Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions Flashcards
1
Q
random variable
A
- a variable whose numeric value is determined by the outcome of a probability experiment
- usually denoted by capital letter (X, Y, Z)

2
Q
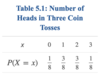
probability distribution
A
a table or formula that gives the probabilities for every value of the random variable X, where all of the probabilities are between 0 and 1, inclusive
0 ≤ P(X=x) ≤ 1
and the sum of all the probabilities is 1
∑ P(X = xi) = 1

3
Q
discrete random variable
A
may have either finitely many possible values or infinitely many possible values that are determined by a counting process
4
Q
discrete probability distribution
A
- probability distribution for a discrete random variable
- rounding rule for variance and standard deviation: round to one more decimal place than the largest number of decimal places given in the values of the random variable except when the type of data lends itself to a more natural rounding scheme (e.g. currency). When calculating the standard deviation, do not round the value of the variance before taking the square root.

5
Q
expected value
A
- the value that we expect the random variable to have on average
- the mean of the probability distribution: E(X) = μ
- rounding rule: round to one more decimal place than given in the data or to the natural rounding scheme (e.g. two decimal places for currency)

6
Q
bionomial distribution
A
- discrete probability function for problems with a fixed number of independent trials, where each trial has only two possible outcomes and one of these outcomes is counted
- round to four decimal places
- binompdf (n,p,x) for X = x
- binomcdf (n,p,x) for X ≤ x
- reduce x by 1 in formula to get X < x
- 1 - binomcdf (n,p,x) for X > x
- reduce x by 1 in formula to get X ≥ x

7
Q
properties of a binomial distribution
A

8
Q
A


