Diverticular disease Flashcards
What is a diverticulum?
An outpouching of the gut wall, usually at sites of entry of perforating arteries

What does diverticulosis mean?
Presence of diverticula
What does diverticulitis mean?
Inflammation of a diverticulum - most often occuring when faeces obstruct the neck of the diverticulum causing stagnation and allowing bacteria to multiply and produce inflammation. This can then lead to bowel perforation (peridiverticulitis), abscess formation, fistulae into adjacent organs, or even generalized peritonitis.
Where do diverticula most commonly occur?
Along the lines where the penetrating colonic arteries thransverse the colonic wall between the taenia coli
What is meant by the term diverticular colitis?
Refers to cresenteric inflammation on the folds in areas of diverticulosis
What is thought to be the cause of diverticulosis?
Unknown
How do diverticula form?
There is thickening of the muscle layer and, because of high intraluminal pressures, pouches of mucosa extrude through the muscular wall through weakened areas near blood vessels to form diverticula.
An alternative explanation is cholinergic denervation with increasing age which leads to hypersensitivity and increased uncoordinated muscular contraction.
What are symptoms of diverticulosis?
Majority asymptomatic, but if painful diverticular disease:
- Altered bowel habit
- Left sided colic relieved by defecation
- Nausea
- Flatulance
What are symptoms of diverticulitis?
Features of diverticulosis, plus:
- Low grade Pyrexia
- Tender bowels
- Localised/generalised peritoneal abdominal pain - acute abdomen
- Constipation/N+V - obstruction
- Urinary frequency/urgency
Similar to features of acute appendicitis, but on the left hand side rather than the right
What would you find on examination of someone with diverticulitis?
Left side fo the abdomen
- Tenderness
- Guarding
- Rigidity
- Palpable tender mass - LIF
Where in the colon does diverticular disease most commonly affect?
Sigmoid colon
Why can severe pain and constipation occur in severe diverticulosis?
Due to luminal narrowing of the sigmoid colon
How is diverticulosis most commonly picked up?
Incidentaly on imaging
Why can some of those with diverticular disease present with blood in the stool?
Tends to be large volume, dark red clotted rectal blood - due to rupture of peridiverticular submucosal blood vessel
How would you investigate if you suspected diverticulosis?
- Elective barium enema (seen below)
- Could consider colonoscopy - poor investigation for assessing number
- Consider CT scan

How would you investigate someone for suspected acute diverticulitis?
- Bloods - FBC, CRP
- Abdo US
- CT colonography

What might you see on CT in someone with acute diverticulitis?
- Colonic wall thickening
- Diverticula
- Pericolic collections and abscesses
- Streaky increased density extending into the immediate pericolic fat
- Thickening of the pelvic fascial planes

What would you not perform in an acute diverticulitis attack?
Colonoscopy/sigmoidoscopy
What are complications of diverticular disease?
- Pericolic/paracolic abscess
- Peritonitis
- Diverticular fistula
- Stricture formation
- Haemorrhage

Why can peritonitis occur as a complication of diverticular disease?
Perforation of a pericolic/paracolic abscess leads to purulent peritonitis. Direct perforation of acute diverticular segment leads to faeculent peritonitis
Why do pericolic/paracolic abscesses form in acute diverticulitis?
May progress to persistent pericolic infection with thickening of surrounding tissues and the formation of a mass. If this suppurates, a pericolic abscess forms
Enlargement and extension of this leads into the paracolic area -> paracolic abscess
What are clinical features of a paracolic/pericolic abscess?
Symptoms/signs of acute diverticulitis, plus:
- Swinging fever
- Fluctuating tachycardia
- Unresolved abdominal pain
- Tender LIF mass
How do diverticular fistulae form?
Acute infection with paracolic spesis may drain by perforation into adjacent structures. This is typically the posterior vaginal vault in women or bladder in either sex
Where do diverticular fistulae commonly form?
- Posterior vaginal vault
- Colovesical fistula
What are features of a colovesical fistula?
- Recurrent UTIs
- Pneumonuria
- Debris in the urine
What are features of a colovaginal fistula?
Faeculent PV discharge
Why can you get stricture formation as a complication of diverticular disease?
Recurrent inflammation leads to fibrosis and narrowing of the collon
What are features of stricture formation in diverticular disease?
- Colicky abdo pain
- Distention
- Bloating
- Constipation
How would you manage diverticular disease?
- High fibre diet
- Antispasmodics if required - e.g. mebeverine
How would you manage acute diverticulitis?
- Mild - home with bowel rest and Abx
-
Severe - admit
- IV fluids
- Abx
- Monitor for complications
What antibiotics would you use to treat diverticulitis?
3-7 days - AMG protocol
- IV Gentamicin + Metranidazole +/- Amoxicillin (in pen allergic - co-trimoxazole)
- Switch to oral Metranidazole + doxycycline/Co-trimoxazole

How would you manage perforation in diverticular disease?
- Antibiotics
- Segmental resection with Hartmann’s procedure
- Consider anastamosis when peritonitis has resolved
How would you manage major haemorrhage from diverticular disease?
- Angiographic embolisation
- Colonic resection
How would you manage someone with a stricture caused by diverticular disease?
Elective resection or balloon dilatation
When is resection indicated in diverticular disease?
- Acute inflammation failing to respond to medical management
- Undrainable paracolic sepsis
- Free perforation
- Stenosis
- Fistulae
- Recurrent bleeding
How would you manage paracolic/pericolic abscess?
Antibiotics +/- ultrasound/CT-guided drainage me be needed
What is a Meckel’s Diverticulum?
Meckel’s Diverticulum is a true congenital diverticulum - a slight bulge in the small intestine present at birth and a vestigial remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct (also called the vitelline duct or yolk stalk).
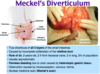
What is a Meckel’s Diverticulum a remnant of?
Omphalomesenteric duct (also called the vitelline duct or yolk stalk)
What would be your first line imaging investigation for diverticulitis?
Abdominal CT with contrast
If a patient had diarrhoea in diverticular disease/diverticulitis, what test would you want to perform to rule out other causes?
Stool culture
Why should you avoid colonoscopy in someone with acute diverticulitis?
Risk of perforation
When and why would you perform colonoscopy diverticulitis?
6 weeks after, and to look for extent and risk of malignancy
What are differential diagnoses to consider for the presentation of diverticular disease?
- CRohn’s/UC
- Colorectal cancer
- Intestinal ischaemia
- Acute appendicitis
- Ileus


