Dermatologic Viral Based Diseases Flashcards
What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of Pox Virus family?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of Varicella zoster?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of Chicken pox?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of HHV-6?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of HHV-7?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of HHV-8?

What antivirals are indicated in the treatment of HHV-8 infection?

What is the MOA of Acyclovir and Valacyclovir?
• Toxicity?
MOA: acyclovir and valacyclovir drugs prevent DNA chain elongation because they act as deoxyguanosine analogues lack the 3’ OH group needed to tack on the next nucleoside. Exonucleases are then unable to remove the Drug.
Toxicity: Neurotoxicity including Seizures
What is the MOA of Ganciclovir and Valganciclovir?
MOA: ganciclovir and Valgancyclovir HAS a 3’ OH group therefore DNA pols can continue to make viral DNA but chain elongation is slowed with this drug
Toxicity: Pancytopenia (or one or the other), TERATOGEN
What is the MOA of Cidofovir?
MOA: Cidofovir prevents DNA chain elongation by acting as a competitive inhibitor of deoxycytosine.
Toxicity: Nephrotoxic => Probenacid is coadministered to reduce this effect
What is the MOA of Foscarnet?
MOA: Foscarnet binds to DNA pols at the phosphate binding site rather than the nucleoside binding site to prevent pyrophosphate cleavage that is needed to install more nucleotides.
Toxicity: Electrolyte imbalance from chelation of Ca2+ ions
What are the only two drugs that do not require viral kinases to be activated?
Cidofovir and Foscarnet
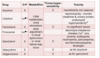
Which of the antivirals do you need to dose adjust for in the event of renal insufficiency?
ALL b/c they are all eliminated via renal elimination
You have a patient that develops and allergy to Gancilcovir. What are your other antiviral options for this patient at this point?
Most of these drugs cross react so only Foscarnet and Cidofovir will be useful

