Contact dermatitis Flashcards
What percent of contact derm is irritant vs allergic?
- 80% irritant!! - 20% allergic
Most common cause of allergic contact derm (ACD) world-wide: - in the US:
- worldwide is nickel - USA is poison ivy
Which populations have increased risk of contact dermatitis?
- infants, elderly, and Atopic derm patients due to increased penetration of contactants
Pathogenesis of Irritant contact derm (ICD)
- direct damage of keratinocytes by irritant - does NOT require sensitization and pretty much everyone who comes into contact with these substances will have this reaction
Acids or bases are stronger irritants to the skin?
- Bases
Pathogenesis of allergic contact dermatitis:
- immune-mediated, delayed- type IV hypersensitivity reaction - requires initial sensitization to allergen - preexposure to allergen–> T cell mediated release of cytokines/chemotactic factors–>eczema within 48 hours
How often do you need an exposure to allergen to keep ACD reaction going?
- once every 3 weeks
What is a cross-sensitization in ACD?
- sensitization to one compound results in sensitization to a similar compound, even if you haven’t been exposed to the other compound
Symptoms of irritant CD
- burning may be more common than itch
most common sites involved in ICD?
- # 1 is hands - #2 is face
Pustular/acneiform ICD results from which irritants?
- metals!! or metal-like liquids - tars, greases

Airborne irritant CD resembles a photo allergic reaction, but involves_______ (parts of body)
- upper eyelids, philtrum, submental region
Pathogenesis of phytophotodermatitis?
- fucocoumarins + UVA light–>erythema +/- blistering within 24-72 hours—> followed by hyperpigmentation 1-2 weeks later
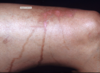
Berloque dermatitis presents clinically as_____ and is caused by _____
pigmentation of neck/trunk/arms from cologne application containing bergamot oil

Clinical presentation of allergic contact dermatitis:
- erythema/edema/papules/oozing/vesicles with sharp demarcation between uninvolved skin.
Subacte allergic contact dermatitis will have _____ present clinically which is not typically seen in acute.
- scale/crust!
- histopath will show acanthosis
Chronic ACD will present with:
- marked lichenification no vesicles, less well-defined than acute, and may spread beyond site of exposure
Distribution of contact dermatitis will depend on the exposure:
- Linear ACD commonly due to _____
- rhus (poison ivy/poison oak/poison sumac)
Contact derm on fingertips in florists most commonly due to ____
- allergic contact to Tulips
ACD resulting perioral/baboon syndrome is due to which allergens?
- flavorings, foods, cosmetics, shellac, meds, and sunscreens
Periocular/eyelid ACD is commonly due to which allergens?
Nail products (tosylamide > acrylates, formaldehyde, resin, glutaraldehyde, and benzalkonium chloride)
Cosmetics (false eyelashes, adhesives, mascara, rubber sponges for make-up, and eye-shadow)
Other allergens: gold (rings), other metals, volatile gases, fragrances/balsam of Peru, neomycin, surfactants, and preservatives
ACD on earlob most commonly caused by:
- Nickel
ACD on wrist is commonly caused by:
- Chromates in leather watches (check out my chrome watch)
Clothing dermatitis: spares the ____ and is accentuated _____
- skin folds (axillary vault)
- accentuated where clothing fits tightly (Waist)
Most common clothing allergens:
Fabric finishers (i.e., anti-wrinkle and stain repellant): formaldehyde and formaldehyde releasers
Dyes (disperse blue dyes 106 and 124)
Rubber (bleached underwear → bleaching causes release of carbamates)
Number 1 and 2 most common cosmetic ACD are:
- # 1= Fragrance!
- # 2= preservatives
Shoe dermatitis generally spares the ______
- toe webs and plantar surface
Causes of shoe ACD:
- Colophony in adhesives
- mercaptobenzothiazole in rubber
- Chromates
Which topical antimicrobials are the biggest culprits for ACD:
- Bacitracin and Neomycin (polymyxin B much less common)
- remember BNP for the triple antibiotic ointments, P is the last letter and least likely to cause ACD.
Airborne ACD usually caused by _____ with ____ being the number 1 chemical involved
- Plants cause airborne ACD most frequently
- Compositae is the compound most commonly involved
Most reactions to adhesives are ____ (ACD or ICD)
- ICD
Histopath of ICD:
- mild spongiosis, scattered necrotic keratinocytes (from direct toxic injury 2/2 irritant), and mild perivascular inflammation
Histology of ACD:
spongiotic dermatitis (may be acute/subacute/chronic, depending on stage), more prominent dermal inflammation
vs ICD: ↑spongiosis, ↑dermal inflammation w/ eosinophils, and lacks necrotic keratinocytes
- chronic will have more acanthosis and less spongiosis
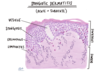
What test can you do to confirm Allergic contact derm?
- patch testing
Describe timeline of patch testing in clinical practice.
- day 1 place patches on skin free of dermatitis (monday)
- after 48 hours, remove patches and record reactions (wednesday)
- after another 1-3 days, make a second recording (friday)
Reactions on patch test that fade between the first and second reading are caused by____
- irritants
Reactions that continue or develop between first and second readings on patch test are due to ______
- allergen (as opposed to irritant, which would improve between the two readings)
Which substances can cause a delayed positive patch test?
- corticosteroids and gold! (as well as neomycin dodecyl gallate, palladium, p-phenylenediamine)
What materials contain chromates?
- dyes (green felt fabric on pool table), yellow-green pigment (tattoos/cosmetics), leather (shoe dermatitis), cement
- picture Dr. Grumpy pants in a pool bar, wearing a leather jacket, with a green-yellow tattoo walking barefoot on cement floor.
Cobalt is present in what products?
metal products, cosmetics, dyes (blue-green dyes, paint, tattoos), glass/pottery, cement, vitamin B12 injections (can lead to intractable hand dermatitis), and artificial joints
Mercury allergy is commonly seen in what situation?
- in mouth with dental amalgams causing oral lichenoid reaction.
Most common cause of persistently positive patch test reaction is caused by _____
- gold


