Cells and Tissues of the Immune System Flashcards
(65 cards)
What are secondary lymphoid tissues?
Secondary lymphoid tissues are where white blood cells migrate to interact and generate an effective, adaptive immune response
Lymph nodes, tonsils, spleen, lymphoid tissues (MALT, GALT, BALT)
What does the lymphatic system consist of?
- Lymph veseels
- Tissues and organs w/ high density of lymphocytes
- Lymph nodules
- Lymph nodes
- Thymus gland
- Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue
- Bone marrow
What kind of cell is this?

Neutrophil; Multi-lobed nucleus

What kind of cell is this?

Eosinophil;
Bi-lobed cells with bright pink cytoplasmic granules

What kind of cell is this?

Basophil;
Deep blue, dark cytoplasmic granules

What kind of cell is this?

Mast Cell;
Deep blue dark cytoplasmic granules

What kind of cell is this?
Where are you likely to find it?

Monocyte; kidney shaped nucleus, lilac cytoplasm
Found in peripheral blood

What does the stroma of lymphatic nodules, nodes, and spleen consist of?
Reticular fibers (small diameter collagen fibers w/ high sugar content)
Produced by reticular cells
What does the stroma of the thymus consist of?
Branching interconnecting epithelioreticular cells
Which cell types are surveillance cells?
- Macrophages
- Langerhans cells (epidermis)
- M cells (intestinal epithelium overlying lymph nodules)
- Dendritic cells (lymphatic tissues)
What kind of cell is this?
Where is it found?

Macrophage;
Reside in tissues
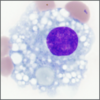
What kind of cell is this?

Plasma Cell;
Fried egg appearance, “clock face” chromatin pattern in nucleus

What is unique about high endothelial venules in lymphatic tissues and organs?
The endothelium is cuboidal instead of simple squamous.
purpose of high endothelial venules: To concentrate lymph to increase chance that antigen will encounter antigen-presenting cell
What kind of cell is this?

Natural Killer Cell;
Granules produce cytotoxins to kill other molecules

Where are T lymphocytes mainly found?
Diffuse lymphatic tissue of lymphatic organs or loose connective tissue of GI, respiratory, urinary tracts
What are the components of lymph nodules?
Dense aggregations of mostly B cells in meshwork stroma of reticular fibers
found in GALT, lymph nodes, spleen
What is the main component of lymph nodules?
B cells
Why is the germinal center of dividing B cells in a lymph nodule lighter staining?
Larger cells w/ more cytoplasm and more euchromatin in the nucleus. shows that an immune response is taking place
Where do blood vessels enter and leave a lymph node?
Hilum
Where are the efferent lymphatics located in a lymph node?
Hilum
What are lymph nodes composed of?
- Connective tissue capsule
- Outer cortex w/ nodules (B cell zones)
- Inner cortex w/ diffuse T cell lymphatics
- Innermost medulla w/ T cell medullary cords
Describe the pathway for lymph flow through a node
- Cortical afferent lymphatics
- Subcapsular sinus
- Trabecular sinuses
- Medullary sinuses
- Efferent lymphatics exiting at hilum
What does the deep cortex of lymph nodes contain?
High endothelial venules (simple cuboidal epithelium)
What are the functions of the high endothelial venules in the deep cortex?
- Primary site of entry of lymphocytes from other parts of body
- High density of water channels that allow passage of fluid in lymph into bloodstream to concentrate lymph in sinuses




