex. diabetes), clotting disorders, warfarin/aspirin, sickle cell, surgery - in children possible abuse
- Dx:
- significant pain, vision loss, NAV, photophobia
- Tx:
- opthalmologist referral
- address any trauma, eye sheild, bed rest/elevate head, avoid light
- ocular anesthetics: Proparacaine
- oral/IV narcotics
24
Q

A
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
- bleeding in small vessels in conjunctiva that can look like blood will “pour out of eye” from sneezing, coughing, straining, vomiting
- usually benign - no pain, photophobia, vision loss
- resolves over 1-2 weeks
- caveats:
- in presense of trauma evaluate rupture of globe - opthalmologist referral
- if recurrent evaluate for bleeding or dyscasias (imbalance in blood)
25

Cataracts
* leading cause of blindness - progressive "myopic shift" from increasing opacity of lens
* Dx:
* darkened red reflex
* opacities visible within red reflex
* obscure fundus exam
* Tx:
* non-urgent referral to opthalmologist
26

Strabismus
* misaligned eyes the majority of cases thought to be genetic but also palsy of cranial nerves controlling eyes, prematurity and low birth weight increase risk
* if adult: think thyroid disease or myasthenia gravis
* Eval:
* history: birth & family hx, age of onset, freq., trauma, toxins, other med cond.
* physical: complete incl neuro, PERRLA (pupils equal round reactive light accommodation), EOMI (extra occular movement intact), corneal light reflex, cover test
* **Bruckner Test:** red reflection more intense in deviated eye
* Tx: referral to pediatric opthalmologist
27
causes and treatments

Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
* any disorder where one eye functions better die to visual cortex development in early childhood - dominant eye "takes over" and other does not develop normally
* crucial time period is age months to 7-8
* Causes:
* strabismus- varying images causes one to be suppressed (training, surgery)
* anisometric amblyopia (unequal refraction)- born with significant refraction differences between eyes (glasses)
* deprivation amblyopia- obstruction of image, usally results in vision loss if not treated quickly (remove/correct problem)
* this is a referral
* eye terminology:
* hypotropia
* hypertropia
* exotropia
* esotropia
28

Central Retinal Artery Occlusion (CRAO)
* "stroke of the arteries of the eye" most commonly caused by atherosclerosis
* S/s:
* _acute onset vision loss_ (painless) - can be preceeded by transient loss
* Dx:
* cherry red spot on macula ("Jupiter")
* complete or relative pupillary afferent defect
* \>50 get ESR and CRP to check for temporal arteritis
* Tx:
* SEND TO ER: opthalmic emergency
29

Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
* 2nd most common vascular cause of blindness after diabetes
* Types:
* CRVO- entire retina affected by thrombus
* branch RVO- distal retina involved
* HemiRetinal VO- half of retina involved
* Dx:
* acute onset of painless vision loss
* "blood and thunder" appearance (Venus/venous)
* "cotton wool" spots
* Tx: immediate referral to opthalmologist
30

Retial Detachment
* separation of neurosensory retina from underlying retinal pigment epithelium and choroid ("folded appearance" of retina) - typically due to trauma, surgery, CMV retinitis, myopia, flouroquinolones
* S/s:
* photopsia (flashing light), floaters, "curtain falling"
* Dx:
* visual acuity test, confrontational visual field test, opthalmoscopy
* Tx:
* immediate referral to opthalmologist
31

Age Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
* degeneration of macula due to age, tobacco, genetics, CVD, hx cataract surgery
* Dry:
* slow/gradual vision loss
* scotomas (blind spot)
* difficulty reading
* Wet:
* loss of central vision over weeks/months (can start in one and progress
* Metamorphopsia (distortion in visual field- Amsler grid)
* Tx: opthalmology referral
32

Open Angle Glaucoma (90%)
* _diminished_ drainage of aqueous humor through trabecular meshwork
* risks: AA \>40, diabetes, myopia, fam hx
* Dx:
* cupping of optic disc head
* asymptomatic peripheral vision loss
* increased intraocular pressure (33-50% of pts.)
* Tx: w/ opthalmologist (topical tx or surgery)
* incr. outflow: prostaglandins, a-adrenergic/cholinergic agonists
* decr. aq. prod.: a-adrenergic agonists, b-blockers, carbonic anydrase inhib.
33
headache
decreased vision
halos
eye pain
NAV
cloudy cornea, conjuntival redness, shallow anterior chamber, poorly reactive pupil

Angle Closure Glaucoma
* lens too far foward and abducts iris _stopping_ flow of aqeuous humor
* S/s:
* dramatic vision loss in hours-days
* Tx:
* EMERGENCY- send to ER or opthalmology immediately
* b-blocker and other meds then laser iridotomy
34

Diabetic Retinopathy
* prolonged/chronic hyperglycemia
* Non-proliferative:
* early in disease (end 10-20yrs)
* microaneurysms, hemorrhages, cotton-wool spots (nerve infarcts), lipid deposits
* Proliferative:
* growth of new vessels (neoplasia)
* Tx:
* annual monitoring/exams
* laser photocoagulation of vessels
35

Vitreous Hemorrhage (clear gel-like substance filling eye)
* aging/trauma/DM causes liquification and shrinking then posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) and bleeding
* Dx:
* bleeding, vision loss, floaters, blurring, cobwebs
* Tx:
* emergent opthalmology referral if trauma/tear
* surgery by retinal specialist
36
flame hemorrhages
hard exudates ("yellow fat")
AV nicking and narrowing
cotton wool spots

Hypertensive Retinopathy
* malignant HTN causing changes in retina, choroid and optic nerve - blindness or vision changes rare
* Tx:
* treat underlying HTN
37

Malignant Hypertension
* optic disk swelling: BP \> 200/130, increased ICP
* S/s:
* headache, scotoma, diplopia, decreased vision, photopsias (flashes of light)
* more damaging than chronic HTN
* Tx:
* rapid lowering of BP: 10-15% first hr and 25% by end of day
38
warm, swollen, red auricle

Perichondritis
* Pseudomonas (mcc), S. aureus, S. pyogenes: piercings, cuts, burns, sports
* Dx:
* compare ears facing forward
* Tx:
* Flouroquinolones-
* Levofloxacin 750mg qd x 7d
* Ciprofloxacin 500mg bid x 7d
* remove all ear jewelry
* 48-72hr follow-up and ENT immediately if no improvement
39

Cerumen Impaction
* apocrine and eccrine gland secretions mix with squamous epithelium to form ph4-5 protective cerumen
* Dx:
* visual observation, hearing loss, pain or onset of otalgia
Tx (removal):
* OTC Debrox (carbamide peroxide)
* irrigation w/ hydrogen peroxide
* DO NOT FLUSH if TM perforated or cannot confirm
40
rapid onset of pain
tenderness w/ tragus palpation
otorrhea
white/yellow cerumen appearance
edamatous canal

Otitis Externa ("swimmer's ear")
* Principles of Tx:
* pain management
* remove debris
* topical meds
* avoid contributing factors (water, etc)
41

Acute Infective Otitis Media
* typically swimmers
* Tx:
* debridement
* topical therapy:
* ciprofloxacin/hydrocortisone (Cipro HC)
* ciprofloxacin/dexamethasone (Ciprodex)
* hydrocortosone/acetic acid (bacterial or fungal)
* ruptured TM: Ofloxacin otic drops
* Otowick if canal swollen
42

Necrotizing Malignant Otitis Media
* granulation tissue or exposed bone, purulent otorrhea \> 1mo, persistent otalgia
* cranial n. involvement and facial palsy
* Tx:
* Hospital admission
* CT scan for temporal bone involvement and culture
* surgical debridment
* IV Ciprofloxacin
43

Fungal Otitis Externa (Otomycosis)
* aspergillus (mcc) often from abx overtreatment or trapped moisture
* Dx:
* thick white/gray discharge or fuzzy appearance
* Tx:
* Acetic acid otic (VoSol) EXCEPT if TM perforated - refer to ENT

44

Eczematous Otitis Media
* includes: atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, lupus, eczema
* dry, itchy, flaky skin
* Tx:
* topical steroid drops
* Fluoinolone otic (DermOtic)
45

Herpes Zoster Oticus
* "shingles of the ear" - burning pain followed by eruption of rash
* Ramsay-Hunt Syndrome
* Tx:
* antivirals
* Acyclovir
* Famciclovir
* Valcyclovir
* oral steroid: prednisone

46

Normal Tympanic Membrane
* cone of light indicates no fluid or infection behind membrane
48
* retracted tympanic membrane (measured w/ tympanogram)
* short process of malleolus at 12 o'clock position appears shorter
* S/s:
* conductive hearing loss
* sensation of fullness
* gurgling, crackling, popping/snapping noises in ear
* decreased TM mobility
* allergic symptoms

Eustacian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
* Tx (treat the source):
* oral decongestant- pseudoefedrine (Sudafed) 60mg PO q8hr
* intranasal decongestant - oxymetabolism (Afrin)
* antihistamines
* Allegra 180mg/day
* Loratadine 10mg/day
* expectorant - Mucinex OTC
* no improvement after 6 weeks consider myringotomy with tubes
49
Non-Otologic Causes of Otalgia (ear pain)
normal appearance of canal and TM
* malignancy:
* nasopharynx, pharynx, tonsil, tongue, larynx
* tobacco/alcohol
* infection
* herpes zoster, tonsillitis
* neurologic
* trigeminal neuraligia (Tx: carbamazepine- anticonvulsant)
* TMJ
* pain/clicking with jaw movement, bruxism - grinding
* refer to dentist, NSAIDs, mm relaxants, mouth splints
50

Serous Otitis Media
* "honey" behind TM
* Tx
* watchful waiting (3mo) as often resolves spontaneously- eval hear/speech
* autoinsufflation ("popping ears")
* decongestants
* pseudoepedrine (Sudafed) / phenylephrine (Sudafed PE)
* antihistamines
* myringotomy for persistent cases
* Abx not recommended (but often used)
51
mild to severe/disabling otalgia (unilateral or bilateral)
children may have fever, NAV, diarrhea
hearing loss, irritability

Acute Otitis Media
* bacterial or viral infection (may be associated with upper respiratory symtoms and fever)
* bacteria (head big 3): H. influenza, M. catarrhalis, Group A strep
* virus: RSV, corona virus, adenovirus, influenza, human metapneumovirus
* if neurologic signs (headache, confusion, facial paralysis, vertigo) - **send to ER**
52

Acute Otitis Media Bullous Myringitis
* appearance of hemorrhagic blebs on TM resulting from infection
54
Otitis Media Definitions
* Acute "suppurative" OM
* inflammation of the middle ear and TM - viral or bacterial **infection**
* Serous "non-suppurative" OM
* residual effusion **post-acute infection** or related to ETD
* acute: \<3wk, subacute: 3wk-3mo, chronic: \>3mo
* Chronic OM
* **infection** present in middle ear with tympanic membrane perforation
* may have cholesteatoma
55

Mastoiditis
* complication of acute otitis media days-weeks after onset
* strep pneumoniae infection of mastoid air cells
* Tx:
* Vancomycin + ceftriaxone IV
* culture if no improvement with Abx after 48hrs
* mastoidectomy if tx fails
* Cx:
* perforation of TM or postauricular subperiosteal abscess
* temporal lobe abscess or septic thrombosis of the lateral sinus
56

Chronic Otitis Media
* can result from AOM or eustachian tube obstruction, mechanical trauma, blasts, PE tube, thermal/chemical burns
* Dx:
* P. aeruginosa, Proteus species, S. aureus infections
* Drainage cultured if: choleseatoma or other complications suspected
* febrile patient / vertigo / otalgia
* CT or MRI to check for labyrinthitis, ossicular, temporal erosion and abscesses
57

Cholesteatoma
* prolonged ETD and retraction of TM creating squamous lined sac filled with desquamated keratin leading to chronic infection
* erodes bone and ossicular chain, affects facial nerve over time
* Tx:
* surgery
59

Tympanosclerosis
* hard white plaque on the TM ("scarring" of the TM)- fibrosis due to frequent infections causing hemorrhage in the layers of the TM
* asymptomatic but cat lead to conductive hearing loss
* Tx:
* none if asymptomatic
* if hearing loss: explore tympanotomy or tympanoplasty
* hearing aid
60

Tympanic Membrane Perforation
* due to infection, trauma, PE tube placement
* S/s:
* sudden severe pain (if traumatic) then bleeding from ear
* hearing loss is ossicular chain disrupted
* _tinnitus_
* vertigo suggests inner ear injury
* audible whistling during sneezing/nose blowing
* purulent otorrhea- may begin after 24-48hrs if water enters
* Tx:
* NO air or irrigation of canal until perforation is ruled out
* no tx if acute due to trauma- keep ear dry
* topical abx if due to infection or contaminated water
* surgery if perforation lasts \>2mo
* spontaneous closure if right size, location, associated patho condition
*
63
Tx of Acute Otitis Media in Children
* acetaminophen or ibuprophen for pain
* antihistamines & decongestants NOT effective in children unless allergies
* NO OTC COLD MEDS if \<6
* Auralgan drops OTC
* Tx or watchful waiting:
* \<6 mo OR 6mo-2yr w/ bilateral OM - treat
* 6mo-2yr w/ unilateral - observe 48-72hr or treat
* 2+yr - treat is severe symptoms, if mild can observe w/ follow-up and agreement b/t parents and HCP
* Abx:
* Amoxicillin 90mg/kg divided 2 doses (max 3gm/d) unless:
* given in last 30 days (resistance)
* concurrent purulent conjunctivitis
* PCN allergy
* Cefdinir
64
Tx of Otitis Media in Adults
* Amoxicillin 875 mg PO BID -or- 500mg TID 5-7d / 10d if severe
* if PCN allergy:
* Azithromycin (Z-pak) 500mg on day 1, then 250mg days 2-5
* Clarithromycin 500mg bid
68
Chronic OM Tx
* keep ear dry, cleaned/debrided, granulation tissue removed
* topical corticosteroids and abx
* systemic abx and surgery for severe cases only
* attic perforations or chronic central TM- tympanoplasty
* cholstesteatoma or mastoid invovlement w/ TM perf- mastoidectomy and tympanoplasty
71
* SERIOUS: abnormal replacement of normal bone with sponiotic or sclerotic bone- leads to fixation of stapes to margins of oval window
* results in progressive **_bilateral_** conductive hearing loss
* strong genetic inheritance
* mostly caucasians and 2x more likely in females
Otosclerosis
* Dx:
* hx, audiogram, progressive conductive HL
* exacerbated by pregnancy and estrogen therapy
* often presents in 3rd decade of life
* Tx:
* hearing aids (temporary)
* surgery: total/partial stapedectomy
72

Leukopenia
pre-malignant lesion
* white keratotic plaque that cannot be wiped away
* may show dysplasia
73

Erythroplakia
premalignant lesion
* red plaque-like lesion with HIGHER risk of developing into oral cancer than leukoplakia
* more likely to occur on buccal & mandibular mucosa, palate, tongue, floor of mouth- may show dysplasia
74
Oral Cancer Exam
* if SMOKER/DRINKER and mouth/neck issues keep CA in differential
* cervical lymph node enlargement
* difficulty speaking if tongue affected
* numbness of chin if lesion on lip and affects mental nerve

75
Features Suggestive of Oral Cancer
* **tooth mobility of unknown cause\*\***
* **non-healing dental extraction site\*\***
* unexplained ulceration
* unexplained red and white patches that are painful, swollen, bleeding
* unexplained ear pain/neck pain - esp. w/ limited mouth opening but normal otoscopy
* irregular pigmented mucosal areas (suggestive of melanoma)
* tongue numbness or fixation
* TX:
* referral to dentist

76

Geographic Tongue (benign migratory glossitis)
Non-cancerous lesion
* cause unknown (may be linked to psoriasis)
* Tx:
* no tx necessary and not contageous
77

Torus Palatinus
Non-cancerous lesion
* bony prominance of the hard palate- composed of bone, linked to genetics
* Tx:
* surgically removed if causes pain or discomfort
79

Paranasal Sinus Cancer
* CA usually affecting maxillary sinuses (sometimes ethmoid), uncommon
* Risks: chem exposure/pollution, tobacco, HPV
* Dx:
* looks like sinusitis or asymptomatic
* facial pain, dental pain, nasal obstruction, epistaxis- perisistant/chronic
* CT of mass
* Tx:
* surgical resection (endoscopic)
* radiation (sometimes chemo)
80
* Risk:
* acohol, tobacco, **HPV infection** (16,18,31,33)
* young men if no alc/tob, mult sexual partners
* S/s:
* dysphagia
* throat pain/fullness
* oral bleeding
* referred ear pain
* voice changes
* **2 WEEK time limit on throat pain/symtoms**
Orophryngeal Cancer

86
* cancer associated with salted/cured foods, Chinese herbs, rancid butter/sheep's fat and my be triggered by reactivation of EBV
* In US/Europe associated with tobacco and alcohol use (maybe HPV)
* S/s (triad):
* neck mass
* serous OM and resultant hearing loss / tinnitis
* nasal obstruction or pain
* Tx:
* referral to ENT
* CT, small mirror/nasophayngoscope visualization, biopsy
Nasopharyngeal Cancer
89
Diagnosing Tumors of Head & Neck
* Thorough Hx:
* tobacco and alcohol use especially
* length of symptoms (normal throat pain/symtoms resolve in 2 weeks)
* fatigue, weight loss, appetite loss/dysphagia, spread to other organs
* Complete physical:
* Full HEENT and oral exam
* Full lymphantic system exam
* Full cardiovascular and respiratory exam
* ENT referral
* CT -\> panendoscopy -\> biopsy -\> Tx based on TNM staging (tumor, lymph node, metastases)
90
Infection & Allergy Symptoms
* Bacterial
* mild/moderate pain, red eye, foreign body sensation, purulent discharge, glued eyes on awakinging, unilateral
* Viral
* no/mild pain, gritty sensation, watery discharge, unilateral, upper respiratory infection (URI)
* Herpes
* pain and tingling followed by rash and conjunctivitis
* Allergic
* BILATERAL, tearing, intense itching, stringy discharge, diffuse hyperemia
91
Infective Agents
* Bacterial
* S. pneumoniae, H. flu, S. aureus, chlamydia, gonorrhea
* Viral
* adenovirus, herpes zoster
* Contact lenses - pseudomonas
92
Viral Tx
* No meds usually
* **NO STEROIDS**- prevent healing, glaucoma risk
* cold compresses
* ocular decongestants to reduce redness (avoid)
* oxymetazoline, tetrahydozoline (eg. Visene)
* artificial tears
* Herpes:
* trifluridine drops (Viroptic)
* oral antivirals for systemic infections
93
Bacterial Tx
* normally self-limiting and resolve within a week (except gonorrhea)
* think about what is most likely to cause infection, cost, friendliness of course
* Gentamicin/Tobramycin toxic- but may need to be used b/c G-
* Frequent:
* Moxifloxacin
94
Allergic Conjuntivitis Tx
* Antihistamines:
* Azelastine (Optivar)
* Emedastine (Emadine)
* Ketotifen (Zaditor, Alaway, etc) OTC
* Mast cell stabilizers
* not as effective
95
Ocular NSAIDs & Steroids
* NSAIDs:
* block COX-1 (platelett aggregation) & COX-2 (pain, inflammation)
* use: opthalmic procedures post op
* SE: delayed woud healing, keratitis, reactivate HPV
* Steroids:
* block phospholipase A2 -\> blocks COX-1 & COX-2
* opthalmic injury, post op, anterior uveitis
* SE: do not use if infection (may cause), glaucoma/nerve damage/cataracts, increased intraocular pressure, delayed healing, no contact wear with loteprednol
96
Glaucoma Tx
* prostaglandin analogs
* reduce IOP via increases **uviscleral** outflow in open-angle glaucoma
* SE:
* increased/misdirected eyelash growth, herpes activation, allergy, hyperpigmentation, migrane, keratitis
* Rx (1x at night):
* Latanoprost (Xalatan)
* Bimatoprost (Lumigan)
* Travoprost (Travatan Z)
* Tafluprost (Zioptan)
* Beta-blockers
* **decrease beta-receptor** stimulation production of aqueous humor
* SE: allergy, keratitis, systemic effects (cardio)
* Rx (BID):
* Betaxolol (Betoptic-S)
◦Far more selective for beta-2
* Timolol (Betimol, Istalol, Timoptic, Timoptic-XE)
◦Non-selective
◦Short-term escape, long-term drift
* Carteolol
* Levobunolol (Betagan)
* Metipranolol


