DNA & Protein Synthesis Vocabulary Flashcards
DNA

Definition:
A molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
Example:
DNA is responsible for our inherited traits.
Double Helix

Definition:
A pair of parallel helices intertwined about a common axis.
Example:
DNA is in the shape of a double helix.
Gene
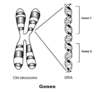
Definition:
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
Example:
Our genes come from our parents.
Chromosome

Definition:
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
Example:
Every person is made up of 46 chromosomes.
Trait

Definition:
A genetically determined characteristic.
Example:
Everyone has different traits.
Genetic Code

Definition:
The nucleotide triplets of DNA and RNA molecules that carry genetic information in living cells.
Example:
The genetic code can be expressed as either RNA codons or DNA codons.
Nucleotide
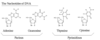
Definition:
A compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group.
Example:
An example of a nucleotide is Adenine.
Sugar

Definition:
Any of the class of soluble, crystalline, typically sweet-tasting carbohydrates found in living tissues.
Example:
We put sugar on our food to make it taste sweet.
Phosphate

Definition:
An ester of phosphoric acid.
Example:
Phosphate is an inorganic chemical.
Base

Definition:
Substances that accept protons from acids.
Example:
Thymine is an example of a base.
Adenine

Definition:
A compound that is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic acids.
Example:
Adenine is paired with Thymine.
Thymine

Definition:
One of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid of DNA.
Example:
Thymine is part of the pyrimidine family.
Guanine

Definition:
One of the four nucleotide bases of genetic code.
Example:
Guanine is part of the Purine family.
Cytosine

Definition:
A compound found in living tissue as a constituent base of nucleic acids.
Example:
Cytosine is paired with Guanine.
Uracil
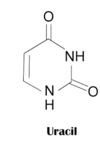
Definition:
A compound found in living tissue as a constituent base of RNA.
Example:
Uracil takes the place of Thymine in RNA.
Complementary Base Pairs

Definition:
Either of the nucleotide bases linked by a hydrogen bond on opposite strands of DNA or double-stranded RNA.
Example:
The complementary base pairs of DNA are Adenine-Thymine and Guanine-Cytosine.
Complementary Strands

Definition:
A section of one nucleic acid chain that is bonded to another by a sequence of base pairs.
Example:
DNA has complementary strands.
Hydrogen Bond

Definition:
A chemical bond in which a hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to an electronegative atom.
Example:
A hydrogen is a weak type of bond.
Deoxyribose
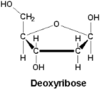
Definition:
A sugar derived from ribose by replacing a hydroxyl group with hydrogen.
Example:
Deoxyribose is a monosaccharide.
DNA Polmerase

Definition:
An enzyme that creates DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides.
Example:
DNA Polymerase duplicates our genetic information.
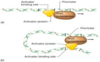
DNA Replication

Definition:
The process of producing two identical replicas from one original DNA molecule.
Example:
During DNA replication, both strands of the double helix act as templates for the formation of new DNA molecules.
Semiconservative

Definition:
Relating to or denoting replication of a nucleic acid in which one complete strand of each double helix is directly derived from the parent molecule.
Example:
The semi-conservative model of DNA replication states that the two strands of DNA are separated and individually copied.
Replication Fork

Definition:
The point at which the two strands of DNA are separated to allow replication of each strand.
Example:
The replication fork is y-shaped.
Helicase

Definition:
A class of enzymes vital to all living organisms whose main function is to unpackage an organism’s genes.
Example:
Helicase unzips both DNA and RNA.
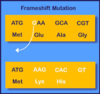
Amino Acid

Definition:
Biologically important organic compounds composed of amine and carboxylic acid functional groups.
Example:
Amino acids bond together to make long chains.
Protein
Definition:
Any of a class of nitrogenous organic compounds that consist of large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids.
Example:
Protein plays a vital role in the body, like building and maintaining muscles, organs and other tissue.
Polypeptide

Definition:
A linear organic polymer consisting of a large number of amino-acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of (or all of) a protein molecule.
Example:
Proteins are made up of one or more polypeptide molecules.
Peptide Bond

Definition:
A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule.
Example:
A polypeptide bond usually occurs between amino acids.
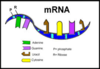
Protein Synthesis

Definition:
The process by which individual cells construct proteins.
Example:
Protein synthesis is the process by which individual cells construct proteins.