Dyslipidemia and Cardiac PT Encounters Flashcards
A patient has chest pain and is not in severe repirtory distress or shock.
- The patient has sharp pleuritic pain that radiates to the shoulders and the back.
- The patient reports that they learn forward to relieve the pain.
What is your top Ddx?
Pericarditis

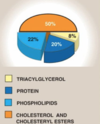
What lipoprotein is this?


Describe the general mechanism for Familial hypercholesterolemia

What are the Lipid effects of statins?

- What is Lymphangitis?
- What is seen on the skin?
- What can result from it?

What are the First drugs of choice to reduce blood-lipid levels? In what order to you give them?
- Statins
-
Least potent first then go down the line
- Simvastatin is least potent so you start them there.
- Pravastatin is MOST potent.
What is the Primary vs. Secondary Endpoint for cholesterol clinical trials
- Primary
- Better Cardiovascular Outcomes
- Secondary
- Lower LDL levels
What are the pros and cons of PCSK9 inhibitors?
Longterm effects are also unknown

- Concerning the 4 main healthy lifestyle changes that people can make to change their lipid profile for the better:
- What are they?
- Which one does not decrease LDL?

A patient has chest pain and is not in severe repirtory distress or shock.
- The patient has atypical angina pain, along with a low risk of coronary artery disase.
What is your top Ddx?
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Digestive Pain
- MSK Pain
- Psychogenic Pain
What is Mönckeberg medial sclerosis?

For Thoracic aorta dissection
- What are the essentials for dx?
- How do you dx? How do you classify it?
- What tests do you run?
- What are the associated symptoms?
- How do you manage it?
- include drugs
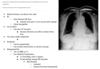
Describe how size relates to AAA rupture risk

What are the pathological outcomes of varicose veins?


D
Complete each step


Relate pulmonary embolism and DVT

What are the Bile-Acid Sequestrants (BAS)?

What is the channel that Ezetimibe actually blocks?

Describe the multiplicative effects of RFs for Atherosclerosis

What are the two common/concerning tyoes of cardiac related dyspenia?
- Dyspenia Types
-
Orthopenia
- shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair.
- Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
- Attacks of severe shortness of breath and coughing that generally occur at night. It usually awakens the person from sleep, and may be quite frightening.
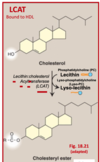
What enzyme is described?


- The response-to-injury hypothesis views atherosclerosis as a chronic inflammatory response of the arterial wall to endothelial injury. According to this model, atherosclerosis results from what process? (Describe the EC injury causes, the role of lipoproteins, platelets, monocytes, SMCs, and macrophages)

Label these