Development of the Nervous system Flashcards
Describe the formation of the neural tube:
- Proliferation of the ectoderm in the dorsal midline of the embryonic disc called the neural plate
- Thickens and starts to fold up at the sides
- Two folds fuse dorsally to form a tube
Describe the formation of the neural crests:
A little bunch of cells at the tip of the neural fold separate from the neural tube and lie alongside it
What is present at the end of Early development of the nervous system?
At the end of this process you have a neural tube lying in the midline dorsally in the embryo and on either side of this you have two strips of neural crest tissue

What are the Neural Tube and Neural Crest sources of?
Neural Tube = All CNS cells
Neural Crest = All PNS cells
What is the neuroepithelium?
The wall of the neural tube
What three types of cells come from the neuroepithelium?
Neuroblasts
Glioblasts
Ependymal Cells
What do Neuroblasts differentiate into?
All neurones with cell bodies in the CNS
What do Glioblasts differentiate into?
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes
(Neuroglia)
What are Ependymal cells?
Cells lining the ventricles and central canal
They remain close to the inner membrane of the neural tube and they spread out and form a lining around the developing ventricular system
What do Neural crest cells differentiate into?
- Sensory neurones of the dorsal root ganglia
- Postganglionic autonomic neurons
- Schwann cells
- Non-neuronal derivatives e.g. melanocytes
Where do Motor Neurones originate from?
Neuroepithelium as they are neuroblasts because they have almost all their axons in the PNS but their cell bodies are in the CNS
Describe the organisation of the Neuroepithelium tissue:
Outer membrane
Neural Tube cells (Pseudostratified)
Dividing cells at the bottom
Inner membrane
Describe the process of Neuroepithelium differentiation:
- Cells withdraw from outer membrane towards inner membrane and undergo mitosis
- One daughter cell stays attached to the inner membrane and continues dividing
- The other migrates away from the inner membrane then develops into a neuroblast
- They develop processes (one will become the axon) which are further directed away from the inner membrane
What is the structure of the Neuroepithelium after initial differentiation has occurred?
Three layers:
White Matter - Axons
Grey Matter - Cell Bodies
Ependymal Layer - Dividing cells

What is the difference between the differentiation of Neuroblasts and Glioblasts?
Glioblasts show similar pattern of differentiation but can also migrate into White matter as well
Glioblasts do not develop axons (but do develop processes)
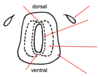
Label the layers of the Neural Tube in Cross-section

What controls the differentiation of cells?
Signalling molecules secreted by surrounding tissue which interact with receptors on the surface of neuroblasts
•Control migration & axonal growth by attraction and repulsion depending on concentration gradient & timing
What happens to the Neural Canal as the spinal cord further develops?
It becomes even smaller relative to the thickenss of the wall
What happens to the grey matter as the spinal cord develops further?
It splits into two types:
Alar Plate - Dorsal
Basal Plate - Ventral
What happens in the Alar Plate?
The interneurones are becoming specialised to receive sensory information and this information comes from the developing dorsal root ganglia that have developed from the neural crest
What happens in the Basal Plate of the developing spinal cord?
Development of Motor Neurones - The Basal Plate has a motor function - the axons leave the spinal cord to go towards the muscles
What happens to the neural crest cells in the developing spinal cord?
They form sensory neurones in the dorsal root ganglion
Label this Mature Spinal Cord:


What becomes of the neural canal in the mature spinal cord?
It becomes the central canal carrying CSF