Ch 8: 5.1.19 Weekly Quiz material Flashcards
a material with no electrical resistance
superconductor
what type of material does not allow electricity to flow through it?
an insulating material
examples: rubber, plastic, wood
what can be thought of as the “push” electroncs feel to move?
electric potential
note: similiar to the relationship between water pressure and the movement of water
semiconducting materials can act as what in certain conditions, and act as what else in others?
conductor or insulator
example: graphite
a current where electrons flow one way
direct current (DC)
example: anything that runs off a battery (cell phone, a car, etc)
equation: Ohm’s law
electric potential (E, in volts [v]) is current (I, in amps [A]) times resistance (R, in ohms, [Ω])
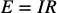
a circuit with only one path
series circuit
example: “old-style” xmas lights (one bulb goes out, they all go out)
what are two drawbacks of using a superconductor?
- they must be very cold
- they are brittle (i.e., easy to break)
equation: Coulomb’s law (electrical force)
electrical force is a constant (K) times abs. value of first charge times abs. value of second charge over center-to-center distance squared
note: the constant (K) = 9.0 x 10^9

electrical potential energy per unit charge
in common parlance, “voltage”
electric potential
“one jump” of electrons
static electricity
example: lightning
___ can hurt you, but ___ can kill you.
voltage can hurt, but current can kill
equation: power
power (Watts) is current (amps) times electric potential (volts)
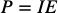
the continuous flow of electrons
curent electricity
examples: lights (once turned on); essentially anything that runs on electricity
how do “new style” xmas lights work?
each bulb has a shunt resistor that acts as a bypass if the filament breaks




