Chapter 24 - Magnetic fields Flashcards
What is a magnetic field?
Force field surrounding a magnet or current-carrying wire which acts on any other magnet or current-carrying wire placed in a field
Where is a magnetic field of a bar magnet strongest?
At north-seeking or south-seeking poles
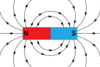
What is a line of force of a magnetic field?
Line along which a north pole would move in the field
When will a wire in a magnetic field experience a force?
When it carries current
What is the motor effect?
When a current carrying wire placed at non zero angle to the lines of force of an external magnetic field experiences a force due to the field.
Force is perpendicular to the wire and to the lines of force
How can the direction of the force on a current carrying wire be worked out?
Fleming’s left hand rule
What is the force on the current-carrying wire when the wire is parallel to the magnetic field
zero
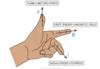
What does each finger represent in fleming’s left hand rule?
First finger = Field
seCond finger = Current
Thumb = Force
What is magnetic flux density, B, of the magnetic field?
Force per unit length per unit current on a current-carrying conductor at right angles to the magnetic field lines
unit: Nm-1A-1 or Tesla (T)
What is the equation for the force on a wire carrying a current in a uniform magnetic field, at 90º to the field lines?
F = BIL
where B = magnetic flux density
I = current
L = length of wire
For a straight wire at angle theta to the magnetic field lines, how do you calculate the force on the wire?
Due to component of the magnetic field perpendicular to the wire, Bsin(angle)
therefore F = BILsin(angle)
How can the magnnitude of a force on a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field be investigated?
Stiff wire frame is connected in series with a switch, an ammeter, a variable resistor, and a battery. When the switch is closed, the magnet exerts a force on the wire which can be measured from the change of the top pan balance reading.

How is a couple created on a rectangular coil that has n turns in a magnetic field?
Long sides of the coil are vertical and each wire down each long side experiences a force BIL where L = length of each long side, therefore each wire experiences F = (BIL)n in opposite directions at right angles to the field lines.
The pair of forces acting on the long sides form a couple as the forces are not directed along the same line.
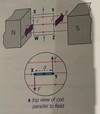
What is the equation for torque of the couple on a coil ?
Torque = Fd, where d = perpendicular distance between the line of action of the forces on each side. If the plane of the coil is at angle alpha to the field lines, then d = wcos(alpha) where w = width of coil
torque = Fwcos(alpha) = BLnwcos(alpha) = BIAncos(alpha) where A = lw
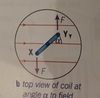
What is the torque when the coil is parallel to the field?
alpha = 0 so the torque = BIAn as cos(0) = 1
What happens to charged particles in a magnetic field?
experiences a force due to the magnetic field. Causes a beam of charged particles to be deflected
Why does a current-carrying wire in a magnetic field experience a force?
Electrons moving along the wire are pushed to one side by the force of the field
What is the difference between the direction of force on moving positive and negative charged particles when in a magnetic field?
Forces in opposite directions
Use fleming’s left hand rule for positive particles and right hand rule for negative particles
What is the equation for force on a particle of charge moving in a magnetic field, perpendicular to the field lines?
F=BQv
where v = speed
as: I = Q/t and L = vt, so F=B(Q/t)vt
What does it mean for a charged particle in a magnetic field, that the constant force is perpendicular to the velocity and field?
The particle travels in a circular path
How does the constant force being perpendicular to the velocity mena it follows a circular path?
Force changes velocity (direction) but stays perpendicular to the velocity, meaning the path is a complete circle with the force always acting towards the centre of the circle. Force causes a centripetal acceleration
What is the equation for the radius of a charged particle in circular motion acted on by a magnetic force?
BQv = mv2/r
r = mv/BQ
when does the radius of a charged object in circular motion decrease?
- If B is increased or if v is increased
- If particles with a larger specific charge Q/m are used
What is a cyclotron used for?
- Used in hospitals to produce high energy beams for radiation therapy
- Producing radioactive tracers


