Chapter 13 Flashcards
What is vesicular transport?
The exchange of components between membrane compartments by the budding of transport vesicles from a donor compartment followed by fusion of the vesicle to the target compartment
Vesicular transport is the exchange of components between membrane compartments by the budding of transport vesicles from a donor compartment followed by what?
Fusion of the vesicle to the target compartment
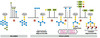
Identify A and B

A: Donor compartment B: Target compartment
In eukaryotes, transport along the secretory and endocytic pathways occur by what?
The fusion of topologically equivalent membrane bound compartments
This flow of material between topologically equivalent membrane compartments is highly what? (3 answers)
Organized, balanced, and directional
The flow of material between topologically equivalent membrane compartments allows for what? (3 answers)
- The secretion of select proteins, 2. The uptake of extracellular material 3. The remodeling of the plasma membrane
The secretory pathway (red arrows) includes the outward movement of material from what? (3 answers)

- The ER to the Golgi 2. The Golgi to the plasma membrane 3. The Golgi to the lysosome
The endocytic pathway (green arrows) is uptake of what? Their fusion with what?

The uptake of plasma membrane material and their fusion with the lysosome
The retrieval pathway is what?
The movement from the plasma membrane to the Golgi and from the Golgi to the ER
Formation of transport vesicles requires a what? where?
A specialized ‘protein coat’ on the outside of the membrane vesicle
The specialized ‘protein coat’ perform what two main functions?
- Selects the membrane proteins required for transport 2. Generates the shape of the vesicle by influencing the curvature of the membrane
What is flat and stiff due to its cholesterol rich composition and its attachment to the underlying cytoskeleton?
The plasma membrane
For the plasma membrane, what are essential for the generation of the force required to introduce membrane curvature?
Coat proteins
What based vesicle formation is less dependent on coat-proteins for membrane curvature as vesicles form at curved regions of the membrane?
Golgi based
For the Golgi, coat proteins are primarily used for what?
Cargo selection
What are the 3 major types of coated vesicles distinguished by their coat proteins?
- Clathrin-coated vesicles 2. COPI-coated vesicles 3. COPII coats
What vesicles were the first identified and the best characterized coat type?
Clathrin-coated vesicles
What vesicles form on buds that exit from the Golgi
COPI-coated vesicles
Vesicles form at the plasma membrane and are ssential for endocytosis?
Clathrin-coated vesicles
What form on vesicles leaving the ER
COPII coats
Identify pathway A (in green):

Clathrin
Identify pathway B (in blue):

COPI
Identify pathway C (in red):

COPII
The formation of transport vesicles are mediated by the formation of what? where?
A specialized ‘protein coat’ on the cytosolic side of the membrane vesicle.