Chapter 2 Flashcards
(53 cards)
What happened to the growth rate of per capita income after the industrial revolution?
Except for some bumps, per capita income growth has been close to 2% since 1900 in developed countries
What happened to differences between 1800 and 1950 in per capita income?
Increased in an extreme way as Western Europe, Australia, Canada, New Zealand and the US separated themselves from the rest of the world
What is the relationship between real per capita income and the rate of population growth?
Negatively correlated
What is the impact of higher female labour participation in developed countries?
means that they are having less kids and there is less of an incentive to have many kids as you would want to focus on one and the cost of childcare (E.g. University) is costly therefore costs would want to be saved
What were the conditions before the industrial revolution?
- No growth of any kind in any country
- GDP was constant
- Plauges and wars were common
What are the use of kids in developing countries?
maintain subsistence, as they are extra manpower and the cost of childcare is not high
What happened to the average hours worked in developed countries?
Tend to decreases
What tends to be growth rate for rich countries?
Around 2% and it tends to be alike unlike poor countries
What are the assumptions of the production model?
- Single, closed economy
- One consumption good
- No government
What are the three ways we can change Y?
- Capital stock changes
- Labour force changes
- Ability to produce goods with given resource changes
What does the production function show?
Shows how much output (Y) can be produced given any number of capital and labour
What are the inputs in the production process, as fixed amounts?

What is the production function?
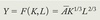
What does Y represent?
Output
What does this represent?
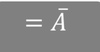
Productivity parameter
A lower level of TFP implies that workers produce less output for any given level of capital per person.
What represents the productivity parameter?
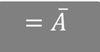
What does this represent?
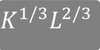
What does the bar on top of letters show?
It is constant
What are the inputs in the equations?
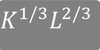
What does a higher value of the TFP mean?
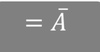
The higher the number, the greater amount of goods you are able to produce given capital and labour. Measure at how efficient the workforce in mixing capital and labour and therefore the overall efficiency of the production process. Differs with each countries. It includes regulations, institutions which make the production process possible and etc.
Why can we not explain why TFP changes overtime?
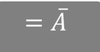
Assumed to be exogenous
What is the Cobb-Douglas Production Function?

What does α show?
Represents the GDP share of K & L
What is the returns to scale of the Cobb-Douglas Production Function?
Constant returns
- If K and L increase by x%, then Y also icreases by x%
- F(αK, αL) = αF(K,L) (Homogenous function, with a degree of 1)
- The addition of the powers on capital and labour add to one which signals to a constant return















