Duffy Lecture 5 Flashcards
Distribution of blood flow in the circulatory system
Great vessels associated with the heart

What are the branches of the ascending aorta
Coronary arteries
Brachiocephalic trunk - right subclavian and right common carotid
Structure of arterial wall

Branches of descending aorta
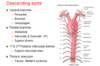
What’s emerging at T8
IVC
Right phrenic nerve
What’s emerging at T10
Oseophagus
Vagi
What’s emerging at T12
Aorta
Thoracic duct
Azygos vein (venous drainage of chest wall)
Where does the abdominal aorta enter abdomen
Where does it end
Behind median arcuate ligament
Ends at L4 (bifurcation)
4 unpaired branches of the abdominal aorta
- T12 coeliac trunk
- L1 superior mesenteric
- L3 inferior mesenteric
- L4 median sacral
4 paired branches of the abdominal aorta
- T12 inferior phrenic
- L1 middle adrenal
- L2 renal
- L2 gonadal
Femoral triangle
Femoral artery becomes superficial and deep femoral

Angiogram of femoral artery

Blood supply of the head and neck
Carotid divides at the Adam’s apple (C4)
Internal and external carotid
Internal goes into cranial cavity - supplies brain and some of cerebellum
External is outside - supplies muscles of face, head and neck
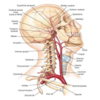
Branches of the external carotid
Some Look Forward Others Are Posterior
- Superior thyroid
- lingual
- Facial
- Occipital
- Ascending pharyngeal
- Posterior auricular
- Maxillary - terminal
- Superficial temporal - terminal
Carotid branches 1

Carotid branches 2

Carotid branches 3

What does the internal carotid a. give rise to
Anterior and middle cerebral arteries
What does the subclavian a. give rise to in the brain
Posterior cerebral artery
What is a stroke
Rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain
Can be due to ischaemia caused by blockage (thrombosis, arterial embolism) or a haemorrhage
Anterior cerebral stroke
Contralateral hemiplegia and anaesthesia
Middle cerebral stroke
Contralateral hemiplegia and anaesthesia and/or aphasia
Posterior cerebral stroke
Contralateral hemianopia
Vertebrobasilar stroke
Focal brainstem syndrome
What is associated with higher risk of stroke
Atrial fibrillation
- We want all walls contraction towards AV valve
- AF - walls contract differently and clot forms
- To stop it we need blood flow
- Clot in atrial appendage moves from atria to ventricle and then to carotid - causing stroke because the least path of resistance is the common carotid
What does the jugular vein drain
What does the SVC drain
Head and neck
Upper limbs and head and neck

Major veins of the head, neck and brain



