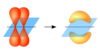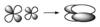Chapter 4 - Symmetry and Group Theory Flashcards
(30 cards)
symmetry elements
mirror planes, axes of rotation, inversion centers, etc
symmetry opration
the actual reflection/rotation/inversion operation
Identity operation
E, no change in molecule
Rotation operation
Cn, rotation through 360º/n
Reflection operation
σ, reflection through mirror plane
Inversion operation
i, each point moves through the center of the molecule to a position opposite the original position and as far from the central point as where it started
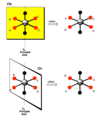
Rotation-reflection operation
Sn, aka improper rotation: rotation of 360º/n followed by reflection through a plane perpendicular to a axis of rotation
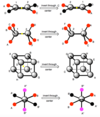
E
Identity operation, no change
Cn
Rotation operation, 360/nº each time
σ
Reflection operation through mirror plane
σh
Horizontal reflection operation when the plane is perpendicular to the principal axis of rotation
σv/σd
Vertical reflection operation when the plane contains the principal axis of rotation
σd: Dihedral passes through fewer atoms (dihedral to the angle of the bonds). Dihedral, same plane as v but related by half a rotation of the principle axis
σv: Vertical, parallel to/passing through the principal axis (primary rotation axis)
i
Inversion, each point moves through the center of the molecule to a position opposite the original position and as far from the central point as where it started
Sn
Rotation-reflection/improper-rotation operation, rotation of 360º/n followed by reflection through a plane perpendicular to a axis of rotation

Principal axis
The Cn axis with the largest value of n
Point group
a set of symmetry operations that best describes the molecule’s overall symmetry
Groups of low symmetry
C1 - no symmetry other than the identity operation
Cs - only one mirror plane
Ci - only an inversion center
Groups of high symmetry
C∞v - Linear molecule with an infinite number of rotations and an infinte number of reflection planes containing the rotation axis (e.g. H-Cl). Do not have a center of inversion.
D∞h - Linear molecule with an infinite number of rotations and an infinite number of reflection planes containing the rotation axis.
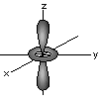
d orbital: z2
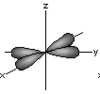
d orbital x2-y2
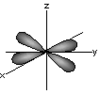
dxy
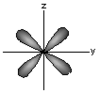
dyz
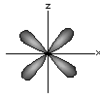
dxz
σ-bond
orbitals are symmetric to rotation about the line connecting the nuclei
no nodes that include the line between nuclei