Chapter 2 part 1 Flashcards
Horizontal divergence is expressed mathematically as

When thedivergence is positive, the air parcel
grows (i.e., its area increases)
If the divergence is negative, it is called
convergence, then the air parcel shrinks (i.e., area decreases).
The relationship between horizontal divergence and the change in a parcel’s area
(A) can be expressed as:
The above equation states that the fractional change in the area is equal to the
horizontal divergence.
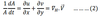
The relationship between horizontal divergence and the vertical velocity can be
obtained from
the continuity equation as:

In the troposphere, the vertical velocity is
close to zero (w~0) at two altitudes
In the troposphere, the vertical velocity is close to zero (ݓ~0) at two altitudes.
The first is Earth’s surface, which forms a solid boundary.
• The second is the tropopause, above which the rapid increase in stratospheric potential temperature strongly inhibits vertical motion.
Divergence aloft is associated with
air throughout the troposphere
Divergence aloft is associated with air throughout the troposphere, which
is associated with
pressure and at the surface
Convergence aloft is associated with
sinking air throughout the troposphere
Convergence aloft is associated with sinking air throughout the troposphere,
which is associated with
high pressure and divergence at the surface
So, starting at the surface, the vertical velocity becomes
more with height when there is surface convergence, reaches some maximum vertical velocity, and then becomes positive with height becoming divergence aloft
Similarly, starting again at the surface, the vertical velocity becomes more negative
with height when there is
surface divergence, reaches some maximum negative velocity, and then becomes less negative with height again near convergence aloft.
When the surface divergence (or convergence) with height changes into
upper air convergence (or divergence)
When the surface divergence (or convergence) with height changes into upper air
convergence (or divergence), at some level in the troposphere (called
the level of non-divergence, LND), the divergence becomes zero.


