Ch. 3 Flashcards
synthetic proof
proof built using a system of postulates & theorems in which the prop’s of figures, but not their actual measurements r studied
justifications of synthetic proof
given statements
definitions
postulates
previously proved theorems
Bisecting Diagonals Th
If the 2 diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram.
implications
if-then statements that can be represented by symbols
Ex: p → q reads “If p, then q”
logically equivalent
either both true or both false
original & contrapositive
not logically equivalent
just cuz original = true, doesn’t mean converse & inverse r too
converse
q → p
If q, then p
inverse
~p → ~q
If not p, then not q
contrapositive
~q → ~p
If not q, then not p
median (of triangle)
a segment joining a vertex to the midpt of the opp. side
coordinate proof
a proof based on a coord. system in which all pts r represented by ordered pairs of #’s
justifications for coordinate proof
distance & midpt formulas
parallel lines have the same slope
perp. lines have slopes tht r neg. reciprocals of each other
a geometric figure may be placed anywhere in the coord. plane
distance formula

midpt formula
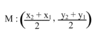
Isosceles Median Theorem
in an isosceles triangle, the medians drawn to the legs r equal in measure
isosceles trapezoid
a trapezoid w/ a line of symmetry that passes through the midpts of the bases
Isosceles Trapezoid Theorem
In an isosceles trapezoid:
- the legs r equal in measure
- the diagonals r equal in measure
- the 2 angles @ each base r equal in measure
inclusive definition
a definition that includes all possibilites
exclusive definition
a definition that excludes some possibilities
quadrilateral chart
past postulates & theorems
Addition, Subtraction, Mult, Div Prop’s of Eq Post’s
Reflexive Prop of Eq Post
Substitution Property Post
Distributive Prop. Post
If 2 angles r supp’s of same angle, then r equal in measure
if 2 angles r complements of same angle, then equal in measure
Straight Angle Post - if the sides of an angle form a straight line, then the angle is a straight angle w/ measure 180o
Angle/Segment Addition Post - For any seg or angle, the measure of the whole is equal to the sum of the measures of its non-overlapping parts
vertical angles r equal in measure
the sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180o
an exterior angle of a triangle is equal in measure to the sum of the measures of its 2 remote interior angles
if 2 sides of a triangle r equal in measure, then the angles opp those sides r = in measure
if 2 angles of a triangle r =, then the sides opp those angles r =
If a tri is equilateral, then is also equiangular, w/ three 60o angles
If a tri is equiangular, then its also equilateral
if 2 parallel lines r intersected by a trans, then corr angles r =, vv
If 2 parallel lines r intersected by a trans, then alt int angles r =, vv
If 2 parallel lines r intersected by a trans, then co-int angles r supp, vv
If 2 lines r perp to the same trans, then they r parallel
If a trans = perp to one of 2 parallel lines, then its perp to the other one also
Thru a pt not on a given line, there’s 1 and only 1 parallel line to the given line
If a pt is the same distance from both endpts of a segment, then it lies on the perp bisector of the seg
A seg can be drawn perp to a given line from a pt not on the line
AA similarity - if 2 angles of 1 tri r = to 2 angles of another tri, then the 2 tri’s r similar
If a line is drawn from a pt on 1 side of a tri parallel to another side, then it forms a tri similar to the original tri
In a tri, a segment that connects the midpts of 2 sides is parallel to the 3rd side & half as long
ASA, AAS th’s
SAS, SSS Post’s
If the alt = drawn to the hyp of a right tri, then the 2 triangles formed r similar to the original tri & to each other
Pythagorean Th
If the alt is drawn to the hyp of a right tri, then the measure of the alt is the geometric mean b/w the measures of the parts of the hyp
the sum of the lengths of any 2 sides of a tri is greater than the length of the 3rd side
in an isosc tri, the medians drawn to the legs r equal in measure
in a parallelogram, the diagonals have the same midpt
In a rectangle, the diagonals r equal in measure
In a kite, the diagonals r perp to each other
in a parallelogram, opp sides r equal in measure
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then consecutive angles r supp
If a quad is parallelogram, then opp angles r =
the sum of the measures of the angles of a quad = 360o
if both pairs of opp angles of a quad r equal in measure, then the quad = a parallelogram
Interior Angle Measures in Polygons Th
the sum of the angle measures of an n-gon is given by the formula
S(n) = (n - 2)180o
exterior angle measures in polygons th
the sum of the exterior angle measures of an n-gon, 1 angle at each vertex, is 360o
regular polygon
iff all its sides r equal in measure & all its angles r = in measure
inscribed
drawn inside the figure
circumscribed
drawn outside the figure
chords
segments whose endpoints are on the circle
Perpendicular bisector of a chord th
The perp bisector of a chord of a circle passes thru the center of the circle
central angle
an angle w/ its vertex @ the center of the circle
measure of an arc intercepted (cut off) by a central angle = the measure of that central angle
minor arc
< 180
can be named with 2/3 letters (just remember that a major arc is named w/ 3 letters to distinguish it from a minor arc w/ the same endpts)
semicircle
= 180
named w/ 3 letters
outside letters = diameter; Ex: arcSTU ⇒ SU is a diameter
major arc
180 < arc < 360
named w/ 3 letters
inscribed angle
an angle formed by 2 chords that intersect at a point ON a circle
intercepted arc
the arc that lies w/in an inscribed angle
inscribed angle measure th
the measure of an inscribed angle of a circle = 1/2 the measure of its intercepted arc
inscribed right angle th
equal inscribed angles th
If 2 inscribed angles in the same circle intercept the same arc, then they r = in measure
intersecting chords theorem
the measure of an angle formed by 2 chords that intersect INSIDE a circle = 1/2 the sum of the measures of the intercepted arcs
.5 (a + b)
secants & tangents th
the measure of an angle formed by 2 secants, 2 tangents, or a secant & a tangent drawn from a pt outside the circle = 1/2 the diff of the measures of the intercepted arcs
.5 (big - small)
tips for finding angles
continue radius to diameter
use systems of equations
remember perp rule
tangent
a line in the plane of a circle & intersecting the circle in exactly 1 pt
secant
a line intersecting the circle in 2 pts
Short Point Postulate
a segment can be drawn perpendicular to a given line from a point not on the line
the length of this segment is the shortest distance from the point to the line
Perpendicular Tangent Th
If a line is tangent to a circle, then the line is perpendicular to the radius drawn from the center to the point of tangency.
Converse of Perpendicular Tangent Th
If a line in the plane of a circle is perp to a radius at its outer endpt, then the line is tangent to the circle.
Equal Tangents Th
If 2 tangent segments are drawn from the same pt to the same circle, then they r equal in measure.
semiperimeter
half the perimeter
how to find area of circumscribed polygons using trig
- total degrees = 360o
- divide 360 by # of vertices to find all internal angles
- divide internal angles by 2 to find angle in new right triangle
- use trigonometry to find sides (already have radius & angle & know its right triangle)
- find area of original triangle
- multiply by # of vertices
Ex: pentagon w/ radius 30cm
- total degrees = 360
- 360 / 5 = 72
- 72 / 2 = 36
- tan36o = x / 30; x = ~ 21.8
- 21.8 • 2 = 43.6; 1/2bh = 1/2(30)(43.6) = 654cm2
- 654 • 5 = 3,270cm3
area of a circumscribed polygon
The area of any circumscribed polygon is the product of the radius (r) of the inscribed circle & the semiperimeter (s)
A = rs
polyhedron
a space figure whose faces are all polygons
semiregular polyhedron
a polyhedron w/ faces that r all regular polygons, & w/ the same # of faces of each type @ each vertex
regular polyhedron
a polyhedron w/ faces tht r all the same type of regular polygon, & w/ the same # of faces @ each vertex
5 regulars; tetrahedron, hexahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron, icosahedron
tetrahedron
4 equilateral triangles
hexahedron
6 squares
octahedron
8 equilateral triangles
dodecahedron
12 regular pentagons
icosahedron
20 equilateral triangles
Convex Polyhedron Postulate
In any convex polyhedron, the sum of the measures of the angles at each vertex is less than 360o
net
a 2D drawing showing the connected faces of a space figure & how they r connected.
can be cut out & “folded up” to form the space figure
defect
the angle measure of the gap @ a vertex on a net for a polyhedron
can be found by subtracting the sum of the angles @ that vertex from 360
Euler’s formula
F + V = E + 2
f - # of faces
v - # of vertices
e - # of edges


