Ecology Flashcards
Organism

Definition:
Any contiguous living system.
Example:
My dog is an organism.
Population

Definition:
A summation of all the organisms of the same group or species, who live in the same geographical area, and have the capability of interbreeding.
Example:
The population of elephants are decreasing due to being hunted by humans.
Community

Definiton:
An assemblage or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area and in a particular time.
Example:
These fish are part of an underwater community.
Ecosystem

Definition:
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
Example:
A pond is an example of an ecosystem.
Species

Definition:
One of the basic units of biological classification.
Example:
Cats are a species.
Biome

Definition:
Very large ecological areas on the earth’s surface with animals and plants adapting to their environment.
Example:
This marine biome is dominated by kelp, a kind of seaweed.
Food Chain

Definition:
Shows how each living thing receives its food.
Example:
The Ankole Cattle are primary producers.
Food Web
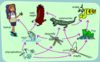
Definition:
Consists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem.
Example:
This food web shows the many ways energy is distributed through the ecostystem.
Producer

Definition:
An organism that can produce its own energy and nutrients.
Example:
This berry plant is a producer.
Photosynthesis

Definition:
A process that plants use to convert the sun’s energy into food.
Example:
The leaf is using photosynthesis to get nutrients.
Consumer

Definition:
An organism on the food chain that depends on producers or other consumers for food, nutrition, and energy.
Example:
The cheetah is a consumer because it eats other animals.
Primary Consumer

Definition:
An organism that eats plants.
Example:
The koala is a primary consumer because it’s diet consists of plants.
Secondary Consumer

Definition:
An organism that eats the primary consumer, and can be an omnivore or a carnivore.
Example:
A bird is a secondary consumer because it eats primary consumers, like caterpillars.
Tertiary Consumer

Definition:
A carnivore that eats other carnivorous organisms.
Example:
The whale is a tertiary consumer because it is eating another fish that seemly, by it’s size, is a carnivore.
Quaternary Consumer

Definition:
A quaternary consumer is an organism that is at the top of the food chain.
Example:
Humans are quaternary consumers.
Herbivores

Definition:
An organism that feeds on plants.
Example:
The sea turtle is an herbivore.
Carnivores

Definition:
A carnivore is an organism that eats meat.
Example:
An osprey is a carnivore.
Omnivores

Definition:
An organism that consumes both plants and meat.
Example:
A black bear eats plants and meat, so therefore it is an omnivore.
Decomposers

Definition:
An organism that breaks down dead material.
Example:
A mushroom is a decomposer.
Abiotic Factor

Definition:
Non-living things that affect the living things in that environment.
Example:
A river is an abiotic factor in this environment.
Biota

Definition:
The animal and plant life of a particular region, habitat, or geological period.
Example:
The biota in a desert area must be able to take extreme heat.
Nutrients

Definition:
Chemical substances found in every living thing on Earth that help break down food to give organisms energy.
Example:
Fruit is considered a nutrient.
Carbon Cycle

Definition:
Series of processes in which carbon atoms circulate through Earth’s land, ocean, atmosphere, and interior.
Example:
The carbon cycle is an important process.
Nitrogen Cycle

Definition:
Chemical circulation of Earth’s nitrogen through the atmosphere, soil, and living and decaying organisms.
Example:
The nitrogen cycle goes through many steps.

































































