Circulatory System Flashcards
(25 cards)
Purpose of circulatory system and blood?
- Helps distribute important nutrients, hormones, and oxygen to cells that are too far away from where these important substances are obtained
Circulation Pathways: systemic vs. pulmonary
- Systemic – delivers blood to all cells and carries away waste
- Pulmonary – eliminates carbon dioxide and oxygenates blood
Evolution of system: differences between fish, amphibian, reptile and mammal
-
Fish hearts:
- Single circuit
- 2 chambers – atrium and ventricle
-
Amphibian hearts:
- Double circuit
- 3 chambers – 2 atria and one central ventricle
- No septum, so deoxygenated blood and oxygenated blood mix causing heart deficiency
-
Mammal hearts:
- Double circuit
- 4 chambers – 2 atria and 2 ventricles
Chambers of heart, structure of heart tissue
- The top two chambers of the heart are the left and right atria (singular: atrium)
- The bottom two are the left and right ventricles
- There is a wall of muscle in between the left and right chambers of the heart called the septum, preventing oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing (in mammal hearts only, not amphibian)
- Tissues:
- Epithelial tissue (inner and outer)
- Myocardium (middle layer)
- Pericardium (outer layer)
Pathway of blood flow through heart -path of deoxygenated and oxygenated blood
- Blood enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cava
- Then goes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle
- Then it moves into the right and left pulmonary arteries to the lungs
- Oxygenated blood is returned to the heart through the pulmonary vein
- Blood flows into the left atrium, then through the bicuspid valve into the left ventricle, then into the ascending aorta
- Blood is next distributed to the rest of the body
Cardiac cycle, systole/diastole
- Cardiac cycle – the sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats
- Systole is the phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood from the chambers into the arteries
- Diastole the phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood
- 1) Heart is relaxed (atrial and ventricular diastole (dub))
- 2) Atria contracts (atrial systole, ventricular diastole)
- 3) Ventricles contract (ventricular systole, atrial diastole (lub))

SA node (pacemaker), AV node, and role in regulation of heartbeat
- The SA node / sinoatrial node: it sends electrochemical signals to the atria to contract
- The AV node / atrioventricular node: it sends electrochemical signals to the ventricles to contract after delaying the signal from the SA node

Names of blood vessels connected to heart and heart valves
- Aorta
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary veins
- Inferior and superior venae cavae
What does an EKG (or ECG) measure?
- Measures the electrical activity of a heartbeat
- It lets people know if parts of the heart are too large, or overworked
Capillaries
- Any of the fine branching blood vessels that form a network between the arterioles and venules
- Made of endothelial cells only
Arteries
- Carry blood to the heart, and capillaries
- Thickest, most elastic walls because of high pressure
- Carry O2-rich blood except for pulmonary artery
- Smallest arteries are arterioles (Largest = aorta)
Vein
- Walls thinner, less elastic, very low blood pressure (near 0)
- Carry Carry O2-poor blood except for pulmonary vein
- Veins have valves to prevent backflow
- Smallest veins are venules
How are capillaries structured to allow for rapid diffusion of nutrients and waste between the circ system and cells/tissues of body?
- They are structured like a net and thin enough to allow chemical exchange, dispersing nutrients throughout the circulatory system
Blood pressure and velocity through different blood vessels
- The force blood exerts against the wall of a vessel
- Rises as we age
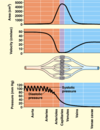
Measurement of blood pressure (sphygmomanometer use and function)
Effects of hypertension (and low blood pressure)
- A cuff is placed around someone’s arm, and systolic pressure is measured when blood in arteries is able to push through the arm in spurts with the cuff on
- When blood flows continuously through the artery, the diastolic pressure is taken
*
Atherosclerosis
- Plaques develop on the inner walls of arteries, narrowing the passageway (resulting in increased blood pressure)
- Thickening & hardening of arteries due to fatty deposits on artery wall, causing narrowing of arteries & thus diminished blood supply
Hypertension
- Blood vessels constantly constricted – diameter decreases, pressure increases
- High blood pressure, heart works harder and causes ruptures in arterial walls, causing plaque buildup
- Causes cardiovascular diseases
Angina pectoris
- Chest pain caused by reduced flow of blood in the heart due to coronary heart disease
Coronary thrombosis
- Blockage of blood flow to heart due to blood clot in an artery
- Can lead to myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction
- ‘Heart attack’, death of heart muscle tissue due to lack of oxygen supply
Stroke
- Death of brain tissue resulting from blockage of arteries/blood flow to the brain
Heart failure
- The heart cannot pump enough blood to supply the body with
Cardiovascular disease risk factors
-
Lifestyle/behavioral change:
- Regular exercise, monitor stress, added fruits & vegetables to diet
-
Limit saturated fat intake:
- Quit smoking, etc
-
Medication (blood pressure, cholesterol):
- Some medications decrease blood pressure and cholesterol
-
Angiography (for diagnosis):
- Used to see inside blood vessels inside the body
-
Cardiac bypass surgery:
- Restores normal blood flow to an obstructed coronary artery by creating a new passageway
-
Angioplasty:
- Inserting a tiny inflatable balloon to compress plaques
-
Stent placement:
- A small metal mesh tube that keeps arteries open.
Blood makeup and function (4)
-
Plasma
- Transports nutrients and proteins, suspends white and red blood cells.
-
WBC’s
- Help fight infections, (white blood cells)
-
RBC’s
- Deliver oxygen to cells and dispose of carbon dioxide (red blood cells).
-
Platelets
- Cell fragments in the blood that help blood clot after an injury.


