Chest, Shoulder, Pectoral Region Flashcards
Large, fan-shaped muscle covering most of the anterior thoracic wall
Pectoralis Major
Muscle that is useful as a landmark for axillary artery, inserts on coracoid process
Pectoralis Minor
Saw-toothed muscle that helps stabilize the scapula - boxer’s muscle -attaches to medial border of scapula on anterior surface, keeps scapula from ‘floating off ribcage’ - protracts (pulls forward) and rotates scapula
Serratus anterior
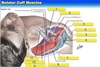
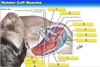
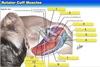
What are the 4 rotator cuff muscles?
S i t S -Supraspinatus - infraspinatus - teres minor - Subscapularis
What innervates the deltoid?
Axillary nerve
What innervates the infraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular nerve
What innervates the Pectoralis minor muscle?
Medial pectoral nerve
What innervates the Serratus anterior?
Long thoracic nerve
What innervates the subscapularis muscle?
Upper and lower subscapular nerves
What innervates the supraspinatus muscle?
Suprascapular nerve
What innervates the Teres minor muscle?
Axillary nerve
What is the function of the deltoid?
After the suprapsinatus muscle initiates abduction of the humerus the 1st 10-15 degrees, the deltoid abducts it to 90 degrees, even to the acromion and clavicle. The trapezius then completes abduction to 180 degrees
What is the most frequently torn rotator cuff muscle? what is it’s function
Supraspinatus muscle - initiates abduction of the humerus (first 10-15 degrees)
What muscles insert into the greater tubercle of the humerus?
Supraspinatus infraspinatus Teres minor
What nerves innervate the Pectoralis major?
Medial and lateral pectoral nerves
Which muscle inserts into the lesser tubercle of the humerus?
Subscapularis muscle
Which rotator cuff muscle is responsible for medial rotation of the humerus?
Subscapularis
Which rotator cuff muscles are responsible for lateral rotation of the humerus when they contract?
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, Teres minor
What are the 3 kinds of fascia?
pectoral axillary clavipectoral
What does pectoral fascia cover?
Pectoralis major muscle
What does axillary fascia cover?
continuation of the pectoral fascia, laterally (armpit area protects arteries, veins, nerves etc passing into upper extremities)
What does clavipectoral fascia cover?
deep to Pectoralis major, encloses subclavius muscle and Pectoralis minor
At what dermatomes are the clavicles located?
Border of C4-C5
At what dermatomes is the level of nipples?
T4
At what dermatomes is the level of umbilicus (navel)?
T10
Compare the 2 ends of the clavicle bone.
Sternal end: small, relatively round Acromial end: much larger, flatter

Supraglenoid tubercle

Greater tubercle (of humerus)

Lesser tubercle (of humerus)

Acromion
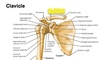
Coracoid Process

Superior Angle of Scapula