Diagnostic Cardiac Imaging Flashcards
In what situations would you use arterial catheterization?
Is this considered left or right heart cath?
Let heart Cath
- Evaluate arterial and LV pressures
- Evaluate left ventricle, aortic valve & mitral valve
- Evaluate coronary arteries (lumenogram)
- LV dysfunction
- CAD
In what situations would you use venous catheterization?
Is this considered left or right heart cath?
Right heart catheterization
- Evaluate venous and right heart pressure
- evaluate cardiac output (thermodilution)
- Evaluate possible shunts
- LV dysfunction
- Valve disease
- myopericardial disease
- intracardiac shunts
What spaces could you inject contrast during a cardiac cath?
What is the name of this procedure?
- Contrast imaging - L Cath
- left ventricle (left ventriculogram)
- coronary arteries
- coronary sinus
- pulmonary arteries (from R cath as well)
- injection of contrast for imaging in the “angiogram/lumenogram”
What are indications for cardiac catherterization?
- When the objective demonstration of the patient’s coronary anatomy, left ventricular funciton, wall motion or valvular structure and function will have a direct bearing on the patient’s diagnosis, prognosis or therapy
- Symptoms of myocardial dysfunction
- Symptoms of myocardial ischemia
- Evaluation and treatment of cardiac electrical disease
What are the absolute & relative contraindications to cardiac catheterization?
- Absolute
- NONE (patient refusal)
- Relative
- uncontroled ventricular irritability
- uncorrected hypokalemia or digitalis toxicity
- uncorrected hypertension (change bleeding from puncture site is higher)
- intercurrent febrile illness
- decompensated heart failure
- anticoagulated state: PT > 18 secs, INR > 2.0
- Severe allergy to contrast agent
- severe renal insufficiency and/or anuria
What are the most common complications to cardiac catheterization?
- Treatable
- arrhythmias
- hematomas
- hemorrhage
- allergic urticaria (rash) to anaphylaxis
- MI
- Neurologic
Patients with what demographics are at a increased mortality risk during cardiac catheterization?
- infants (<1 month) and elderly (>85 years)
- NYHA class IV 10x > class I-II (heart failure)
- Left main CAD 10x > 1-2 vessel CAD
- Severe aortic stenosis with CAD
- LV ejection fraction <30% 10x > EF > 50%
- renal insufficiency, diabetes, advanced cerebrovascular disease or peripheral vascular disease, severe pulmonary disease
What is radiocontrast nephropathy?
What patients are at a higher risk for developing radiocontrast nephropathy?
How is risk calculated?
form of kidney damage in which there has been recent exposure to medical imaging contrast material without another clear cause for the acute kidney injury
- Patient with underlying kidney disease
- Diabetics
- dehydrated patient
- active CHF
Risk is calcualted as a Mehran Score
What steps are taken to prevent radiocontrast nephropathy?
-
Aggressive hydration with saline – KEY
- preoperative, intraoperative & postoperative
- ensure patient is euvolemic at start of procedure
- No NSAID prior to procedure
- Limiting contrast volume is important as it is with ALL patients regardless of renal funciton
What are the most prevalant complications in cardiac catheterization?
vascular
What are the major steps to initiating a cardiac catheterization?
- obtain consent – either informed or emergency
- premedication
- aspirin
- Versed (benzodiazapene) IV – sleep
- off warfarin (INR <1.5)
- if STEMI then all the stemi srugs as well
- Steralize insertion site
- Obtain vasculr access and place guide sheath to pass catheters
Describe right cardiac catheterization techniques?
- Baloon or multipurpose catheter
- baloon on tip to help pass catheter
- SAO2 and pressure measurements in VC, RA, RV, PA adn PCWP
- deflated balloon passed first into right vetricle, float through the pulmonary valve & to the pulmonary artery & continue advancing that until it is in a distal pulmonary artery
- blow up baloon & measure pressure distal to the balloon, which is the Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP)
- essentially occluding the small pulmonary artery, so you are only getting retrograde flow, so it is essentially equivalent to the left atrial pressure
- Cardiac Output by Fick (Q L/m=O2 consumption mL/Min/A-V O2 difference mL/L) or thermodilution
- Contrast imaging
- Pulmonary Vascular Resistance
- by getting cardiac output & central venous pressure
- Temporary intravenous pacemaker
- technically a right heart catheter, but we do not take pressure measurements
- usually femoral or internal jugular approach
What procedure is the gold standard for diagnosing they type of hypertension a patient has?
right cardiac catheter
2Describe the left cardiac catheterization techniques
- LV and aorta pressure measurements
- SAO2 in aorta
- if significant valve problems or looking to shunt it
- Systemic vascular resistance
- Lt ventriculogram
- Coronary arteriography
- 2D visualization
- can adjust the plane of imaging to get more views
- Aortography
The Green, Red & Gray lines indicate waht cardiac cath pressures?

- Grey
- Radial: distal/peripheral line
- notch = dicrotic notch (closure of aortic valve), indicates good flow, may not see it if too distal
- notice pressure does not drop down as far
- highes peak = systolic & lowest point = diastolic
- Radial: distal/peripheral line
- Green:
- Left ventricular pressure
- highest peak = systolic pressure & lowest point = diastolic pressure
- Red
- PCW

Identify the indicated coronary arteries
The catheter enters what artery to perform a coronary arteriography?

From aorta, enters left coronary artery & inject dye
may or may not have to switch catheters to insert dye into the right coronary artery

The is the orientation of what type of angiogram?
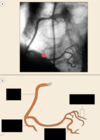

The is the orientation of what type of angiogram?


What procedure is shown in the provided images?
What do each of the images depict?
catheter was advanced into the left ventricle & inject a pretty good amount of contrast to try to fill up the lumen the best as possible (patient will feel a flushing sensation)
can guestimate stroke volume & ejection fraction

Identify the movement problems that can be identified with a ventriculogram

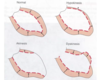
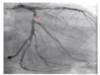
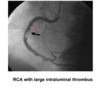
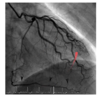
What lesions are identified in the provided images?


What coronary artery diseases are shown in the provided images?

Thrombus: defected flow, not actually stenotic, but not 100% thrombus

what procedure is shown in the provided image?

intravenous ultrasound
center of the picture is the probe & can pass into the coronary arteries
can look at calcium burden (hyperechoic white stuff)
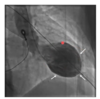
the provided image is a before & after image of what procedure?
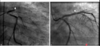
total proximal LAD obstruction before and after PTCA with stenting