Brainstem and Cranial Nerves Flashcards
(43 cards)
Define Brainstem:
◦That part of the CNS, exclusive of the cerebellum, that lies between the cerebrum and the spinal cord
What are the three major divisions of the Brainstem?
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Where is the Pons located in relation to other structures in the brain?
It is the floor of the 4th Ventricle
What and Where is the Pineal Gland?
Located posteriorly in the midline above the Midbrain
It releases Melatonin and is important in regulating the Circadian Rhythm
What does Colliculus mean and where are they located?
Low Lying Hills
4 - Superior and Inferior - Lying on the roof of the midbrain posteriorly
What do the Colliculi do?
Superior Colliculus - important in the coordination of eye and head movements at the same time (think about watching tennis)
Inferior Colliculus - auditory reflexes - if there is a loud bang you tend to look in the direction of the bang immediately
How many cranial nerves emerge from the back of the brainstem?
Which ones?
ONE
Trochlear Nerve (IV)
What can be seen to define the Medulla in the dorsal aspect?
The Dorsal Columns
What is located anteriorly to the brainstem?
(two structures)
Optic Chiasm
Infundibulum (Pituitary stalk)
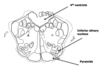
Identify the cranial nerves on this diagram:
9 are here (some are combined)


What cranial nerves emerge from the Pons?
Five to Eight
Trigeminal (V)
Abducens (VI)
Facial (VII)
Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
What Cranial nerves emerge from the lateral medulla?
Nine, Ten and Eleven
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Vagus (X)
Accessory (XI)
Where does the Hypoglossal nerve (XII) originate?
From the Medulla
More medially than IX, X & XI
Show where fibres cross-over on this diagram:
What is this structure called?

At the join between the pyramids at the base of the medulla
Pyramidal Decussation
What are the four functional subtypes of the Cranial nerves?
General Somatic Afferent (GSA)
General Visceral Afferent (GVA)
General Somatic Efferent (GSE)
General Visceral Efferent (GVE)
What do GSA Cranial nerves transmit?
Sensation from skin and mucous membranes
What do GVA Cranial nerves transmit?
Sensation from GI tract, heart, vessels and lungs
What do GSE Cranial nerves transmit?
Motor signals for Eye muscle and tongue movements
What do GVE Cranial nerves transmit?
Preganglionic Parasympathetic signals
What are the three Special Functional Classifications of the Cranial nerves?
What do they do?
Special Somatic Afferent:
Vision, hearing and equilibrium (only the cranial nerves)
Special Visceral Afferent:
Smell (CN I) and Taste (comes from THREE cranial nerves that all go back to the nucleus solitarius)
Special Visceral Efferent:
Muscles involved in chewing, facial expression, swallowing, vocal sounds and turning the head
Where are the different General functional subtypes of nerves located in the embryonic spinal cord?

Where does information enter and leave the spinal cord?
Enters: Dorsal Root
Leaves: Ventral Root
How are the four subtypes of cranial nerves arranged in the Embryonic Rhombencephalon?
How is this different from the Spinal cord?
Why is this?
Motor = Medial Sensory = Lateral
(From medial to lateral)
GSE GVE GVA GSA
- Not Dorsal and Ventral because in the Brainstem the alar plate opens up and there is a ventricle there
Have a guess at the Nuclei of Cranial Nerves in this diagram