Drugs to Treat Skin Cancers Flashcards
(36 cards)
Most skin cancers are cured if treated early, but not if they metastasize. Where does skin cancer commonly metastasize to?
Skin cancer typically metastasizes to:
• Intestines
• Lungs
• Brain
What drugs are used in the treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma? (name 4)
- Aminolevulinic Acid
- Porfimer
- Sonidegib
- Vismodegib
What drugs are used in the treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
- Aminolevulinic Acid
- Afatinib
- Cetuximab
What is the problem with Hedgehog Signaling that leads to cancer?
• what cancers does this most often lead to?
Dysregulation in Hedgehog signaling may lead to basal cell carcinomas, medulloblastomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas.
What is the biochemistry behind why Hedgehog Signaling leads to Cancer?
• Where do we have to block this pathway if we want to inhibit it?
Upregulation of Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic) and VEGF (angiogenesis) are two important causes of cancer
If we want to inhibit this pathway then we must block AT or BELOW the level of the SMO transmembrane protein because the SMO transmembrane protein can stimulate the pathway independent of ligand binding.

Would blocking PTCH 1 be an effective way to go about blocking the Hedgehog pathway?
NOOO, this receptor is before the SMO receptor

What general statements can be made about the toxicity of Targeted Drugs? (2 generalizations)
• what can we do to help prevent this?
- Targeted drugs ironically affect every organ system in the body
- Cumulative Toxicity is a common event
Surveillance and early management is key to preventing symptoms
What is Actinic Keratosis?
• Where is it most commonly seen?
• what are the chances that it will develop into cancer if left untreated?
• What kind of cancer?
Actinic Keratosis is a scaly, crusty growth caused by UV damage. These pop up in heavily sun exposed areas of the body. If left untreated less than 10% develop into Squamous Scale Carcinoma.
What targeted Drugs are used in the treatment of Actinic Keratosis?
Diclofenac
Imiquimod
Ingenol Mebutate
Aminolevulinic Acid
Methylaminolevulinic Acid
What are the symptoms of Vascular Leak syndrome?
• what melanoma fighting drug causes this?
VLS can result in hypotension, pulmonary edema, end-organ damage (LIVER and RENAL failure)
Aldesleukin can have this side effect
What is the role of CTLA-4 in the immune system?
• what drugs bind this?
For T-cell activation/recognition to occur MHC class I/II and CD 80/86 on APCs must bind TCR and CD28 respectively. Like CD28, CTLA-4 also binds CD 80/86 but it prevents T-cell activation.

• Ipilumumab - binds and prevents CTLA-4 from inhibiting immune response - increases immune surveillance
What is the role of PDL1 in the immune system?
• what drugs bind this?
PDL1 is a ligand on cells that can bind to PD1 on Tcells to decrease immune surveillance
* Nivolumab and Pembolizumab bind this

When is CTLA-4 most highly expressed?
CTLA-4 is expressed most strongly in strong immune responses, this helps tone down the body’s immune response to an antigen.
**Note: Niave Tcells do not express CTLA-4, instead it is sequestered in vesicles and is release AFTER TCR stimulation. The amount expressed on the surface is in proportion to the strenght of TCR-MHC interaction
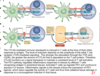
When is PD-1 most highly expressed and what is its role?
PD-1 is most highly expressed in inflammation. It’s expressed by our own cells in peripheral tissues to keep our immune cells from attacking us
***when our cells sense IFN-gamma they know to upregulate PD1 expression
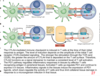
What transduction inhibitors work to inhibit BRAF?

What transduction inhibitors work to inhibit MEK1/2?

What drugs require genotyping before you administer them?
BRAF V600E drugs: Dabrafenib, Vemurafenib
Aminolevulinic Acid
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Aminolevulinic Acid
MOA
Applied topically and acts as a prodrug for protoporphyrin IX. Light excitation of this drug in the presence of O2 leads to a cytotoxic reaction
INDICATION
Basal Cell Carcinoma AND Squamous Cell Carcinoma AND Actinic Keratosis
SIDE EFFECTS – not mentioned
CONTRAINDICATIONS – not mentioned
GENOTYPING – not mentioned
Porfimer
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Porfimer
MOA
Applied topically. It get retained by tumor cells. Light excitation then produces FREE RADICALS in the cell.
INDICATION
Basal Cell Carcinoma
SIDE EFFECTS – not mentioned
CONTRAINDICATIONS – not mentioned
GENOTYPING – not mentioned
Vismodegib
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Sonidegib/Vismodegib
Administratoin
Oral
MOA
Inhibition of SMO in the sonic hedgehog pathway
INDICATION
Basal Cell Carcinoma
SIDE EFFECTS
Extensive CYP metabolism
VERY COMMON – alopecia, GI toxicity, inc. in Creatinine, Endocrine dysfunction
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PREGNANCY – females AND MALES (toxic semen) need protection during and 20 mo.(F) or 8 mo.(M) after therapy
Renal dysfunction – RFTs need to be routine
GENOTYPING – not mentioned
Sonidegib
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Sonidegib/Vismodegib
Administratoin
Oral
MOA
Inhibition of SMO in the sonic hedgehog pathway
INDICATION
Basal Cell Carcinoma
SIDE EFFECTS
Extensive CYP metabolism
VERY COMMON – alopecia, GI toxicity, inc. in Creatinine, Endocrine dysfunction
CONTRAINDICATIONS
PREGNANCY – females AND MALES (toxic semen) need protection during and 20 mo.(F) or 8 mo.(M) after therapy
Renal dysfunction – RFTs need to be routine
GENOTYPING – not mentioned
Afatinib
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Afatinib
Administration – Oral
MOA
Irreversible TKI of EGFR (ErbB1) and HER2 (ErbB2) resulting in reduced ErbB signaling and proliferation
INDICATION
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
SIDE EFFECTS
Numerous. CYP metabolism => Hepatic Dysfunction
Renal Dysfunction
SEVERE RASH
CONTRAINDICATIONS – not mentioned
GENOTYPING – not mentioned
Cetuximab
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Cetuximab
Administration – IV or SC
MOA
EGFR monoclonal antibody blocking phosphorylation and activation of receptor kinases (like RAS, RAF, MEK/ERK).
INDICATION
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
SIDE EFFECTS
• Numerous. EGFR TKIs are known to produce DERMATOLOGIC TOXICITY (Epithelial GFR) leading to dry skin, rash, pruritis
• GI toxicity
• CV toxicity (rare)
CONTRAINDICATIONS– not mentioned
GENOTYPING– not mentioned
Iminquimod
Administration
MOA
INDICATION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
GENOTYPING
Iminquimod
Administration - Topical
MOA
Small molecule that induces tumor-directed immune response via Toll-like receptors leading to increased cytokines and Th1 immune response
INDICATION
Actinic Keratosis, Genital Warts
SIDE EFFECTS
Topical so localized to the skin and include: erythema, prurtis, peeling, burning at application site
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Compromises Condom and Diaphragm integrity when used to treat genital warts
Avoid sun exposure on Treated areas
GENOTYPING – not mentioned


