Ch. 5 - Coordinate Geometry Flashcards
(15 cards)
Coordinate Plane
Rectangular coordinate system
Cartesian plane
A system of two perpendicular axes used to describe the position of a point using a pair of coordinates.
Slope-Intercept Form of the Equation of a Line
y = mx + b
Point-Slope Form of the Equation of a Line
y – y1 = m (x – x1)
The Distance Formula
d = √( (x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2 )
For the two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
Distance in a Three-Dimensional Space
d = √( (x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2 + (z2 – z1)2 )
For two points in 3-D, (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2).
Coordinates of the Midpoint of a Line Segment
M = ((x1 + x2)/2, (y1 + y2)/2)
For the two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2).
Linear Inequalities

Standard Form of the Equation of a Parabola
y = a(x – h)2 + k
Point (h, k) is the vertex.
General Form of the Equation of a Parabola
y = ax2 + bx + c
x-coordinate of vertex is –b/2a.
y-coordinate of vertex is y(–b/2a).
y-intercept is the point (0, c).
Standard Form of the Equation of a Circle
(x – h)2 + (y – k)2 = r2
The center of the circle is the point (h, k).
The length of the circle’s radius is r.
The Ellipse

An ellipse has two vertices at the ends of its long axis and two foci points within the ellipse.
The distances from the two foci to a point on the ellipse always add up to the same number for every point on the ellipse.
General Equation of an ellipse
(x – h)2/a2 + (y – k)2/b2 = 1
The center of an ellipse is the point (h, k).
The width of the ellipse is 2a, and the height is 2b.
Area of an ellipse
A = πab
a and b are the semi-major and semi-minor axes.

General Equation of a Hyperbola
(x – h)2/a2 – (y – k)2/b2 = 1
The hyperbola’s conter is the point (h, k).
If the y-term is negative, then the curves open out to the right and left.

(x – h)2/a2 – (y – k)2/b2 = 1
If the x-term is negative, then the curves open up and down.
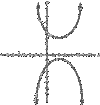
(y – k)<span>2</span>/<span>b<span>2</span></span> – (x – h)<span>2</span>/<span>a<span>2</span></span> = 1


