[DSA Week 1] Atypical Chest Pain, Dysphagia, Odynophagia (McGowan) Flashcards
Define:
Dysphagia
Odynophagia
Dysphagia = Difficulty swallowing
Odynophagia = Painful swallowing
What is atypical chest pain?
Chest pain that is not agina
(30% of chest pain pts have an esophageal source)
Can a history and physical distinguish GI from CV cause?
NO!!!
History and physical can NOT distinguish GI from CV cause of chest pain
When a pt. presents with chest pain, what must you exclude FIRST?
Must exclude Cardiac or Life-threatening causes first
Eg: MI, Aortic dissection, Pulmonary embolus/Pneumothorax
What is the difference b/w iatrogenic and spontaneous esophageal perforation?
Iatrogenic = Related to trauma (NG tube placement or endoscopy)
Spontaneous = Forceful retching/vomiting, hx of alcohol use, Boerhaave’s
What is the special kind of contrast used with a CT Chest w/ contrast?
Gastrografin
(water-soluble)
How can you identify subcutaneous (SubQ) emphysema on CXR?
Observe the air pockets outside of the mediastinum

Etiology of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
Where do they occur most commonly?
Duodenal bulb (duodenal ulcer, DU)
Stomach (gastric ulcer, GU)
What are typical physical exam findings for a pt. with PUD?
Description of epigastric pain as: “Gnawing, dull, aching or hunger-like”
Signs of Gastrointestinal bleeding
What are signs of gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB)?
“Coffee ground” emesis
Hematemesis
Melena
Hematochezia
What must you do if you detect H.Pylori?
MUST STOP PPI for 14 days before fecal and breath tests due to risk of false negative
Define:
Nutcracker esophagus
Hypertensive peristalsis
Swallowing contractions are too powerful
Greater amplitude and duration but normal coordinated contraction
Define:
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Multiple spastic contractions of the circular muscle in the esophagus
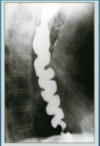
What are hallmark characteristics of diffuse esophageal spasm?
“Corkscrew esophagus”
“Rosary bead esophagus”

What is the difference b/w nutcracker esophagus and diffuse esophageal spasm in their LES function?
Nutcracker = relaxes normally, but has elevated pressure at baseline
Diffuse esophageal spasm = LES function is normal
What are the major shared symptoms of both nutcracker esophagus and diffuse esophageal spasm?
Dysphagia to solids and liquids
Atypical chest pain
What is the major complication associated with GERD that is a precursor to adenocarcinoma?
Barrett’s esophagus
What are the alarm symptoms associated with GERD?
Unexplained weight loss
Persistent vomiting
Palpable mass
Hematemesis
Melena
Anemia
Occult bleeding
If you find any GERD alarm symptoms associated with your patient, what do you do next?
Perform a esophagogastroducodenoscopy (EGD) to examine the lining of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum
What are examples of lifestyle modifications w/ GERD?
- Decrease ETOH and caffeine
- Small low fat meals
- Bed at incline
- Assess psychosocial situation
- PPI
What is a sliding hiatal hernia?
Stomach enters the mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm

What is a paraesophageal hernia?
Herniation of the stomach PLUS the cardia into the mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm

What is a red flag presentation that your patient has an inability to swallow?
Hypersalivation, drooling, froathing, foaming at the mouth
What is globus pharyngeus?
Sensation of a lump lodged in the throat
Swallowing is unaffected










