Critical care medicine Flashcards
1
Q
Reasons for admission
A
- Respiratory support
- Invasive monitoring e.g. pressure, cardiac function
- Renal support
- Decreased conscious level
2
Q
What are we trying to achieve
A
- The maintenance of oxygen perfusion to vital organs
- Removing or treating the causes of the problem
- Treating other problems that are produced
- allowing the body to recover
3
Q
How do we do this
A
- Airways/Breathing
- Circulation
- Sedation and analgesia
- Sepsis
4
Q
Cardiac output
A
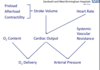
5
Q
How do we measure cardiac function
A
- Indirect measures
- BP: Central venous, arterial
- For the left side of the heart
- LiDCO
- PiCCO
- Oesophageal Doppler
- Swan Ganz/ Pulmonary artery flotation catheters
6
Q
Circulatory failure
A
- Inadequate pre-load
- Maldistribution
- Anaphylaxis
- Septic shock
- Myocardial failure
- Systolic +/- diastolic dysfunction
7
Q
Inadequate pre-load
A
- Measurements
- Central Venous Pressure (CVP)
- Treatment: Give fluid
- Choice
- Crystalloid
- Colloid
8
Q
Maldistribution
A
- Measurement- low systemic vascular resistance (SVR)
- Also known as ‘afterload’ (for the left side of the heart)
- Treatment: Give a vasoconstrictor (Vasopressor)
9
Q
Receptor types
A
- Alpha 1 + 2- vasoconstriction of blood vessels
- Beta 1- Inotropic
- Beta 2
- Vasodilation of blood vessels
- Bronchodilator
10
Q
Noradrenaline
A
- Acts on a1 and b1 (i.e. primarily heart of vascular smooth muscle)
- Results in increased SVR and increased heart rate
- Adverse effects
- Mainly related to decreased organ perfusion leading to ischaemia (e.g. splanchnic bed, digits)
11
Q
Dopeamine (DA)
A
- Low dose- D1-dopaminergic receptors in vascular tissue esp. Renal, mesenteric and coronary beds- leads to vasodilation
- High dose- b1-receptors (i.e. heart)
- Also causes the release of noradrenaline which results in vasoconstriction
- Adverse effects
- Tachycardia
- Arrhythmias
- Myocardial ischaemia
12
Q
Vasopressin
A
- Acts on V1 receptors
- Causes profound vasoconstriction
13
Q
Myocardial failure
A
- Measurement: low cardiac output
- Treatment: Give an inotrope
- Choice
14
Q
Inotrope
A
- Ino = fibre
- trepein - to turn or influence
- Literally- to turn or affect muscle fibres
- Can be positive or negative
15
Q
Dobutamine
A
- B1- agonist (-&+) isomers
- a1- agonist0 (-) isomer
- a1- antagonist - (+) isomer
- B2- agonist
- Net result- Increase contractility, with some effect on rate
- Adverse effects
- Tachycardia & arrhythmias
- Can lead to increased myocardial oxygen consumpton, and hence ischaemia
- Can get tolerance
16
Q
Adrenaline
A
- b1- agonist
- a1-agonist
- b2- agonist
- Net result: Increased contractility and HR
- Adverse effects
- Myocardial ischaemia
- Tachycardia
- Arrhythmias
- Sudden death
17
Q
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
A
- Act to increase cAMP levels in cardiac and smooth muscle
- Results in
- Myocardial diastolic relaxation
- Increased intracellular calcium levels
- Dilation of vasculature
- Relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle
- Dysrhythmias
18
Q
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors
A
- Enoximone and milrinone available
- Not user friendly
- Long half-life
- IV compatibility problems
- In oral form, associated with increased mortality
19
Q
Vasodilators
A
- Aim to decrease afterload, enabling the heart to beat more efficiently
- Examples
- GTN or ISDN
- Furosemide
20
Q
Levosimendan
A
- Calcium sensitiser
- Increases contractility of cardiac myofibrils
- Unlicensed in this country
- Recent study showed no benefit
21
Q
Analgesia
A
- Opioids
- Infusion
- Care with renal/hepatic impairment
- Paracetamol
22
Q
Sedation
A
- BZ
- By infusion
- Care with renal/hepatic impairment
- Propofol
- Intravenous anaesthetic agent
- Antipsychotic agents
- For delirium
23
Q
Paralysing agents
A
- Limited use
- Difficulty in ventilation
- Neuro-injury
- Must have adequate analgesia and sedation on board
- Non-depolarising agents used
24
Q
Clonidine
A
- Adrenergic agonist
- Activates central inhibitory a2-receptors
- Depressive effect on CNS function
- Opioid sparring
- Useful in withdrawal states
- Dexmedetomidine
25
Continuous veno-veno haemofiltration
* Removal of solutes by convection
* Independent of MW
* Modern membrane pore sizes 10,000-30,000 daltons
* active process
26
Haemofiltration

27
Sepsis
* 2016 definition- Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by the dysregulated host response to infection
* Sepsis is one of the 'golden hour' emergencies
28
Consider sepsis if
* RR \>22/min
* Altered mental state
* Systolic BP \<100 mmHg
29
Septic shock
* Sepsis +
* Vasopressor therapy needed to maintain MAP \>65mmHg
* Lactate \>2mmol/L
* Despite adequate fluid resuscitation
30
Sepsis- why is it important
* Estimated 37,000 deaths/year in the UK
* Further 65,000 survive (but many with long term sequelae)
* NCEPOD 2015 report 'just say sepsis'
* Kills more than breast, bowel and prostate cancer combined
31
NICE guideline- NG51
* Sepsis: Recognition, diagnosis and early mangement
* Think: Could this be sepsis for any patient presenting with an infection
32
What happens after critical care
* Rehabilitation
* Long term follow up
* Support groups
* ICU steps
33
Post-discharge/rehabilitation
* Physical state worse than pre-admission
* May take months/years to improve
* Scarring
* Mental state
* Delirium
* Hallucinations
* Anxiety
34


