Dec18 Flashcards
1. to pass FRCR 2a neuro 2. To master neuro (55 cards)
List the differences bwn ependymoma and medulloblastoma (6)
Medulloblastoma:
- Roof of 4th vent (midline- vermis)
- Hypredense
- 10% Ca
- Cysts are rare
- CSF seeding
- diffusion restriction
Syndromes asso with medulloblastoma
- Cowden syndrome
- Gardner syndrome
- Turcot syndrome
- Gorlin syndrome
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Coffin-Siris syndrome
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
What regions are affected in Pick’s dementia?
- frontotemporal lobar degeneration
- Caudate head volumes are also often reduced
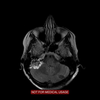
What is the diadnosis?

This is an exaple of frontotemporal lobar degeneration seen in Pick disease.
Striking asymmetry both of involvement of frontal vs temporal lobes, and involvement of left and right hemispheres.
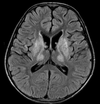
What is the diagnosis?
Describe the findings?
Syndrome associated with this tumour

This is a mass arising from the vermis and roof of the 4th ventricle causing hydrocephalus. Rarely cystic. 10% ca++
CSF seeding- imaging of whole spine needed.
Restricts diffusion
- Cowden syndrome
- Gardner syndrome
- Turcot syndrome
- Gorlin syndrome
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Coffin-Siris syndrome
- Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
List the atrophied regions affected in PSP (3)

atrophy of midbrain, GP and frontal lobes.
Midbrain : pons reduced
Hummingbird sign and mickey mouse sign
Traids of Wernicke encephalopathy:
- acute confusion
- ataxia
- ophthalmoplegia
MRI findings in Wernicke
T2/FLAIR: symmetrically increased signal intensity in the:
- mamillary bodies
- dorsomedial thalami
- tectal plate
- periaqueductal area
- around the third ventricle
CT is usually normal.
Deterioration of conscious level and agitation. Patient had gastric surgery 2 months ago for peptic ulcer.
What is the diagnosis?

Abnormal signal bilateral and symmetrical involving the medial and posterior aspect of both thalami displaying bright signal in DWI, T2 and FLAIR.
Diagnosis: Wernicke Encephalopathy.
Case Discussion
Previous gastric sugery or Bariatric sugeries are predisposing factors to various deficiency syndromes. Thiamine deficiency causes acute encephalopathy usually affects the medial thalamus, tectal plate and periacqueductal grey matter.
What is the diagnosis?
Well circumscribed cysts, with an imperceptible wall, displacing adjacent structures, and following the CSF pattern (hypodense on CT and hyperintense on T2 with low on FLAIR). They can also have a remodelling effect on the adjacent bone.
Arachnoid cyst

Flair axial
Best differentiating method bwn arachnoid and epidermoid
DWI- Epidermoid restricts diffusion.
Be aware of the white epidermoid.
What is the diagnosis?
Progressive unintentional choreoathetoid movements, subcortical type dementia, behavioural changes, and psychosis in a 40 year old man.
On imaging, it is classically characterised by atrophy of the caudate nucleus with concomitant enlargement of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles (<strong>BOX LIKE configuration</strong>). High SI in caudat and putamen on T2.
PET scan shows reduced FDG uptake in basal ganglia and frontal cortex.
Huntington disease
Sign? Which condition?
the red nucleus and substantia nigra are surrounded by high T2 signal.
Panda sign
seen in Wilson disease
Causes of cerebellar atrophy: (9)
- Phenytoin
- Alcohol
- Ataxic telangiectasia
- Paraneoplastc syndrome from bronchial ca
- Marijuanna
- Steroid
- Radiation
- Multisystem atrophy
- Gluten insensitivity
Eye of tiger sign
Hallervorden spatz syndrome
NAA is also reduced
Imaging protocols for mesial temporal sclerosis
How would you plan your scan to reduce volume averaging?

Coronal volume and coronal high resolution T2WI/FLAIR are best to diagnose MTS.
Thin section angled coronal sequences at right angles to the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus are required, to minimise volume averaging.
Paediatric causes of ivory vertebrae (4)
- lymphoma: commonest cause, usually Hodgkin lymphoma
- osteosarcoma
- osteoblastoma
- blastic metastatic disease
- neuroblastoma
- medulloblastoma
- Ewing sarcoma (rare)
Adult causes of ivory vertebrae (7)

- osteoblastic metastases
- prostate cancer
- breast cancer
- lymphoma
- tuberculous spondylitis
- haemangioma
- chordoma
- Paget disease of bone
- SAPHO syndrome
This line is used in evaluation of basilar invagination:
Mc Gregor line
From hard palat to the base of the occiput. The peg should lie 5mm below this level/

Causes of basilar invagination: (4)
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
- FD
- Developmental such as Klippel Feil
Causes of drop mets in paeds (5)
- PNETs
- Medulloblastoma
- Ependymoma
- Germinoma
- Pineobastoma
Causes of drop mets in adults:
ie irregularity and nodularity along the nerve root
- Melanoma
- Breast
Most common locations for chordoma (2)
- sacrum
- clivus
Can mets to liver, lung, LN
Name some features of Cleidocranial dysostosis

Delayed ossification of midline structures.
- absent or hypoplastic lateral clavicles.
- supernumeray ribs
- Hemivertebrae
- Widened pubic symphysis
- absent/short radius
- wormian bones
- widened anterior fontanelle
- large mandible
- Small paranasal sinuses.
- Bell shaped chest