Mitosis, Meiosis, & Cell Cycle Flashcards
Cell Cycle

Definition:
The series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication that produces two daughter cells.
Example:
The cell cycle creates new cells.
Checkpoints

Definition:
Insures that the cell is functioning properly.
Example:
Checkpoints prevent cells that are not functioning properly to continue.
Cancer

Definition:
The uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body.
Example:
Cancer is a very deadly disease.
Tumor

Definition:
An abnormal growth of body tissue.
Example:
Once a tumor is big enough, it can start to show.
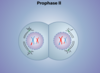
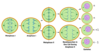
Mitosis

Definition:
A type of cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus.
Example:
Mitosis is part of the cell cycle.
Identical

Definition:
Being exactly alike.
Example:
Identical daughter cells are produced at the end of mitosis.
Asexual

Definition:
Not involving the fusion of gametes.
Example:
Most cells reproduce asexually.
DNA

Definition:
A molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
Example:
All living organisms need DNA.
Chromatin

Definition:
The material of which the chromosomes of organisms other than bacteria are composed.
Example:
Chromatin consists of protein, RNA, and DNA.
Chromosome

Definition:
A threadlike structure of nucleic acids and protein found in the nucleus of most living cells, carrying genetic information in the form of genes.
Example:
Every human has 46 chromosomes.
Gene

Definition:
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
Example:
Genes are what causes us to look like our parents.
Centromere

Definition:
The point on a chromosome by which it is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division.
Example:
Centromeres are in the middle of a chromosome.
Kinetochore

Defininition:
The point inside a centromere by which a cell is attached to a spindle fiber during cell division.
Example:
Kinetochores are inside centromeres.
Sister Chromatid

Definition:
Pieces of identical DNA that are crucial in the process of cell replication and division.
Example:
Sister chromatids are joined by centromeres.
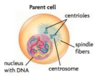
Parent Cell
Definition:
A cell that divides to produce two or more daughter cells.
Example:
At the beginning of mitosis, there is one parent cell.
Daughter Cells

Definition:
Either of the two cells formed when a cell undergoes cell division by mitosis.
Example:
Each daughter cell is genetically identical to the parent cell.
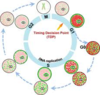
Interphase

Definition:
The stage in the development of a cell following mitosis or meriosis, during which the nucleus is not dividing.
Example:
Interphase is also considered to be the ‘living’ phase of the cell.
G1 Phase

Definition:
The first growth period of the cell cycle, during interphase, in which the cell grows and cytoplasmic organelles are replicated.
Example:
G1 phase is particularly important in the cell cycle because it determines whether a cell commit to division or to leaving the cell cycle.
G0 Phase

Definition:
A period in the cell cycle in which cells exist in a guiescent state.
Example:
Heart muscle cells and neurons will never enter the G1 Phase, but other G0 cells may.
S Phase

Definition:
The period of the cell cycle prior to mitosis, during which the chromosomes are replicated.
Example:
It is likely that during sleep, most cells go through the S Phase.
G2 Phase
Definition:
A period of rapid cell growth and protein synthesis during which the cell readies itself for mitosis.
Example:
G2 phase ends with the onset of prophase, the first phase of mitosis.
Somatic Cells
Definition:
One of the cells that take part in the formation of the body, becoming differentiated into the various tissues.
Example:
Normally mutations that occur in somatic cells affect only that cell and its descendants which are ultimately dispensable.
Centriole

Definition:
Either of a pair of cylinder-shaped bodies found in the centrosome of most eukaryotic organisms other than plants.
Example:
During cell division, the centrioles move apart to help form the spindle, which then distributes the chomosomes in the dividing cell.
Centrosome

Definition:
A specialized region of the cytoplasm that is located next to the nucleus of a cell and contains the centioles.
Example:
The centrosome is copied only once per cell cycle so that each daughter cell inherits one centrosome, containing two structures called centrioles.
Spindle Fiber
Definition:
One of a network of achromatic filaments that extend inward from the poles of a dividing cell, forming a spindle-shaped figure.
Example:
The spindle apparatus is composed of hundreds of proteins.