Drugs acting on the neuromuscular junction PNS (somatic) Flashcards
Which of the following are other pharmacological effects from using depolarizing neuromuscular blockers? (choose all that apply)
- Hyperkalemia due to K+ release from skeletal muscles
- Increased intraoccular pressure due to contraction of ocular muscles
- Hypercalcemia from the buildup of Ca+ in the ER
- Transient bradycardia, increased susceptibility of the heart to the actions of digitalis preparations
- Nicotinic ACh receptors at autonomic ganglia (less sensitive than at the neuromuscular junction)
- Hyperkalemia due to K+ release from skeletal muscles
- Increased intraoccular pressure due to contraction of ocular muscles
- NOPE NO NOPE NOPE WRONG NOPE NO NO NOPE
- Transient bradycardia, increased susceptibility of the heart to the actions of digitalis preparations
- Nicotinic ACh receptors at autonomic ganglia (less sensitive than at the neuromuscular junction)
Summative or synergistic drug interactions of competitive NM blockers with which of the following can be seen? (choose all that apply)
- Other muscle relaxants
- Local anesthetics
- Inhalation anesthetics
- Aminoglycosides
- Magnesium
- Calcium
- Potassium
- Other muscle relaxants
- Local anesthetics
- Inhalation anesthetics
- Aminoglycosides
- Magnesium
Is this describing phase 1 or phase 2 block of Succinylcholine, a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker?: Activation of nicotinic ACh receptors (like acetylcholine), induces prolonged depolarization of the motor end-plate, no complete repolarization prevents stimulation by ACh (depolarization block), and muscle fasciculation.
- Phase 1
- Phase 2 block
- Phase 1
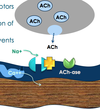
Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers are hydrolyzed by plasma _________________________-ase in the ____________ and _____________.
Pseudocholinesterase (PChE) in the plasma and liver (it is slower than acetylcholinesterase [AChE])
This nondepolarizing/competitive neuromuscular blocker is mostly excreted and unchanged by the kidneys (~40% in humans), has some liver metabolism, and has little excretion in bile.
- Pancuronium
- Atracurium
- Vecuronium
- Mivacurium
- Rocuronium
- Pancuronium
(good for patients with decreased liver function)
This nondepolarizing/competitive neuromuscular blocker has spontaneous degradation in the plasma (outside of the liver and kidney).
- Pancuronium
- Atracurium
- Vecuronium
- Mivacurium
- Rocuronium
- Atracurium
(better for patients with liver and renal disfunction)
T or F. Neuromuscular blockers were developed from dart poisons.
True
T or F. Neuromusclar blockers are peripheral muscle relaxants that paralyze all skeletal muscles, except the muscles associated with respiration.
False! They paralyze ALL skeletal muscles, even the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm. Assisted ventilation is required!
The motor neurons of the somatic nervous system release _______________, which work on _______________ receptors.
- ACh, adrenergic
- ACh, muscarinic
- ACh, nicotinic
- NE, adrenergic
- ACh, nicotinic

T or F. Depolarizing and competitive neuromuscular blockers work on the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction.
True (nicotinic receptors)

T or F. Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers can cause flaccid muscle paralysis, hypotension, and bradycardia.
False! Bradycardia is caused by depolarizing NMB.
Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers can cause flaccid muscle paralysis, mild hypotension from ganglionic blockade (nicotinic receptors at autonomic ganglia are less sensitive than those at NMJ), and transient TACHYCARDIA (not in anesthetized animals).
*REMEMBER, NO MUSCLE FASCICULATION (TWITCHING) unlike Succynlcholine (depolarizing NMB), which can be a good thing*
T or F. Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers cause transient, asynchronous muscle twitching (30 seconds) followed by flaccid paralysis and can be very painful (increase in creatine kinase).
True
T or F. Patients on neuromuscular blockers are unconcious and are under full analgesia.
False, consciousness is not affected. The patient is still fully conscious, under NO ANALGESIA, and is just paralyzed.
T or F. Muscle relaxants such as Hemicholinium, Vesamicol, Botulinum toxin, high Mg++, and low Ca++, work on the postsynaptic neuromuscular junction to interfere with synthesis, transport/storage and/or release of acetylcholine.
False; muscle relaxants (Hemicholinium, Vesamicol, Botulinum toxin, high Mg++, and low Ca++) work on the PREsynaptic neuromuscular junction to interfere with synthesis, transport/storage and/or release of acetylcholine.

(not really used in VetMed)
MATCHING! Which drugs are depolarizing (noncompetitive) or competitive neuromuscular blockers?
A. Depolarizing (noncompetitive)
B. Competitive
- Rocuronium
- Mivacurium
- Vecuronium
- Atracurium
- Succinylcholine
- Pancuronium
A. Depolarizing (noncompetitive) - 5. Succinylcholine (ONLY ONE)
B. Competitive - 1. Rocuronium, 2. Mivacurium, 3. Vecuronium, 4. Atracurium, 6. Pancuronium
(Competitive = Vec Pan Roc At Mi, imagine “Vik is competitive so she’s running with a pan and rock at me”)
Neuromuscular blockers are ALL quaternary compounds. What is characteristic about them?
- Always charged
- Poor oral absorption
- Usually given IV
- Do not cross BBB
T or F. Succinylcholine is used as an adjunct to euthanasia.
False! How awful would it be to be fully conscious during this.
These two nondepolarizing/competitive neuromuscular blockers are primarily metabolized by the liver and excreted in bile and urine.
- Pancuronium
- Atracurium
- Vecuronium
- Mivacurium
- Rocuronium
- Vecuronium and 5. Rocuronium
(better for patients with renal disfunction)
T or F. Depolarizing neuromusclar blockers are given orally.
False, IV and rarely IM
(they have very poor oral absorption, aso want tight control)
Put the affected areas in order (first to last) from depolarizing neuromuscular blockers.
- Swallowing
- Respiratory
- Abdominal muscles
- Limbs
- Tail/face
- Tail/face > 4. limbs > 1. swallowing / 3. abdomial muscles > 2. respiratory (most important one!)
All of the following are adverse effects of Succinylcholine, except:
- Bradycardia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Muscle fiber damage, increased CK, muscle pain post-op
- Apnea
- Increased arrhythmogenicity to catecholamines
- Malignant hyperthermia in susceptible animals
- Hypercalcemia
T or F. Succinylcholine is used to facilitate endotracheal intubation.
True
CAUTION! Which of the following are not cautions for using nondepolarizing blockers?
- Caution with liver or kidney disease (consider Atracurium in those cases)
- Bronchospasm
- Bronchodilation
- Salivation
- Bronchial secretion
- May cause histamine release in dogs/cats (much less so than with tubocurare)
- Bronchodilation
This nondepolarizing/competitive neuromuscular blocker is easily terminated by chelation with cyclodextrins, such as sugammadex and has a very fast onset of action.
- Pancuronium
- Atracurium
- Vecuronium
- Mivacurium
- Rocuronium
-
Rocuronium (not used in Vet Med as much, but it is up and coming)
* Sugammadex* is a reversal agent that takes and removes the drug itself = tight control
T or F. Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers (Succynlcholine) have a very short duration of action at around 2-3 minutes.
True, EXCEPT longer in ruminants and dogs (20 minutes); acts in one circulation time of 30-60 seconds
T or F. Nondepolarizing/competitive blockers are given IV (rarely IM), just like depolarizing neuromuscular blockers.
True
Curare is a ______________ neuromuscular blocker.
- Depolarizing
- Competitive
- Competitve; just like Pancuronium, Atracurium, Vecuronium, Mivacurium, Rocuronium
[Vik (Vec) is competitive so she came At Mi with a Pan and Roc]
Is this describing phase 1 or phase 2 block of Succinylcholine, a depolarizing neuromuscular blocker: Nicotinic ACh receptors do not respond properly to ACh and flaccid paralysis is prolonged. We want to avoid this.
- Phase 1
- Phase 2 block
- Phase 2 block

Which competitive (nondepolarizing) neuromuscular blockers should not be used?
- Pancuronium (Pavulon)
- Mivacurium
- Fazadinium
- Rocuronium (Esmeron)
- Pipercuronium
- Tubocurarine
- Atracurium (Tracrium)
- Vecuronium (Nocuron)
- Gallamine
- Alcuronium
Whichever one is not “Vec came At Mi with a Pan and Roc”
- Fazadinium
- Pipercuronium
- Tubocurarine
- Gallamine
- Alcuronium
T or F. Succinylcholine is used as a muscle relaxant during surgery.
True, but rarely.
CAUTION! All of the following are cautions for Succinylcholine (depolarizing NMB), except:
- Cholinesterase inhibitors, aminoglycosides, other muscle relaxants, digitalis, magnesium
- Keep at room temperature so no precipitates form
- Glaucoma
- Cardiac disease
- Keep refrigerated or on ice to avoid spontaneous hydrolysis of the drug
- Keep at room temperature so no precipitates form
What happens if Succinylcholine was given, but you want to reverse the effects?
There is no specific reversal, so supportive care (ventilation) is needed until the drug is metabolized. Anything that alters metabolism will prolong the effect (exposure to irreversible cholinesterase inhibiters, such as organophosphates, can slow hydrolysis of depolarizing neuromuscular blockers for up to 30 days!)
What happens when competitive NM blockers are given, but you want to reverse its effects?
- Respiratory support (like depolarizing blockers)
-
Cholinesterase inhibitors to anatagonize the effect of nondepolarizing NMBs (neostigmine, edrophonium have reverse drug interactions)
- Cholinesterase inhibitors > less break down of ACh > more ACh in the NMJ > more muscle function
- Atropine/Glycopyrrolate to block muscarinic effects (NOT IN HORSES = COLIC)
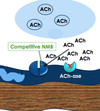
Competitive neuromuscular blockers work by competitive _______________ with acetylcholine for _______________ receptors at the motor end-plates.
- Antagonism, nicotinic
- Antagonism, muscarinic
- Agonism, nicotinic
- Agonism, muscarinic
- Antagonism, nicotinic

(they BLOCK nicotinic receptors and don’t allow ACh to bind, so no initial muscle fasciculation (twitch) stage, just muscle paralysis; kind of like a medical myasthenia gravis)


