Eczema Flashcards
Prevalence of eczema in children
- eczema occurs in around 15-20% of children and is becoming more common
- typically presents before 6 months
- clears in around 50% of children by 5 years of age and in 75% of children by 10 years of age
Locations of eczema in different age group (in children)
- in infants the face and trunk are often affected
- in younger children eczema often occurs on the extensor surfaces
- in older children a more typical distribution is seen, with flexor surfaces affected and the creases of the face and neck
Management of eczema in children
- avoid irritants
- simple emollients: large quantities should be prescribed (e.g. 250g / week), roughly in a ratio of with topical steroids of 10:1.
- topical steroids
- in severe cases wet wraps and oral ciclosporin may be used
How to apply emollients?
If a topical steroid is also being used:
- the emollient should be applied first followed by waiting at least 30 minutes before applying the topical steroid
- Creams soak into the skin faster than ointments
- Emollients can become contaminated with bacteria - fingers should not be inserted into pots (many brands have pump dispensers)
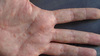
What’s 1 finger tip rule?
Finger tip rule → for applicaiton of topical steroid
1 finger tip unit (FTU) = 0.5 g, sufficient to treat a skin area about twice that of the flat of an adult hand

The potency of topical steroids

Prognostic markers associated with severe disease
- onset at age 3-6 months
- severe disease in childhood
- associated asthma or hay fever
- small family size
- high IgE serum levels
Pathophysiology of atopic eczema
- TH2 driven inflammation
- ↑IgE production
*Most children grow-out of it by 13yrs
Causes of atopic eczema
- FH of atopy common
- Specific allergens
- House dust mite
- Animal dander
- Diet: e.g. dairy products
Presentation of atopic eczema
Face: around eyes, cheeks
Flexures: knees, elbows
Associations with atopic eczema
- Asthma
- Hay fever
Ix for atopic eczema
- ↑ IgE
- RAST testing: identify specific Ag
- Irritant → Contact
Management (in general) of eczema
- emollients
- topical steroids
- UV radiation
- immunosuppressants: e.g. ciclosporin, antihistamines and azathioprine
Education for eczema
Education
- Avoid triggers: e.g. soap
What soup substitutes should be used in eczema?
Soap Substitute
- Aqueous cream
- Dermol cream
- Epaderm ointment
Name of emoillents
Emollients
- Epaderm
- Dermol
- Diprobase
- Oilatum (bath oil)
Steroid therapy for eczema
Topical Therapy with steroids:
- 1% Hydrocortisone: face, groins
- Eumovate: can use briefly (<1wk) on face
- Betnovate
- Dermovate: very strong, brief use on thick skin (palms, soles)
2nd line therapies for Eczema
2nd line Therapies
- Topical tacrolimus
- Phototherapy
- Ciclosporin or azathioprine
What’s eczema herpeticum?
Eczema herpeticum
- a severe primary infection of the skin by herpes simplex virus 1 or 2
- more commonly seen in children with atopic eczema and often presents as a rapidly progressing painful rash
What can be seen O/E of eczema herpeticum?
On examination, monomorphic punched-out erosions (circular, depressed, ulcerated lesions) usually 1–3 mm in diameter are typically seen.