Cranial Nerves 1-6 Flashcards
What kind of fiber is the olfactory nerve?
Special visceral afferent (SVA). Sensory
Where does the olfactory nerve start?
The olfactory nerve originates in the olfactory bulb and passes through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone to enter the olfactory region of the nasal cavity.
What is anosmia?
Anosmia is the loss of smell usually caused by fracture of the ethmoid bone or foster-Kennedy syndrome. - This may also cause a runny nose from cerebrospinal fluid leakage.
What is foster-Kennedy syndrome?
Foster-Kennedy syndrome is associated with tumors of the frontal lobe.
What other than damage to the ethmoid bone or foster-Kennedy-syndrome can cause anosmia?
Most of the time, anosmia and hyposmia are temporary and are caused by inflammation in the nasal cavity which prevents chemicals from reaching the olfactory epithelium
What kind of fiber is the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is SSA (sensory) and SVA (parasympathetic)
What is the function of the SVA - parasympathetic fibers of the optic nerve?
The optic nerve is, in addition to our visual nerve, also the afferent limb of the pupillary light reflex. It is sensory and carries information to the brain about whether to constrict or dilate the pupil.
What is the optic chiasm?
The optic chiasm is the place of crossing of nasal fibers.
What are the nasal fibers of the optic nerve and their function?
The nasal fibers of the optic nerve cross contralaterally in the optic chiasm and provide the temporal vision.

What are the temporal fibers of the optic nerve and what is their function?
The temporal fibers are ipsilateral and provides nasal vision
Where do the optic fibers terminate?
The optic fibers travel from the retina to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe
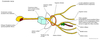
What is the pathway of the oculomotor nerve?
The oculomotor nerve originates in the midbrain, passes along the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus, passes through the superior orbital fissure and goes inside the tendinous ring before it supplies the muscles and the ciliary ganglion.
What two fibers does the oculomotor nerve consist of?
The oculomotor nerve consists of GSE (motor) fibers and GVE (parasympathetic fibers)
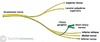
What muscles does the superior branch of the oculomotor nerve supply?
The superior branch of the oculomotor nerve supplies the:
- Levator palpebrae superioris.
- The superior rectus.

What muscles does the inferior branch of the oculomotor nerve supply?
The inferior branch of the oculomotor nerve supplies the:
- Inferior rectus
- Medial rectus
- Inferior oblique
What do the parasympathetic fibers of the oculomotor nerve supply?
The parasympathetic fibers of the oculomotor nerve are responsible for the efferent limb of the pupillary light reflex and supplies:
- The ciliary ganglion
- The pupillary muscles
- The ciliary muscles










