Ch 22(18) Reactions at the alpha carbon of a carbonyl compounds Flashcards
A nucleophile can… to the what carbon
a nucleophile can add to the carbonyl carbon

A…. can remove a proton from an alpha carbon
a base can remove a proton from an alpha carbon
(an alpha carbon is a carbon that is adjacent to a carbonyl carbon)

What is the pKa of one of the hydrogens in CH3CH3
the pKa is greater than 60

Hydrogens attacehd to sp3 carbons have very____pKa values
hydeogens attached to sp3 carbons have very high pKa values

What is a carbon acid? What is the range of their pKa’s?
a compound that contains a relatively acidic hydrogen bonded to an sp3 carbon. The pKa’s range from 16~20 and 25

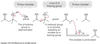
The electrons left behind when a proton is removed from an alpha carbon are _____ onto the ____. Draw a picture
the electrons left behind when a proton is removed from an alpha carbon are delocalized onto an oxygen.

Why are alpha carbons more acidic than other sp3 carbons
the electrons left behind when a proton is removed from an sp3 carbon are localized on the carbon.
The electrons left behind when a proton is removed from an alpha carbon are delocalized onto an oxygen.
deloocalization increases stability
(the more stable the base, the stronger its conjugate acid)
oxygen is better able to accommodate the electrons than carbon

Why are protons on an alpha carbon of an aldehyde or ketone more acidic than a proton on an alpha carbon of an ester? What are their pKa’s? Draw a picture
esters are less acidic thal aldehydes and ketone because delocalization of the electrons left behind when the proton is removed has to compete with the delocalization of the lone pair onto the carbonyl oxygen
aldehydes and ketones 16-20
ester-25

What happens when electrons can he delocalized onto two oxygens? Draw a picture.
The acidity of the alpha hydrogen increases
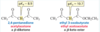
How do tautomes differ? Draw a picture
tautomers differ in the location of the double bond and a hydrogen.

For most ketones the ___ tautomer is more stable than the ___ tautomer. In what caseis the oppsite true.
For most ketones the keto tautomer is more stable than the enol tautomer. When the enol tautomer is aromatic it is more stable.

What is the mech for a base catalyzed keto-enol interconversion? Draw it.
- removal of a proton from the alpha carbon
- protonnation on oxygen

What is the mech for an acid catalyzed keto-enol interconversion? Draw it.
- protionation on the oxygen
- removal of a proton from the alpha carbon

What happens when an alpha carbon is treated with a halogan and an acid catalyst?
one of the alpha carbons is replace by an halogen and HX is produced.

What happen when an alpha carbon is treated with excess halogen and a base catalyst? Draw it.
all of the alpha hydrogens are replaced by the halogen and 2X- is produced

What happens when a carboxylic acid is treated with 1.PBr3 (or P),Br. 2.H2O
The HVZ reaction is used to replace the alpha carbon of a carboxylic acid with Br.

What happen when the bromine of the alpha carbon of an aldehyde or ketone is treated with a waek base?
the Br is replaced by the weak base and Br is released as an ion.

What happens when bromine of the alpha carbon of a carboxylic acid is treated with a weak or strong base?
The Br is replaced by the base.

What can be used to form the enolate ion so the equilibrium lies to the right?
LDA can be use since DIA is produced in the reaction and it is a weaker acid then aldehydes and ketones.

How is LDA synthesized ?
With diisopropylamine ,butyllithium and THF at -78ºC

How do you alkylate the alpha carbon of ketones, esters and nitriles?
With 1. LDA/THF 2. alkyl halide with the desried alkyl group
Polyakylation will occur if a weak base (HO-) is used

How do you snthesize an enamine?
When a ketone or aldehyde is treated with a secondary amine and trace acid an enamine and water are produced.

How can you alkylate an alpha carbon via an enamine?
- secondary amine,trace acid
- akyl halide or acyl halide (eletrophile)(Sn2 Reaction)
- HCl/H2O
enamines react with electrophiles like enolates do

alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones under go _______ and _____
alpha, beta unsaturated aldehydes and ketone undergo direct addation and conjugate?
-poor nucleophiles form the conjugate addation product