E-4 Buffers and Titrations Flashcards
Is the following solution a buffer?
HCl in H2O
not a buffer - this is a strong acid and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
NaOH in H2O
not a buffer - this is a strong base and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
HCl and NaOH in H2O
not a buffer - this is a strong acid and a strong base - this will neutralize to form NaCl and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
HNO2 in H2O
not a buffer - this is a weak acid and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
NaNO2 in H2O
Not a buffer - this is a weak base and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
HNO2 and NaNO2 in H2O
This is a buffer - nitrous acid is a weak acid and the nitrite ion is its conjugate base
Is the following solution a buffer?
HNO2 and NaF in H2O
Not a buffer - nitrous acid is a weak acid but the fluoride ion is not its conjugate base
Is the following solution a buffer?
NaHSO4 and H2O
Not a buffer - This is a weak acid and water
Is the following solution a buffer?
NaHSO4 and Na2SO4 in H2O
This is a buffer - the bisulfate ion is a weak acid the the sulfate ion is its conjugate base
Is the following solution a buffer?
NH3 in H2O
Not a buffer - this is a weak base in water
Is the following solution a buffer?
NH4Cl in H2O
Not a buffer - This is a weak acid in water
Is the following solution a buffer?
NH3 and NH4Cl in H2O
This is a buffer - ammonia is the weak base and the ammonium ion is its conjugate acid
Which solution has the higher buffer capacity?
Current pH = 4
- A 100 mL sample of buffer made from HNO2/NaNO2 when pKa of HNO2 is 3.40
- A 100 mL sample of buffer made from HClO/NaClO when pKa of HClO is 7.5
Solution 1 - pKa of the acid is closest to the pH of the solution which will make the ratio of weak acid to conjugate base closer to 1:1
Which solution has the higher buffer capacity?
- A 100 mL sample of buffer made from from equal amounts of 1.0 M HNO2 and 1.0 M NaNO2
- A 100 mL sample of buffer made from from equal amounts of 0.10 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2
Solution 1 - The higher total concentration has the best buffer capacity
Which solution has the higher buffer capacity?
- A buffer made from from 50mL of 1.0 M HNO2 and 50 mL of 1.0 M NaNO2
- A buffer made from from 20 mL of 0.10 M HNO2 and 80 mL of 1.0 M NaNO2
Solution 1 - the buffer whose ration of weak acid to base is closer to 1:1 will have the higher buffer capacity
Which curve represents a weak acid being titrated with a strong base?

This one

Which curve represents a strong acid being titrated with a strong base?

This one

Which curve represents a strong base being titrated with a strong acid?

This one

Which curve represents a weak base being titrated with a strong acid?
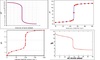
This one

Which point represents the equivalence point?

E
Which point represents the 1/2 equivalence point?

C
At this point a buffer exists where there is more weak acid than conjugate base.

B
At this point a buffer exists where there is less weak acid than conjugate base

D
At this point a buffer exists where the amount of weak acid is the same as the amount of conjugate base

C
At this point a the weak acid has been neutralized and the amount of conjugate base determines the pH.

E
At this point the weak acid has been neutralized and the amount of excess strong base determines the pH?

F
At this (these) point(s) the [H3O+] is greater than the [OH-].

A, B, C, and D - the pH is less than 7
At this (these) point(s) the [H3O+] is less than the [OH-]

E and F - the pH is greater than 7
At this point no strong base has been added and the amount of weak acid determines the pH.

A
Which of the following represents the equivalence point?

E
Which of the following represents the 1/2 equivalence point?

C
The weak base has been nuetralized and the excess strong acid determines the pH.

F
At this point the no strong acid has been added and the amount of weak base determines the pH.

A
The weak base has been neutralized and the amount of conjugate acid determines the pH.

E
At this point a buffer exists where the concentration of the weak base and the conjugate acid are the same.

C
At this point a buffer exists where the concentration of the weak base is greater than concentration of the conjugate acid.

B
At this point a buffer exists where the concentration of the weak base is less than concentration of the conjugate acid.

D
The [H3O+] > [OH-].

E and F - the pH is less than 7
The [H3O+] < [OH-].

A, B, C, and D - the pH is greater than 7


