Chapter 112 Penis and Prepuce Flashcards
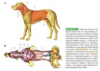
What are the three parts of the penis?
Root, body and distal portion (aka glans)
What is the name of the penile tissue that surrounds the urethra (for the entirety of its length?
Corpus spongiosum
(bulb of penis is a bilobed extension of corpus spongiosum)

What anatomical areas make up body of penis?
Corpus spongiosum + corpus cavernosum
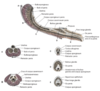
What anatomical areas make up distal penis/glans penis
Bulbus glandis
Pars longa glandis

What is another name for the os penis?
Baculum
What are the four paired extrinsic muscles of the penis?
Ischiourethralis
Ischiocavernosus
Bulbospongiosus
Retractor penis

Where do the retractor penis muscles arise from
Cd vertebrae 1 and 2, then blend with external anal sphincter

Where do bulbospongiosus muscles arise from?
Tunica albuginea and external anal sphicter (and fuse with retractor penis at insertion)

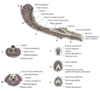
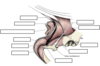
Label he diagram
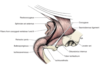
What is the primary vessel supplying the penis
Artery of the penis (from internal pudendal)
- Arteries of the bulb
- Deep arteries of the penis
- Dorsal artery of the penis

Label the diagram
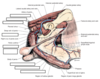
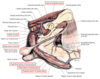
What region does each of the main vessels of the penis supply?
Artery of the penis (branch of internal pudendal)
- Artery of bulb: Corpus spongiosum, penile urethra, pars longa glandis (surprisingly as very dor away an dorsal surface…)
- Deep artery of penis: Corpus cavernosum
- Dorsal artery of penis: corpus spongiosum, bulbus glandis, pars longa glandis

What is the venous drainage of the penis?
Internal and external pudendal
What is the main sensory nerve innervating the penis?
Dorsal nerve of penis
In what % of cats is os penis readiographically visible?
40%
How soon after castration do spines of penis in cats regress?
6 weeks