Consultation & Communication Flashcards
(23 cards)
Visualization of the impact of change on productivity. When change is introduced, there is typically a decrease in productivity and then a gradual return to or, ideally, a surpassing of previous levels of productivity.
J curve

Group decision-making tool in which the group defines the characteristics of a successful decision and then scores each alternative against those criteria.

Multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA)
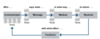
Name the 4 steps in the Consulting Model
Define Problem
Design & implement solution
Measure effectiveness
Sustain improvement

Group decision-making tool designed to analyze the forces favoring and opposing a particular change. A factor is weighted, and the factors on each side are summed and compared.

Force field analysis
Name the 3 steps of Lewin’s Model of Change Process
Unfreezing, moving, refreezing

3 approaches to implementing a change

Cascade. This approach relies on a top-down sequence with complete change at each level. Change at one level or unit high up in the organization eventually transforms the units and levels beneath it.
Progressive. In this model, the change originates at the top and is broadcast to the entire organization. Individuals slowly change with added information, and the change becomes uniform across business units.
Organic. This method relies on independent centers and multiple origins of the change within the organization. Points of origin can be at any level. Organic change radiates out unevenly but accelerates when top leadership supports local change and local leaders.
Create a sense of urgency.
Assemble a strong guiding team.
Provide a clear vision.
Over-communicate.
Empower action.
Ensure short-term successes.
Sustain progress and build on achievements.
Institutionalize.
8 steps from John Kotter’s Change Management

Communication technique to increase the engagement between communicators and their audiences. It involves two-way communication and attention to nonverbal signs that indicate interest and reactions to the message and speaker.
Active listening
Components of a message apart from its words. This could include physical gestures and posture and vocal tones, volume, and speed.
Nonverbals
Process of constructing a message so that an audience sees communicated facts in a certain way and is persuaded to take a certain action.
Framing

In communication, structuring a message to include opportunities for correction or clarification. This requires two-way communication.
Feedback loop
In communication, any factor that can disrupt the sending and receipt of a message. For example, physical factors such as loud environments, cultural factors such as a distinctive accent, or cognitive factors such as the use of unfamiliar jargon.
Noise
Communication used to change the way an audience sees or feels
Reframing
Being an impactful communicator:
How to create credibility and presence?

Communication Model
4 key audience analysis questions

Key planning questions in Communications

Evaluating communication

Three pilars of feedback

4 tools for strategic planning and group decision making

HR’s role in managing change

Managing change spectrum

Integrated view of change



